liwen01 2023.06.04
-
Introduction
-
(1) Conventional Devices
-
(1) Patent Protection
-
(2) Code Encryption
-
(3) Authorization Verification
-
(4) Continuous Updates and Improvements
-
(2) Embedded Devices
-
(1) Polish Key Chip Logos
-
(2) Disable Debug Serial Ports
-
(3) Set Flash Read Protection
-
(4) Encrypt and Obfuscate Key Information
-
(3) Junzheng T-Series Program Cracking
-
(1) Locate the Root File System
-
(2) Decompress and Restore the Root File System
-
(4) How to Prevent Reverse Engineering
-
1. Encrypt the Entire Root File System
-
2. Encrypt Only Key Information
-
Conclusion
Introduction
In product design and development in China, it is difficult to avoid being cloned or imitated. Before establishing a technological barrier, preventing product cloning is an unavoidable issue.
(1) Conventional Devices
The main protective measures for conventional devices include:
- Patent Protection
- Code Encryption
- Authorization Verification
- Continuous Updates and Improvements
(1) Patent Protection
For significant technological inventions or innovations, patents should be applied for as soon as possible. Although the current level of intellectual property protection in China is limited, applying for a patent is still useful, at least to prevent others from applying for the patent first, which could lead to infringement.
(2) Code Encryption
This involves balancing encryption with performance and cost. If the device cost is not very sensitive, an encryption chip can be added; if the program needs to be encrypted, this may affect the execution efficiency of the program.
(3) Authorization Verification
Introduce an authorization verification mechanism in the product, such as using encrypted keys or authorization certificates to verify the legitimacy of the product. This can effectively prevent unauthorized copying and use.
(4) Continuous Updates and Improvements
Timely fix vulnerabilities and defects in the software, and continuously improve and upgrade functionalities. This helps maintain a competitive advantage and reduces the motivation for cloning.
(2) Embedded Devices
For embedded devices, the main considerations involve structural appearance, hardware circuits, and embedded software. In addition to the methods mentioned above, the following approaches can also increase the difficulty of cloning:
- Polish Key Chip Logos
- Disable Debug Serial Ports
- Set Flash Read Protection
- Encrypt and Obfuscate Key Information
(1) Polish Key Chip Logos
In embedded systems, different processors use different cross-compilation tools, and the layout of program partitions varies, which can increase the difficulty of reverse engineering analysis.
(2) Disable Debug Serial Ports
Normal products should disable debug serial ports during mass production for two purposes:
- Avoid signal interference from the debug serial port, which can affect system stability.
- Debug serial ports typically print some debugging and system information, which can be used by others for reverse analysis.
(3) Set Flash Read Protection
Some MCUs allow read protection to be set in their programming tools, meaning that the program inside the MCU cannot be directly read. Regular flash also has protection mechanisms, but the protection level is weak. Adding an encryption chip can prevent the program from being directly copied, but it may affect program efficiency and increase device costs.
(4) Encrypt and Obfuscate Key Information
In embedded systems, due to the limited size of flash memory, the execution program is generally converted in format and then compressed. During execution, it is first decompressed, then converted, and finally run. An additional step can be added here: encrypt and obfuscate key information before conversion and compression, which can significantly increase the difficulty of reverse analysis.
(3) Junzheng T-Series Program Cracking
Below is an analysis based on Junzheng’s solution:
The execution program from Junzheng is placed on the root file system. After the root file system is mounted, some initialization settings are performed, and then the execution program runs directly from the root file system.
To crack an official firmware from the Junzheng T series, the basic process should be as follows:
- Locate the root file system
- Decompress the root file system
- Restore the file system format
- Find the executable program
- Perform decompilation and other operations on the executable program
(1) Locate the Root File System
This involves the starting position and size of the root file system.
Generally, the root file system is in a separate partition, and the partition information can be obtained from the boot parameters, along with the type of the root file system.
For Junzheng’s official firmware, bootargs and bootcmd information can be found in the boot:
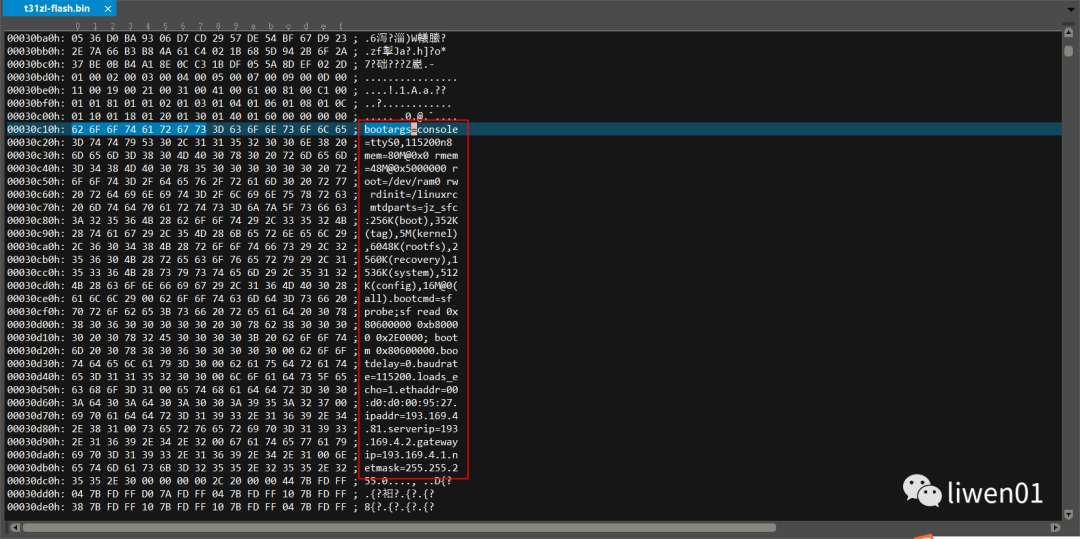
From the above, it can be seen that the size of rootfs is 6048K, and the starting position is 5728K = 0X598000.
(2) Decompress and Restore the Root File System
The official packaging method is:
find . | cpio -H newc -o > ../rootfs_camera.cpio
lzop -9 -f rootfs_camera.cpio -o rootfs_camera.cpio.lzo
find . | cpio -H newc -o > ../rootfs_camera.cpio
This uses the cpio command to package the current files and their subfiles into the rootfs_camera.cpio file, using the newc file format.
lzop -9 -f rootfs_camera.cpio -o rootfs_camera.cpio.lzo
This uses the lzop command to compress rootfs_camera.cpio into rootfs_camera.cpio.lzo file.
If reverse operations are needed, the following commands can be executed:
lzop -d rootfs_camera.cpio.lzo
cpio -i < rootfs_camera.cpio
lzop -d rootfs_camera.cpio.lzo
This decompresses the rootfs_camera.cpio.lzo file to the current directory.
cpio -i < rootfs_camera.cpio
The contents of the rootfs_camera.cpio file will be unpacked and restored to the original file and directory structure, which will appear in the current working directory.
By examining the etc/init.d/rcS file, one can find which programs are started, where the corresponding programs are placed, and finally obtain the desired information through disassembly and other means.
(4) How to Prevent Reverse Engineering
From the analysis of Junzheng’s official design, it is still relatively easy for knowledgeable engineers to crack it. So what measures can be taken to increase the difficulty of cracking?
1. Encrypt the Entire Root File System
Encryption can be symmetric or asymmetric. In embedded systems, symmetric encryption algorithms, such as AES, are recommended.
Compilation and Packaging Process
- Select AES key length
- Generate the key
- Use the key to encrypt files
- Package the encrypted
rootfs_camera.cpio.lzointo the firmware package
Device Operation Process
- The kernel will copy the root file system to memory during startup, and then decompress it.
- Before decompression, use the key from the packaging process to decrypt it, and then continue executing as per the original process.
Advantages and Disadvantages
- Advantages: The entire file system can be encrypted, making cracking more difficult.
- Disadvantages: It may affect startup speed; this method can impact systems requiring fast boot times.
2. Encrypt Only Key Information
For embedded systems, key information may include:
- Certain key algorithm libraries
- Product serial numbers and other information
- Algorithm model files, etc.
The encryption and decryption methods are similar to those for encrypting the root file system, with the difference being that decryption occurs at different stages of system operation.
- Advantages: It does not affect the system’s startup speed.
- Disadvantages: Relatively easier to reverse engineer.
Conclusion
All encryption can potentially be cracked. Actual product design should consider the security level of the industry to design different levels of encryption. While it is not encouraged to clone or crack others’ devices, it is essential to protect one’s intellectual property reasonably.
Continuously updating and improving product design solutions can create technological barriers, reducing concerns about product cloning.
Note
Due to recent changes in WeChat public account push rules, to prevent missing articles, you can star and pin this account, so that every article pushed will appear in your subscription list.
You may also like:
Discussing Compatibility in Embedded Software!
I am a loyal fan of Teacher Wei Dongshan!
Reply with1024 in the public account chat interface to obtain embedded resources.