Recommended Videos





In embedded ARM development, when faced with a variety of operating systems, how can one make the best decision for the project? This article will outline the characteristics of common systems to help you quickly understand their advantages and disadvantages, enabling you to better choose the right system.
 IntroductionIn embedded ARM development, choosing the right operating system is one of the keys to project success. Common operating systems include Buildroot, Ubuntu, Debian, Android, and OpenHarmony. Each system has its unique features, advantages, and limitations, suitable for different application scenarios. Understanding these system characteristics can help developers make more informed choices based on project requirements.
IntroductionIn embedded ARM development, choosing the right operating system is one of the keys to project success. Common operating systems include Buildroot, Ubuntu, Debian, Android, and OpenHarmony. Each system has its unique features, advantages, and limitations, suitable for different application scenarios. Understanding these system characteristics can help developers make more informed choices based on project requirements. Comparison of Common Operating Systems
Comparison of Common Operating Systems 1. Buildroot: A Lightweight and Open Source Embedded Linux SolutionBuildroot is a tool for building embedded Linux systems, known for its low system overhead, complete open-source nature, small firmware size, and fast boot speed. It is suitable for embedded devices with limited storage space, and the system starts quickly, meeting strict requirements for boot time.However, Buildroot’s software dependencies often require users to add them manually, and all applications need to be cross-compiled on a PC before they can be used.2. Ubuntu: A Powerful Resource for Desktop Linux SystemsUbuntu is a desktop operating system based on the Linux kernel, providing a wealth of deb package resources, allowing users to quickly set up a development environment through apt. Its deb package management system is very comprehensive, suitable for most developers for compilation and development.However, Ubuntu’s file system is relatively large, typically occupying over 2GB of storage space, making it less suitable for resource-constrained embedded devices.3. Debian: A Pure and Stable Open Source Operating SystemDebian is a completely free operating system, natively clean and unadulterated, with a small system footprint and smooth, stable operation. Its repository contains software packages that are almost devoid of any embellishments, making it suitable for scenarios with high stability requirements. Additionally, Debian has strong community support, providing a wealth of documentation and resources.4. Android: An Open System for Mobile DevicesAndroid is an open-source operating system based on Linux, primarily used in mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets. It is characterized by strong openness, flexible UI development, and ease of use, boasting a large application ecosystem.However, Android’s security is relatively weak, and issues of OS fragmentation and solidification are quite serious.5. OpenHarmony: An Emerging Operating System for the Internet of EverythingOpenHarmony is an open-source project incubated and operated by the OpenAtom Open Source Foundation, aimed at building a framework and platform for intelligent terminal device operating systems in an all-scenario, all-connection, and all-intelligent era. It features hardware cooperation, resource sharing, and one-time development with multi-end deployment, making it suitable for the Internet of Things and smart device fields.
1. Buildroot: A Lightweight and Open Source Embedded Linux SolutionBuildroot is a tool for building embedded Linux systems, known for its low system overhead, complete open-source nature, small firmware size, and fast boot speed. It is suitable for embedded devices with limited storage space, and the system starts quickly, meeting strict requirements for boot time.However, Buildroot’s software dependencies often require users to add them manually, and all applications need to be cross-compiled on a PC before they can be used.2. Ubuntu: A Powerful Resource for Desktop Linux SystemsUbuntu is a desktop operating system based on the Linux kernel, providing a wealth of deb package resources, allowing users to quickly set up a development environment through apt. Its deb package management system is very comprehensive, suitable for most developers for compilation and development.However, Ubuntu’s file system is relatively large, typically occupying over 2GB of storage space, making it less suitable for resource-constrained embedded devices.3. Debian: A Pure and Stable Open Source Operating SystemDebian is a completely free operating system, natively clean and unadulterated, with a small system footprint and smooth, stable operation. Its repository contains software packages that are almost devoid of any embellishments, making it suitable for scenarios with high stability requirements. Additionally, Debian has strong community support, providing a wealth of documentation and resources.4. Android: An Open System for Mobile DevicesAndroid is an open-source operating system based on Linux, primarily used in mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets. It is characterized by strong openness, flexible UI development, and ease of use, boasting a large application ecosystem.However, Android’s security is relatively weak, and issues of OS fragmentation and solidification are quite serious.5. OpenHarmony: An Emerging Operating System for the Internet of EverythingOpenHarmony is an open-source project incubated and operated by the OpenAtom Open Source Foundation, aimed at building a framework and platform for intelligent terminal device operating systems in an all-scenario, all-connection, and all-intelligent era. It features hardware cooperation, resource sharing, and one-time development with multi-end deployment, making it suitable for the Internet of Things and smart device fields. 3568 Series Core Board: Supporting Multiple Systems, Empowering Development
3568 Series Core Board: Supporting Multiple Systems, Empowering Development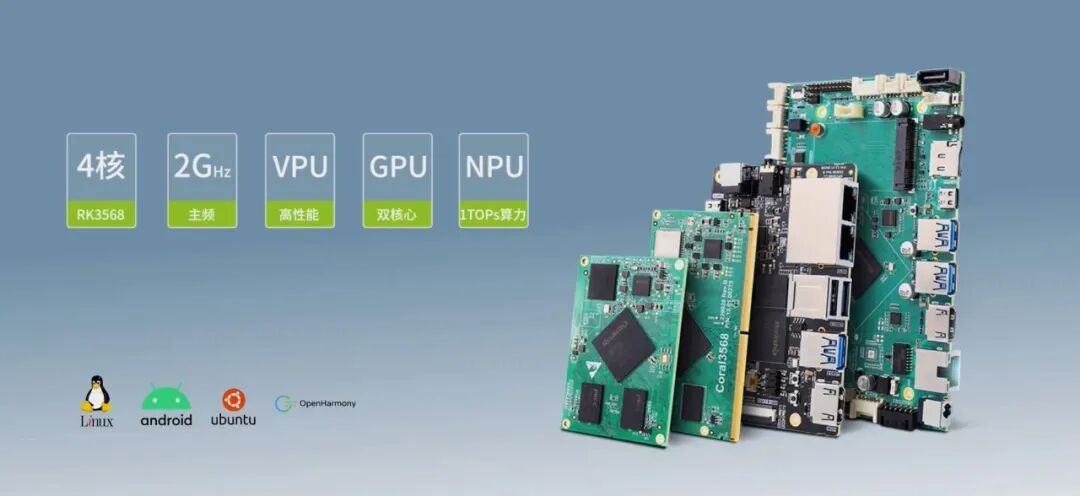 ZLG Zhiyuan Electronics’ 3568 series core board supports multiple operating systems such as Buildroot and Ubuntu, providing rich development materials and technical support to help customers quickly launch projects. It uses the high-performance RK3568 chip, equipped with rich peripheral interfaces and multimedia functions, suitable for various complex application scenarios.Learn more:https://www.zlg.cn/ipc/ipc/product/id/286.html
ZLG Zhiyuan Electronics’ 3568 series core board supports multiple operating systems such as Buildroot and Ubuntu, providing rich development materials and technical support to help customers quickly launch projects. It uses the high-performance RK3568 chip, equipped with rich peripheral interfaces and multimedia functions, suitable for various complex application scenarios.Learn more:https://www.zlg.cn/ipc/ipc/product/id/286.html
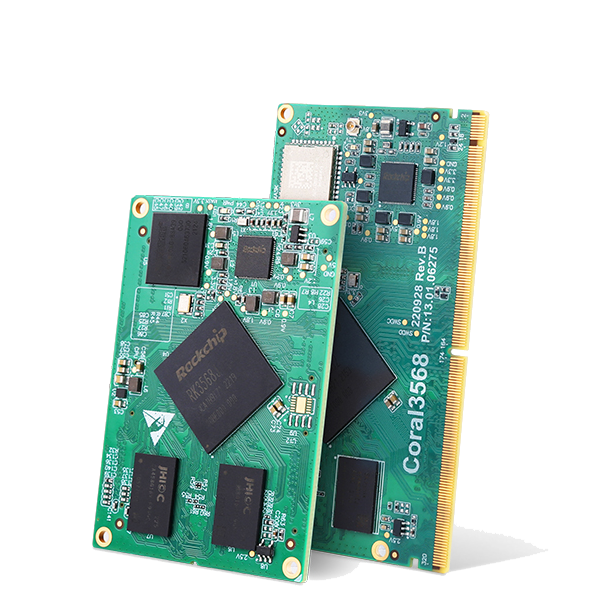 |
3568 Series Core Board |
Long press to purchase |









