
| Source: SIMIT Strategic Research Office (ID: SIMITSRO)
Shanghai Institute of Microsystem and Information Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences
In the era of the Internet of Everything, the objects connected to the network are expanding from people to things.According to IDC statistics, by 2020, there will be over 50 billion terminals and devices connected to the network, with 50% of IoT networks facing bandwidth limitations, and 40% of data needing to be analyzed, processed, and stored at the network edge.This indicates that with the rapid growth of the IoT scale, centralized data storage and processing models will face insurmountable bottlenecks and pressures. At this time, providing data processing capabilities and services at the network edge, close to where data is generated, will be the next important driving force for the development of the ICT industry.
Thus, the concept of Edge Computing was born.In 2014, the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) established the Mobile Edge Computing Industry Specification Group to promote related standardization work.In 2016, ETSI expanded this concept to Multi-Access Edge Computing (MEC), considering the scenario requirements of Fixed-Mobile Convergence (FMC).In April 2016, 3GPP SA2 also officially accepted MEC as a key technology in the 5G architecture.Edge Computing has become a supporting platform for emerging applications in the Internet of Everything and is now an inevitable trend.This series of articles aims to introduce the relationship between edge computing and cloud computing, its basic characteristics and attributes, reference architecture, main application scenarios, and its role in 5G communication. The first part introduces the relationship between edge computing and cloud computing as well as their basic characteristics and attributes.
1. Edge Computing and Cloud Computing Form a Complementary Relationship
According to the definition by ETSI, Multi-Access Edge Computing provides edge intelligent services near people, objects, or data sources through an open platform that integrates core capabilities such as networking, computing, storage, and applications, to meet the critical needs of industry digitization in agile connectivity, real-time business, data optimization, application intelligence, security, and privacy protection.It can serve as a bridge connecting the physical and digital worlds, enabling smart assets, smart gateways, smart systems, and smart services.
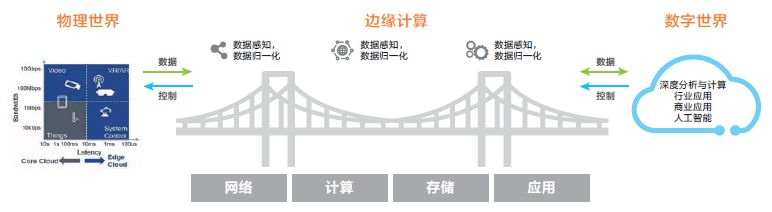
Figure: Edge Computing becomes an important bridge between the physical world and the digital world
With cloud computing in place, why is edge computing still needed?There are several reasons:
1) Network bandwidth and computing throughput have become performance bottlenecks for cloud computing:The cloud center has powerful processing capabilities and can handle massive amounts of data.However, how to quickly transmit massive data to the cloud center has become a challenge in the industry.Both network bandwidth and computing throughput are performance bottlenecks in cloud computing architecture, and user experience is often inversely proportional to response time.The 5G era places higher demands on data real-time processing, and some computing capabilities must be localized.
2) The explosive growth of data in the IoT era raises higher demands for data security:In the near future, most electronic devices will be able to connect to the network, generating massive amounts of data.Traditional cloud computing architectures cannot timely and effectively process these massive amounts of data. If computation is placed at the edge nodes, it will greatly shorten response times and alleviate network load.In addition, some data is not suitable for cloud storage; keeping it at the terminal ensures privacy and security.
3) Terminal devices generate massive amounts of “small data” that need real-time processing:Although terminal devices spend most of their time acting as data consumers, today, devices like smartphones and security cameras have the capability to produce data, significantly changing their roles.Terminal devices generate massive amounts of “small data” that require real-time processing, which is not suitable for cloud computing.
If “cloud computing” can achieve large-scale integration, then “edge computing” is more about being “small and beautiful,” starting from the data source to achieve complementary applications with “cloud computing” in a “real-time, quick” manner.Comparing the two, cloud computing focuses on non-real-time, long-cycle big data analysis, providing a basis for business decision support;edge computing focuses on real-time, short-cycle data analysis, better supporting the real-time intelligent processing and execution of local businesses.
Gartner’s annual list of the top ten technology trends has always attracted attention. At the end of 2018, Gartner listed edge computing as one of the top ten strategic technology development trends for 2019, with “Cloud to the Edge” viewed as an important trend for future technological development.
Figure: Gartner lists edge computing as one of the top ten technology trends for 2019
2. Basic Characteristics and Attributes of Edge Computing
Based on the definition of edge computing provided in the white paper released by the Edge Computing Consortium (ECC) and the Industrial Internet Consortium (AII) at the end of 2018, edge computing, as a bridge connecting the physical world and the digital world, has basic characteristics and attributes including connectivity, constraint, distribution, integration, and data first entry.
Connectivity
Connectivity is the foundation of edge computing.The diversity of connected physical objects and application scenarios requires edge computing to possess rich connectivity features, such as various network interfaces, network protocols, network topologies, network deployment and configuration, and network management and maintenance.Connectivity needs to fully draw on and absorb advanced research results from the networking field, such as TSN, SDN, NFV, Network as a Service, WLAN, NB-IoT, and 5G, while also considering interoperability, interconnection, and interoperation with existing industrial buses.
Data First Entry
As a bridge from the physical world to the digital world, edge computing serves as the first entry point for data, possessing large amounts of real-time, complete data that can be managed and value-created based on the entire data lifecycle, better supporting innovative applications such as predictive maintenance, asset management, and efficiency improvement;at the same time, as the first entry point for data, edge computing also faces challenges such as data real-time performance, determinism, completeness, accuracy, and diversity.
Constraint
Edge computing products need to adapt to relatively harsh working conditions and operating environments in industrial sites, such as electromagnetic protection, dust resistance, explosion-proof, vibration resistance, and current/voltage fluctuation resistance.In industrial interconnection scenarios, there are also high requirements for the power consumption, cost, and space of edge computing devices.Edge computing products need to consider integration and optimization of software and hardware to adapt to various constraints, supporting the diversity of industry digitization scenarios.
Distribution
Edge computing is inherently distributed in its actual deployment.This requires edge computing to support distributed computing and storage, achieve dynamic scheduling and unified management of distributed resources, support distributed intelligence, and possess distributed security capabilities.
Integration
The integration of OT and ICT is an important foundation for industry digital transformation.As the key carrier of “OICT” integration and collaboration, edge computing needs to support collaboration in connectivity, data, management, control, application, and security.
This article is original from the SIMIT Strategic Research Office. For reprints, please contact [email protected]
