Although power management is crucial for almost all electronic devices, it often does not receive the attention it deserves. Power management systems can enhance product reliability and performance, often supporting many other functionalities.
Power Management Integrated Circuits (PMICs) are compact, efficient, and flexible in design, making them particularly important in battery-powered electronic devices such as smartphones and wearables.
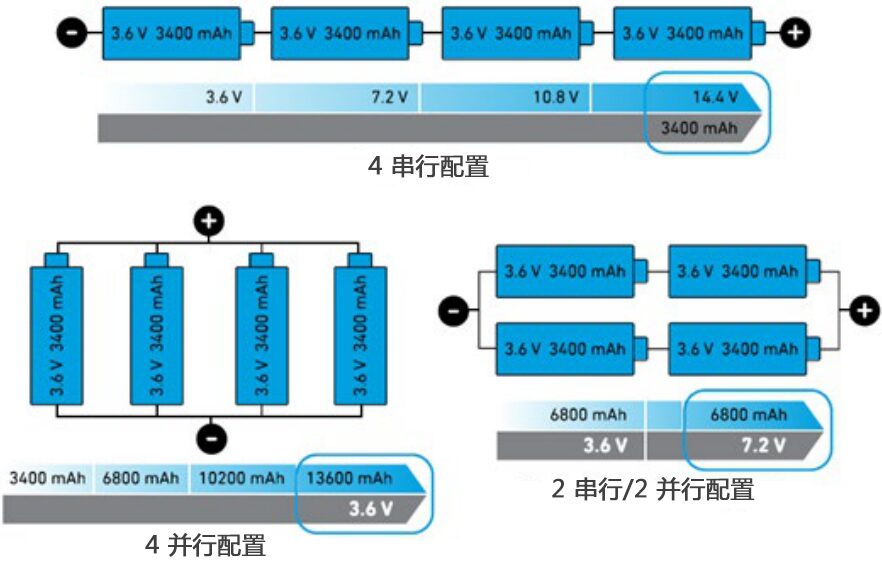
Figure 1: Batteries can be connected in different ways to provide various current and voltage outputs.
DC Battery Configurations
The type of power management subsystem used in electronic devices depends on the power source. These sources can include AC, DC, or ultra-low-power DC sources such as solar power. Many devices are powered by a single battery or a battery pack (containing multiple batteries) that provides DC power. These batteries can be connected in various ways to provide different current and voltage outputs. In the example shown in Figure 1:
● Connecting batteries in series increases the peak voltage and capacity of the battery pack.
● Connecting batteries in parallel does not increase the voltage of the battery pack but can enhance its overall current capability and capacity.
● Using both series and parallel battery connections can improve voltage, current, and capacity.
Types of DC Voltage Regulators
In some battery-powered applications, system components may not be able to use the battery power directly and require DC-DC converters to monitor and stabilize the voltage supplied to the system. These converters, also known as voltage regulators, stabilize the output voltage. Voltage regulators can be classified into two types based on the method of voltage conversion.
● Linear regulators use linear (resistive) components to stabilize and regulate Vout, converting the input voltage (Vin) to a different output voltage (Vout). They are typically used in low-power output applications. Linear regulators can achieve low noise output, suitable for sensitive analog components such as sensors. However, their efficiency is not very high.
● In contrast, switching regulators are efficient, flexible, and compact but generate high-frequency noise. Switching regulators use Field Effect Transistors (FETs) to convert the DC input voltage into an AC waveform, which is then transformed into a different DC output voltage using capacitors and inductors.
Switching Regulators
Switching regulators are classified based on the relationship between their input and output voltages.
● Buck switching regulator: Vout is less than Vin.
● Boost switching regulator: Vout is greater than Vin.
● Buck-Boost switching regulator: Vout can vary: it may be less than, greater than, or equal to Vin.
Below, Figure 2 compares four common regulator topologies: Low Dropout Linear Regulators (LDOs) and three types of switching regulators (buck, boost, and buck-boost).
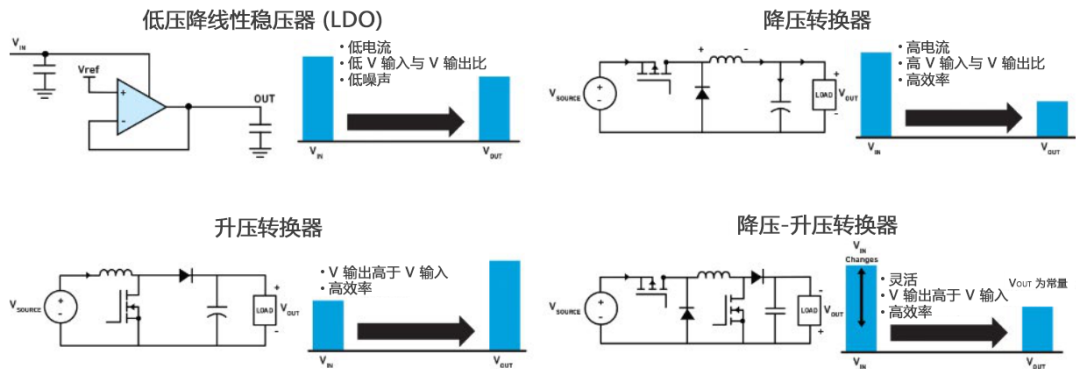
Figure 2
Modern Power Management Integrated Circuits (PMIC)
PMICs are small multifunctional integrated circuits used for voltage conversion, voltage regulation, and battery management (Figure 3). Today’s PMICs can handle multiple or even all voltage regulation functions required in electronic devices. They can be adapted for different applications simply by changing firmware or register settings, without the need for costly hardware changes. This helps accelerate the development of new applications at lower costs.
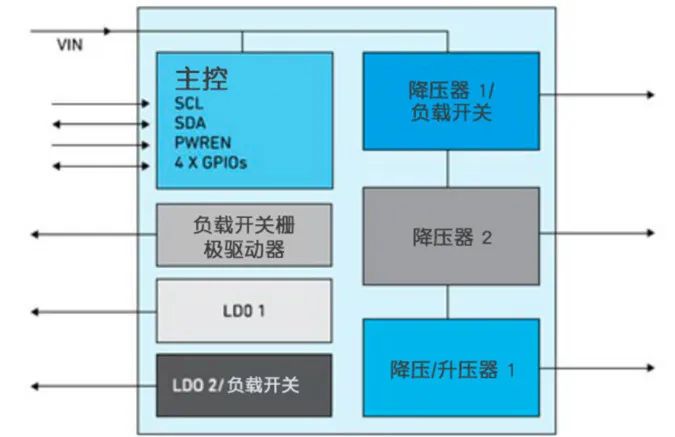
Figure 3: PMICs are small multifunctional integrated circuits used for voltage conversion, voltage regulation, and battery management.
PMICs can be used across various industries and product types. They can provide multiple functionalities, including charging, power loss protection, and DC-DC voltage conversion and regulation. PMICs are compact and energy-efficient, making them suitable for many small devices such as wearables, audible devices (e.g., earbuds), mobile devices, sensors, and Internet of Things (IoT) devices. They can significantly enhance product performance and efficiency, improve design flexibility, reduce material costs, and help manufacturers lower overall costs and accelerate time to market.
 Disclaimer:This article is reprinted from the “Internet” and the copyright belongs to the author. If there is any infringement, please contact us for removal!
Disclaimer:This article is reprinted from the “Internet” and the copyright belongs to the author. If there is any infringement, please contact us for removal!👇Click Follow, Technical content delivered on time!👇

-
This is a must-read book for all electronic engineers, the printed version of “New Concept Analog Circuit”!
-
Why are domestic chips still referred to as “datasheet” in English?
-
The wonderful operational amplifier circuits
-
Why is it 50 ohms???
-
The most detailed basics of diodes
-
What is a BSP engineer?
-
How to play with the ubiquitous ESP8266?
-
General principles of PCB layout and routing in AD.