A paper published in August 2022 by Hiroyuki Kojima, Atsushi Sofuni, and other scholars from the Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Tokyo Medical University, in J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci.

Literature Interpretation
Key Points of This Article:
1. Pancreatic SWE aids in the diagnosis of Chronic Pancreatitis (CP). Combining with CT values makes the diagnosis more accurate.
2. SWE measurements at the pancreatic body (the easiest site to measure via abdominal ultrasound) are comparable to the CT values of CP patients.
3. Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) and endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography do not provide objective assessments for diagnosing CP and carry a high risk of complications. SWE and SWD can achieve objective assessment and non-invasive diagnosis of CP.
4. The results of this study show that as CP progresses, the elasticity of pancreatic parenchyma significantly decreases, which is statistically significant.
5. Logistic regression analysis indicates that alcoholism, smoking, and type 2 diabetes are risk factors for Chronic Pancreatitis. No significant correlation was found regarding gender and the skin-pancreas distance.
Research Objective
To study the applicability of shear wave elastography (SWE) in assessing the pancreas and its potential in diagnosing Chronic Pancreatitis.
Research Methodology
Using the Aplio i800 ultrasound system (Canon Medical) and convex array probe PVI-475BX (3.5 MHz), SWE examinations were performed on 59 patients undergoing abdominal ultrasound, and pancreatic CT values were measured. They were divided into three groups: Normal Pancreas (NP) group, Early Chronic Pancreatitis (ECP) group, and Chronic Pancreatitis (CP) group. The shear wave elasticity (SWE), shear wave dispersion slope (SWD), and CT values of each group were analyzed.
Research Results
There were significant differences in SWE between the CP group and the NP/ECP groups (NP vs. CP: p=0.001, ECP vs. CP: p=0.026); however, SWD showed significant differences only between the NP and CP groups (NP vs. CP: p=0.001); significant differences in CT values were noted between the CP group and NP/ECP groups (NP vs. CP: p=0.0006, ECP vs. CP: p=0.0027).
Research Conclusion
SWE and CT values of the pancreas assist in the diagnosis of Chronic Pancreatitis. SWD may reveal the progression of ECP.
SWE and SWD
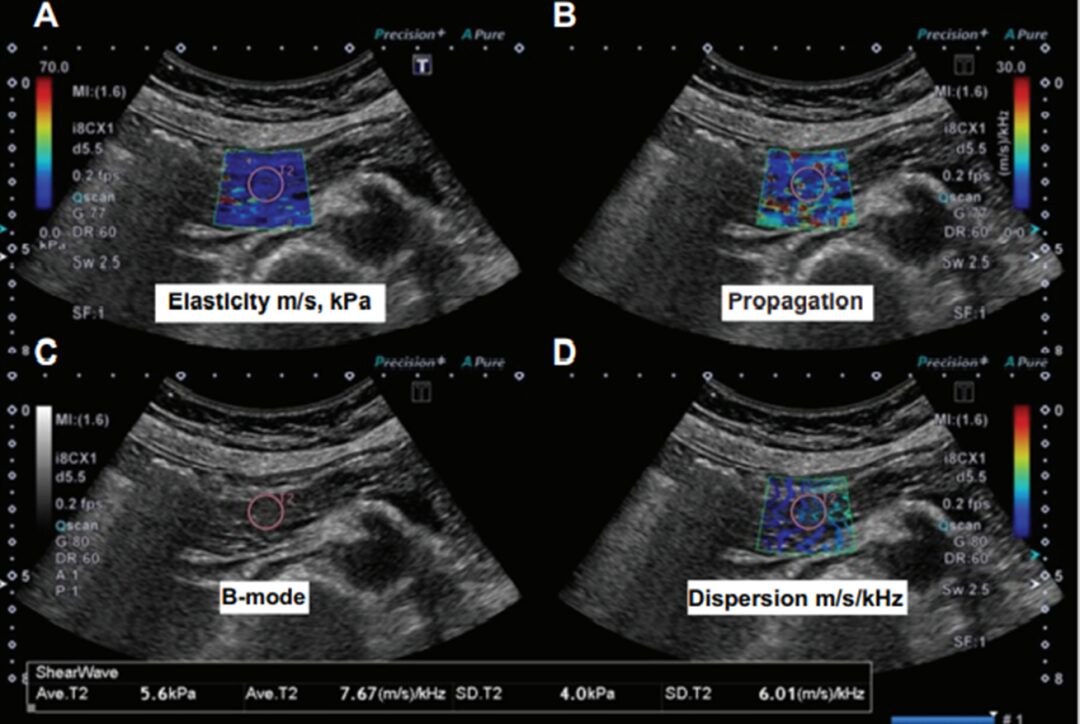
Figure 1: SWE (Aplio i800) measurements showing A: Elasticity map (SWE), B: Propagation map, C: B-mode image, D: Dispersion map (SWD)
Data Collection
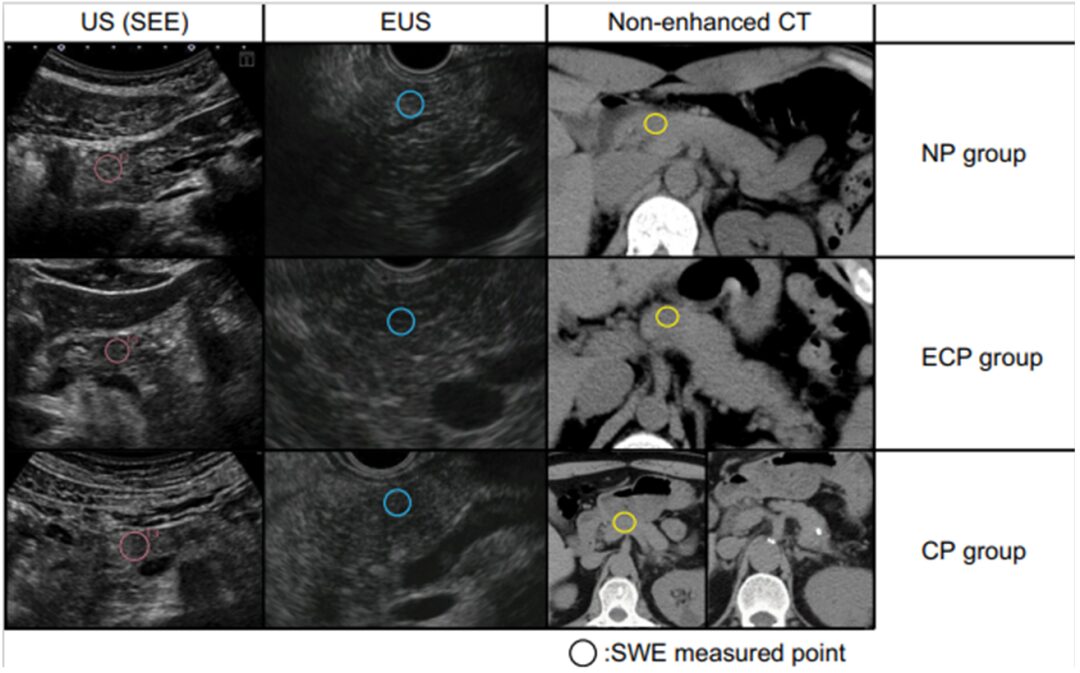
Figure 2: Comparison images of ultrasound, EUS, and non-contrast CT for each group showing the actual ultrasound images during SWE measurements, EUS images of the same region, and non-contrast abdominal CT images of the same area. Each image was compared against the pancreatic background, showing no significant differences. (US: Ultrasound; EUS: Endoscopic Ultrasound; CT: Computed Tomography; NP: Normal Pancreas; ECP: Early Chronic Pancreatitis; CP: Chronic Pancreatitis)
Data Comparison and Statistics
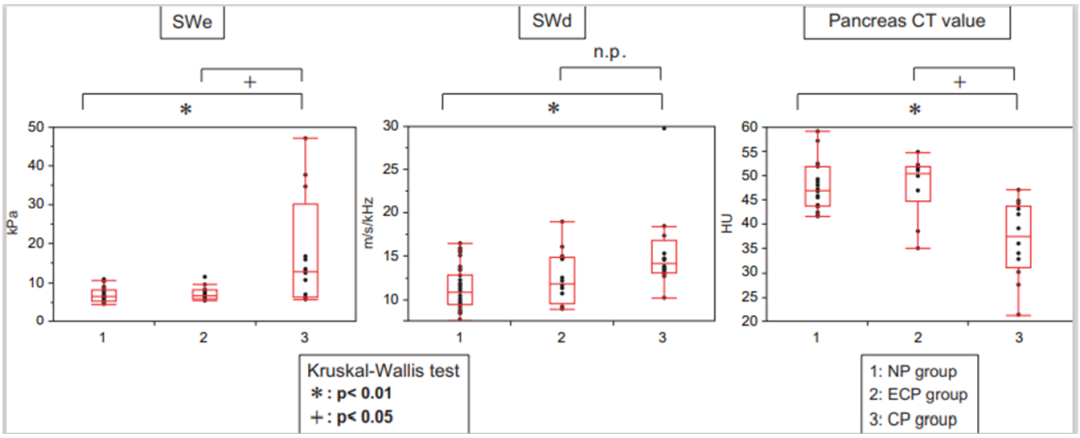
Figure 3: Comparison and statistics of SWE, SWD, and pancreatic CT values for each group
SWE: There are statistically significant differences between the CP group and NP group as well as between the CP group and ECP group;
SWD: There is a statistically significant difference between the CP group and NP group, but no significant difference between the CP group and ECP group;
Pancreatic CT values: There are statistically significant differences between the CP group and NP group and between the CP group and ECP group.
Statistical Results
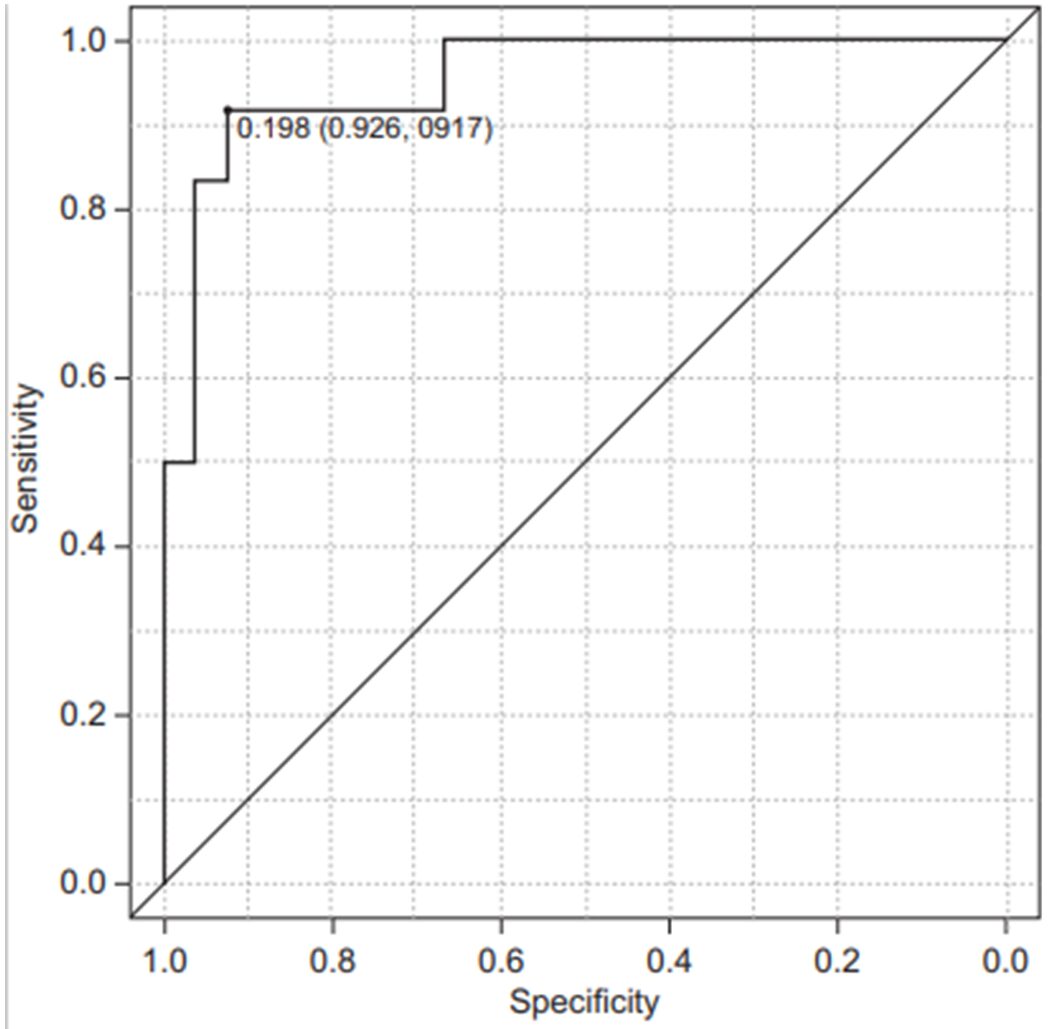
Figure 4: ROC curve for SWE and pancreatic CT values. Result AUC=0.954. (ROC: Receiver Operating Characteristic curve; SWE: Shear Wave Elastography; CT: Computed Tomography)
Keywords: Ultrasound, Chronic Pancreatitis, Diagnostic Ultrasound, Ultrasound Imaging, Pancreatitis
Original link: https://doi.org/10.1002/jhbp.1224
Translation and Compilation: Wang Yong, Yang Weimin
Reviewed by: Zhou Lansong
〢Recommended Reading
Shanghai Electric and Fujian Health Commission discuss high-end medical layout
Shanghai Electric participates in drafting the first standard for intelligent nucleic acid sampling machines
Shanghai Electric and Zhongshan Hospital discuss a new cooperation pattern
Electric Medical wins two industry awards
Shanghai Electric and Siemens Healthineers reach strategic cooperation
