

Guest Speaker: Dou Chao, Alibaba Technical Expert
Editor: Wang Shuai, Kingsoft Cloud
Produced by: DataFunTalk
Introduction:The Alibaba Cloud Graph Database (Graph Database, GDB) is a self-developed, real-time, reliable online graph database service supporting the Property Graph model for handling highly connected data queries and storage.GDB is the only graph database product in China to enter the Forrester Wave evaluation report and is the best practice graph database within Alibaba Group.GDB references the Volcano model executor and NUMA’s Morsel parallel execution operator to construct the GDB parallel executor, significantly enhancing performance in multiple star applications of Alibaba, such as DingTalk and Hema Fresh’s recommendation and query scenarios.Since its launch, GDB has over 100 application scenarios and is widely used both internally and externally within Alibaba Group, covering multiple industries.
Today’s introduction includes the following four aspects:
-
Product Introduction
-
Product Capabilities
-
Graph Executor
-
Application Scenarios
01
Graph Database GDB – Product Introduction
1. Self-developed Product by Alibaba
The Graph Database (GDB) is a self-developed product by Alibaba, supporting the Property Graph model for real-time, reliable online graph database services for handling highly connected data queries and storage.
Product Homepage: https://www.aliyun.com/product/gdb
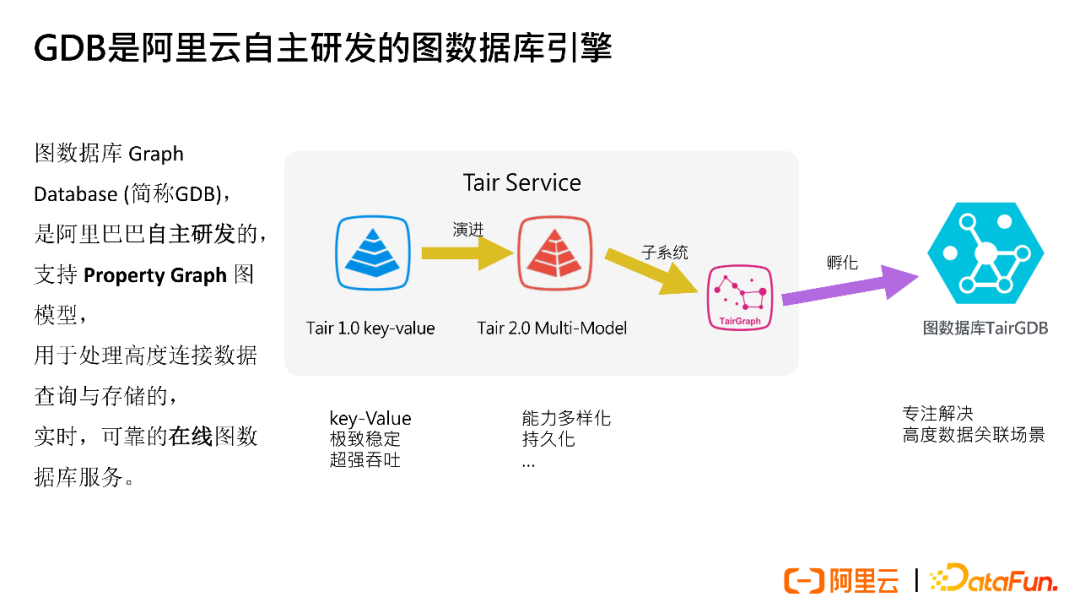
GDB originated from the Tair Key-Value model, evolving into Tair Multi-Model for high concurrency queries and writes within the group. With the trend of cloud migration, the Tair GDB graph database was incubated, primarily targeting highly associated complex scenarios.
2. Product Advantages
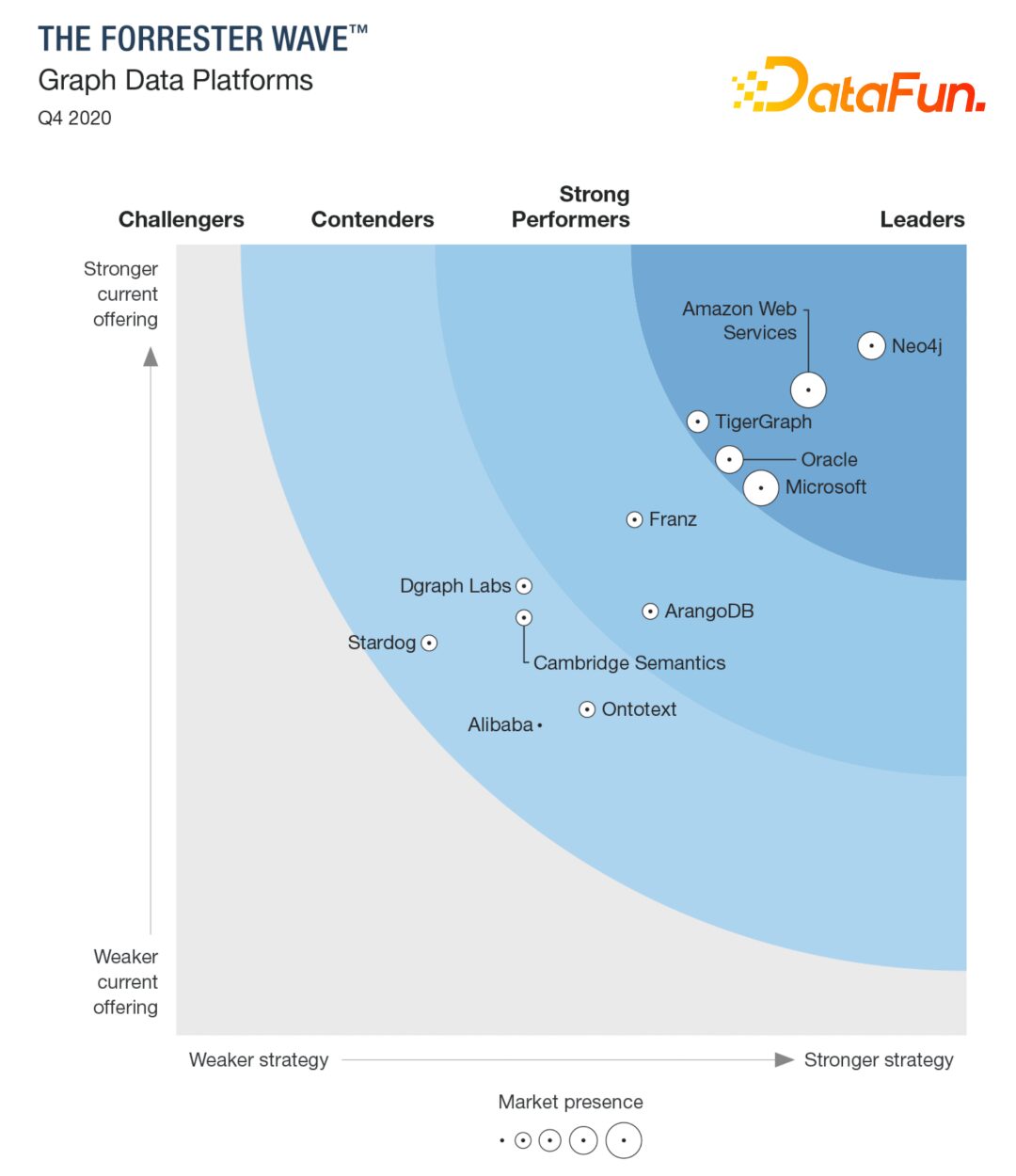
GDB is the only graph database product in China to enter the Forrester Wave evaluation report. It is the best practice graph database within Alibaba Group: continuously refined through over 30 star applications such as Hema Fresh, Tmall Supermarket, DingTalk, Gaode, Cainiao, and Ele.me, with more than 100 internal and external best practices since moving to the cloud.
① Compatible with Mainstream Graph Query Languages: Supports property graphs – compatible with mainstream query languages Gremlin and Cypher, reducing development barriers.
② High Performance, Low Cost:
-
Compared to self-built Neo4j, costs are reduced by 40%.
-
Performance for large-scale data queries outperforms Neo4j, Neptune, etc.
-
Read-only nodes support will soon be available to further improve read performance.
③ High Availability: Instances are highly available with automatic failover of nodes, ensuring business continuity with a 99.95% SLA guarantee.
④ Ease of Use and Maintenance:
-
Supports ACID transactions; automatic indexing, Schema-Free.
-
Includes commonly used graph algorithms.
-
Supports clients in Go, Java, Python, etc.
-
Provides various data import functions.
-
Offers backup and recovery, automatic upgrades, monitoring alarms, failover features, significantly reducing maintenance costs.
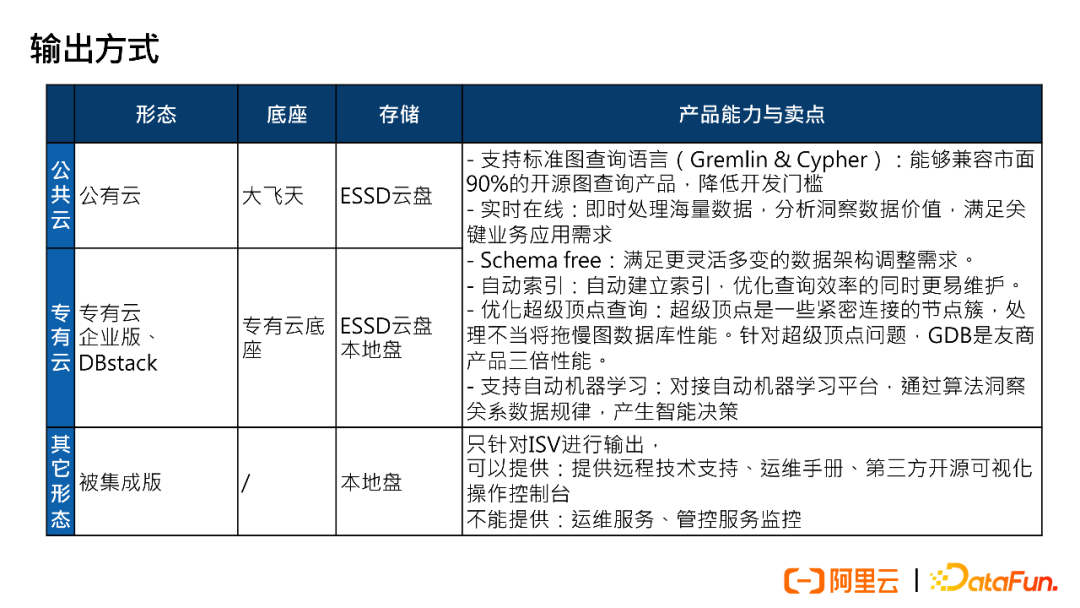
3. Output Methods
GDB includes various forms such as public cloud, private cloud (for banks and research institutions), and integrable versions (for evaluation scenarios). The table below introduces the base, storage, product capabilities, and selling points of each form.
02
Graph Database GDB – Product Capabilities
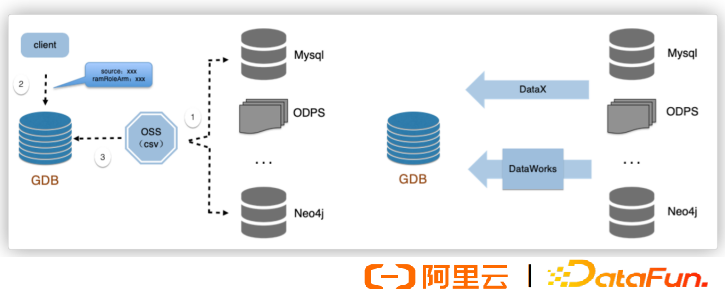
1. Convenient Access to Graph Services
The Graph Database GDB is compatible with various query languages, allowing users to migrate smoothly, and can import data from multiple data sources and channels.
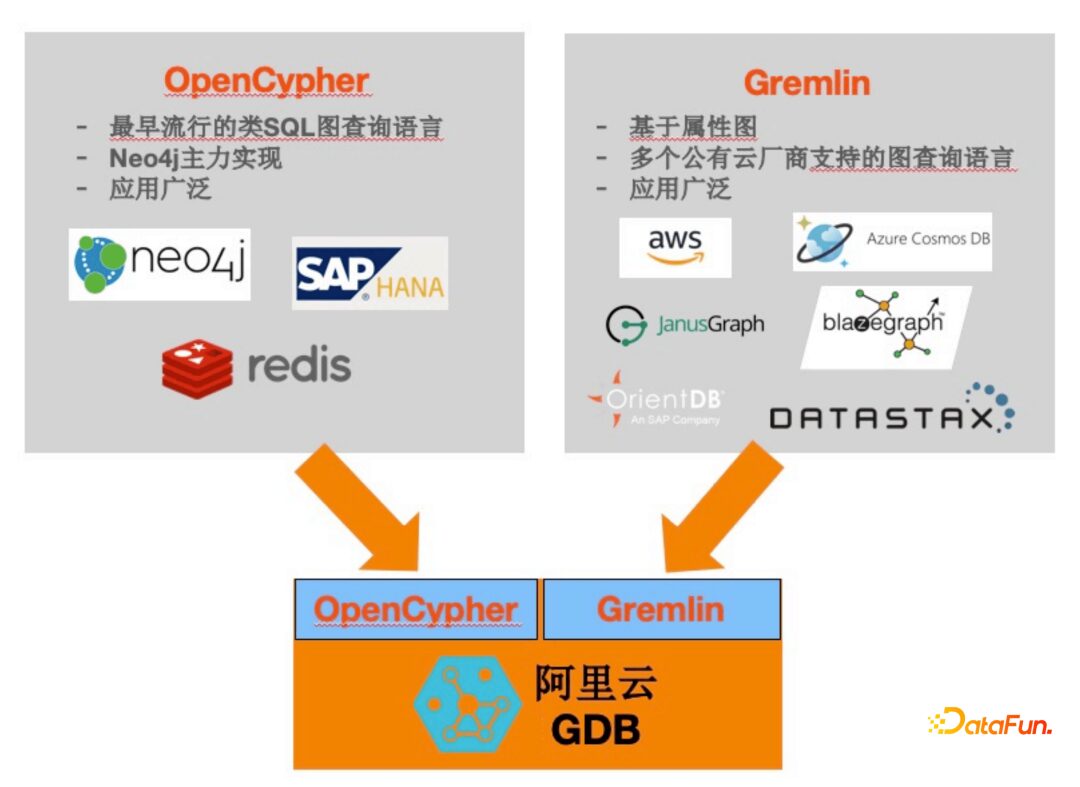
① Query Languages
-
Compatible with the two major mainstream graph query languages, Gremlin and Cypher, facilitating smooth migration to Alibaba Cloud’s GDB.
-
Supports open-source TinkerPop 3.3.3 (and above) version Driver.
-
The official guarantees compatibility for Java, Python, Go, .Net, REST.
-
Supports Gremlin Console.
② Data Import
-
Supports multiple data sources like neo4j, MySQL, odps…
-
Supports multiple data channels like OSS DataWorks.
2. Graph Instance Management & Maintenance-Free
After moving to the cloud, GDB implements graph instance management, and if used on Alibaba Cloud, maintenance costs can be waived.
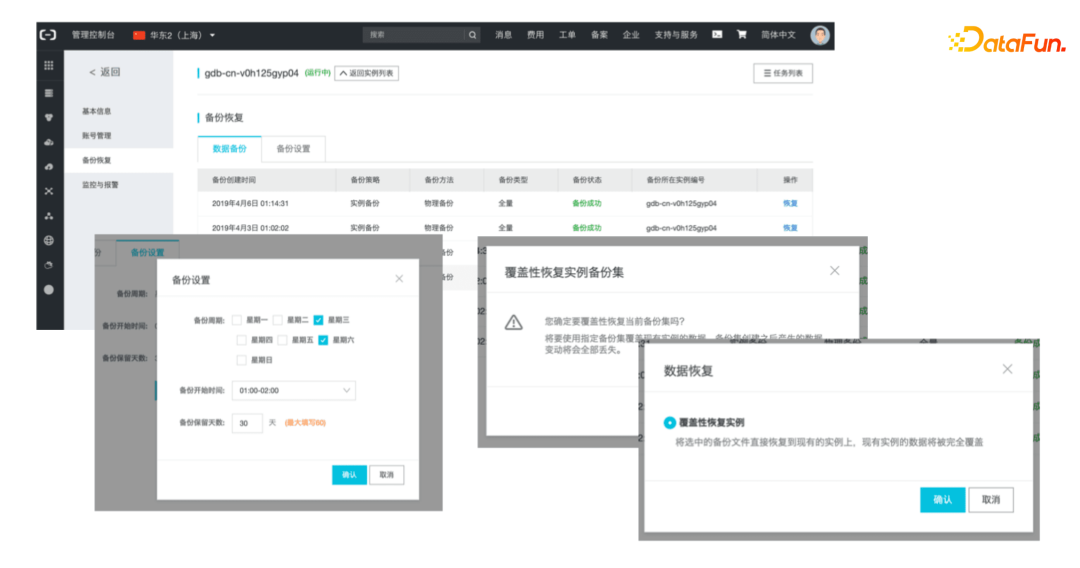
(1) Periodic Backup, One-Click Recovery
Data is periodically backed up, and in case of damage or loss, can be recovered with one click.
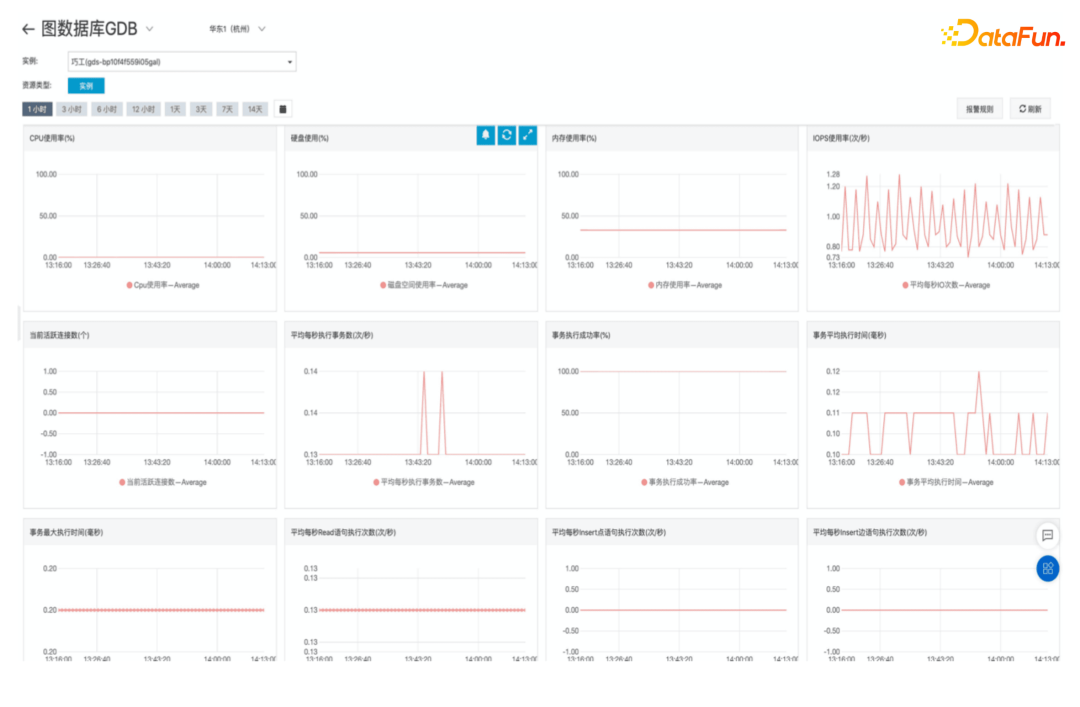
(2) 24-Hour Monitoring, Custom Alerts
Instances can be monitored 24/7, with customizable alerts and configurations, such as CPU saturation and data anomalies—data unavailability can trigger phone alerts.
(3) One-Click Resizing, Elastic Scaling
Based on customer traffic increases and decreases, one-click resizing and elastic scaling of storage capacity can be achieved.
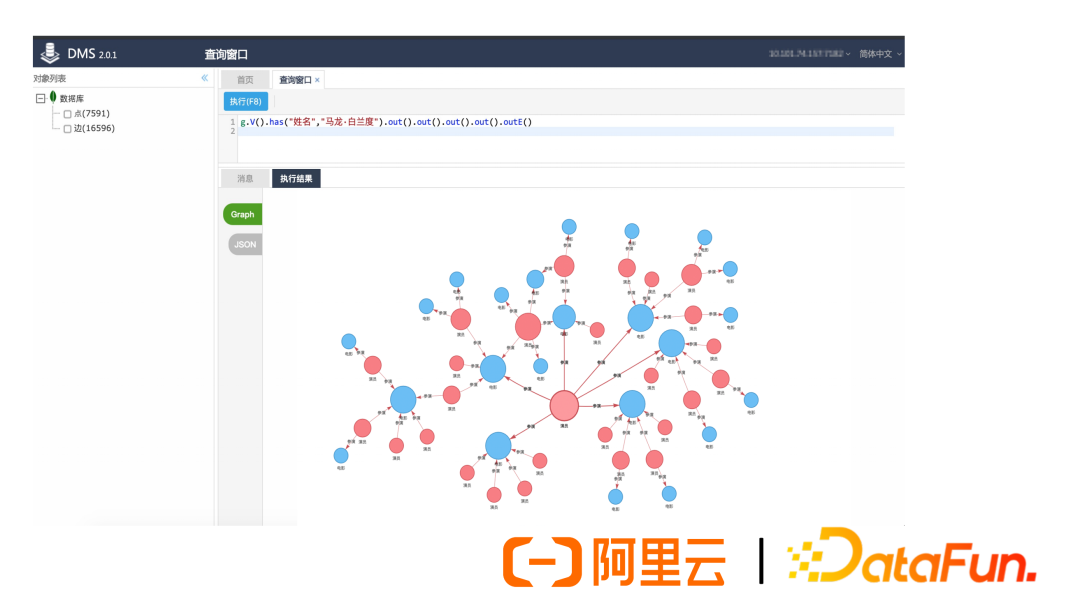
(4) Graph Visualization
Provides native visualization services, allowing testing based on this visualization product.
3. Product Forms
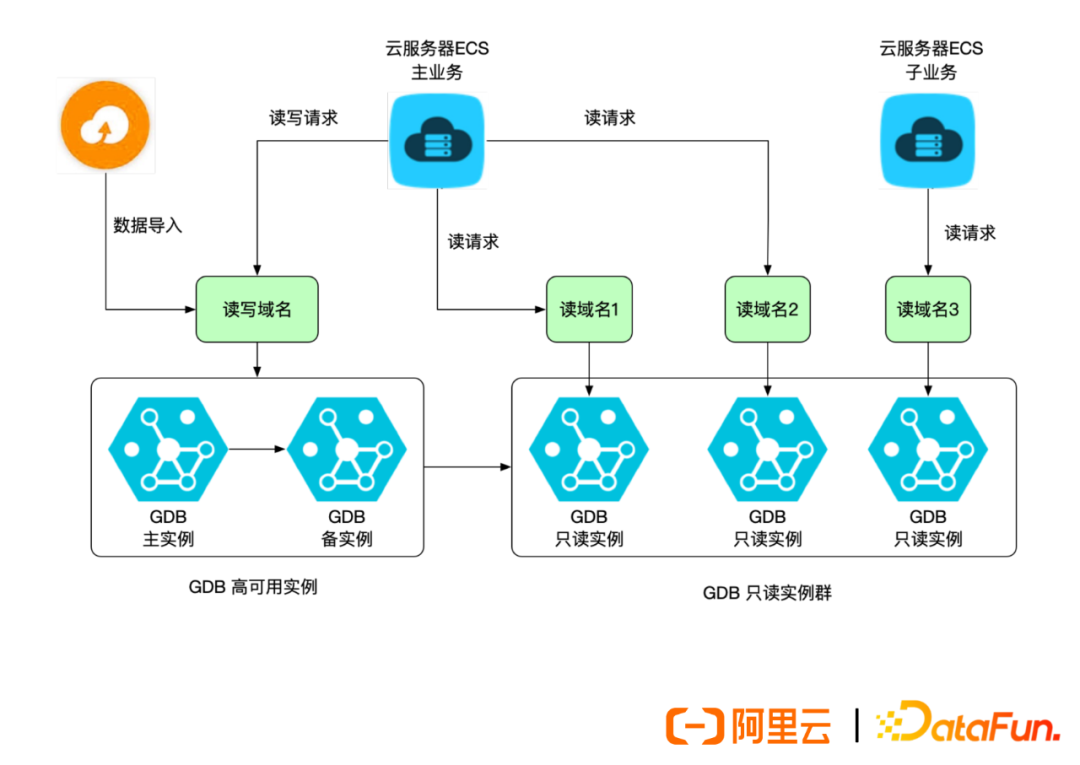
(1) Basic Instances
Basic instances are single-node instances with the following characteristics:
-
Low cost
-
No high availability requirement
(2) High Availability Instances
High availability instances use a primary-backup architecture with the following characteristics:
-
Failover in seconds
-
Automatic backup recovery
(3) Read-Only Instance Clusters
If customers have high QPS demands, they can use read-only instance clusters with the following characteristics:
-
Horizontal query scaling
-
Read-write separation
03
Graph Executor
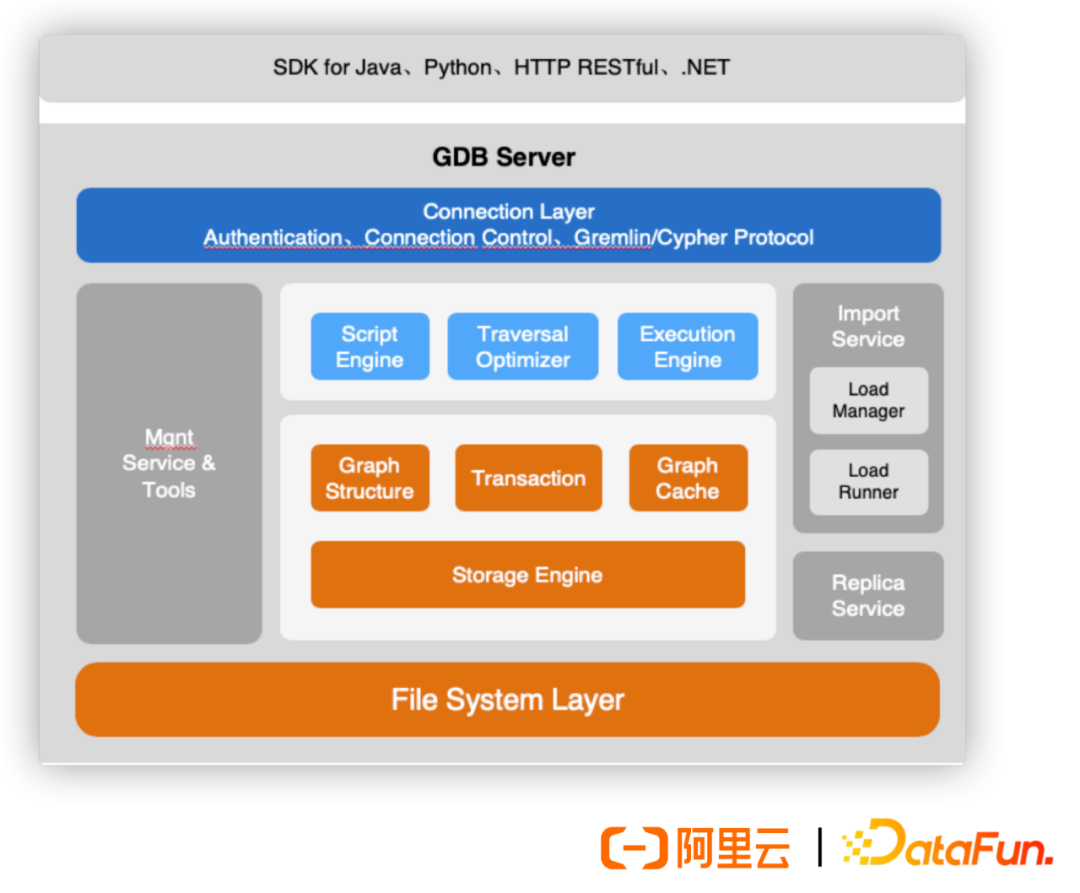
1. Overall Architecture
(1) Diverse Access
At the access layer, it is compatible with the two major industry mainstream syntaxes, Gremlin and Cypher, while covering multi-language SDKs as well as permission management, authentication management, and account management.
(2) Self-developed Parser
Compared to the native parser, the speed has significantly improved.
(3) Query Optimizer
Includes rule-based optimizer (RBO) and cost-based optimizer (CBO).
(4) Graph Executor
The graph executor can perform mixed loads and parallel execution.
(5) Graph Storage Engine
The graph storage engine is native graph storage, including automatic indexing and ACID transactions.
(6) Efficient Import, Service Control
2. Database Executor
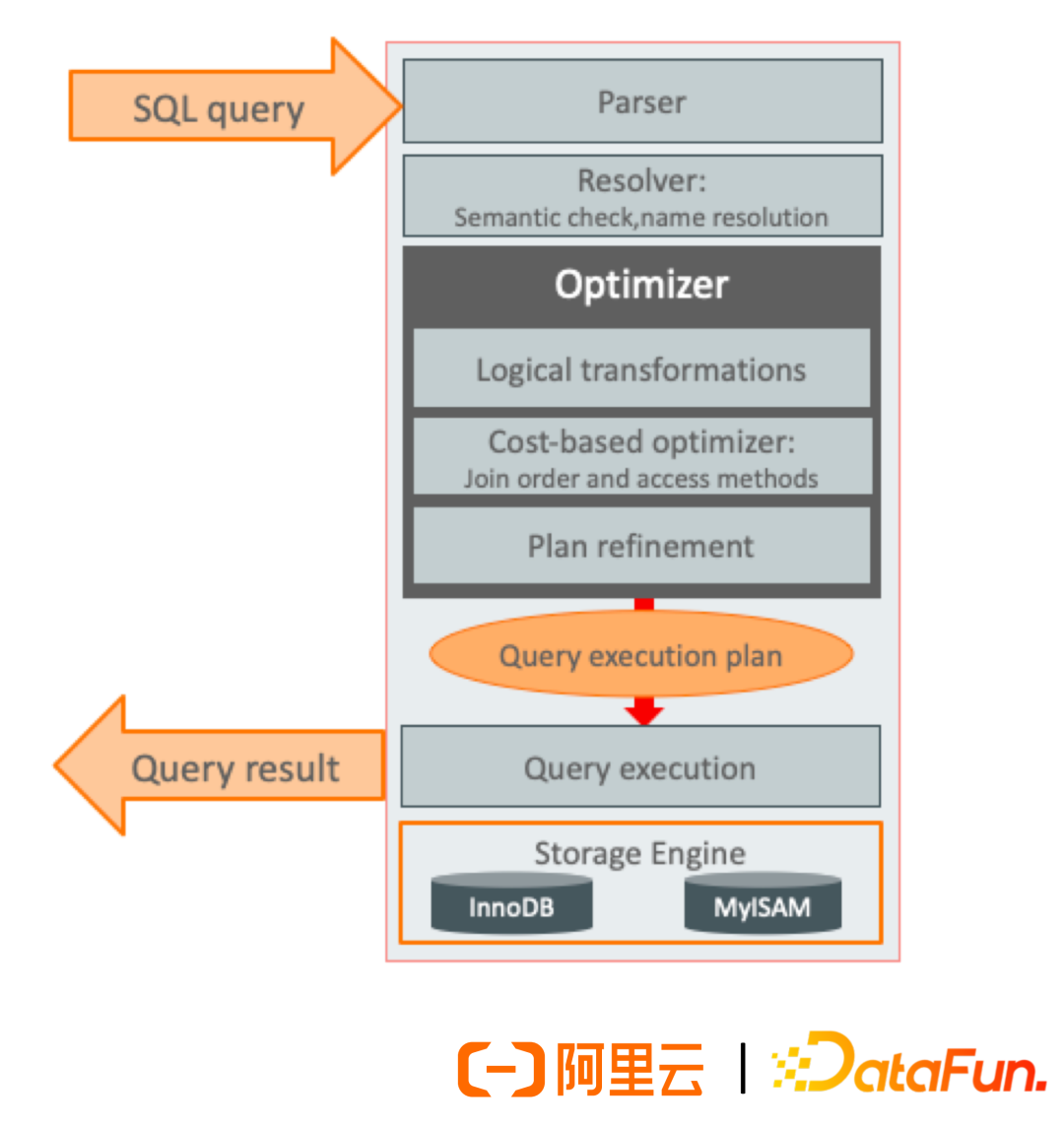
In the history of database system development, the optimization of SQL statement query optimizers has always been a focus in the database SQL engine industry, but during the execution of calculations, equally important are the query schedulers and plan executors that execute the execution plans generated by the optimizer.
In the early development of relational databases, constrained by computer IO capabilities, the time spent on calculations during queries was not significant, at which point the roles of schedulers and executors were diminished. The quality of a query mainly depended on the optimizer’s selection of execution plans.
With advancements in computer hardware and enhanced IO capabilities, schedulers and executors have gradually highlighted their importance.
3. Volcano Model Executor
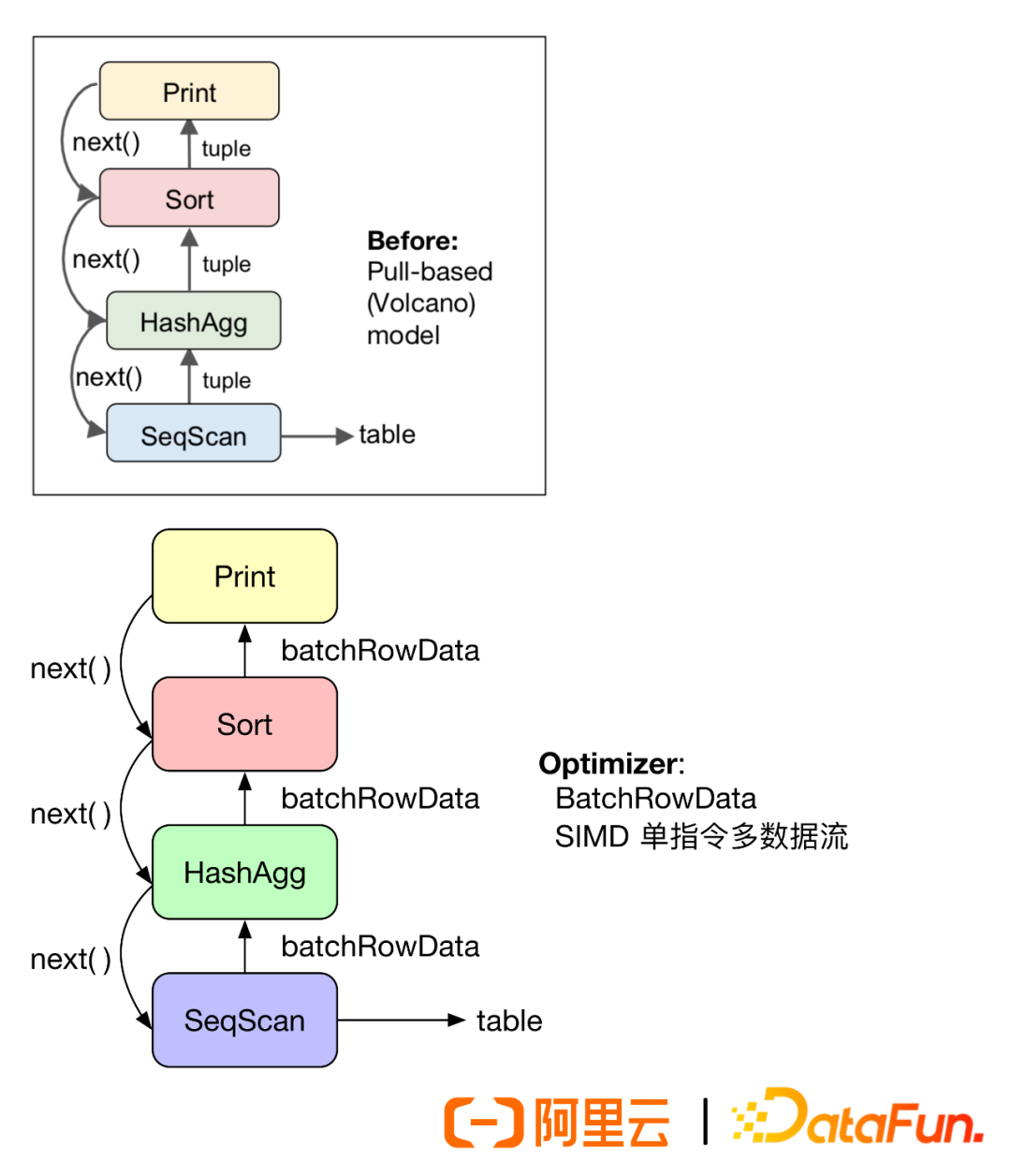
① The Volcano model is a mature interpretive computation model in the database field, characterized by:
-
Relational algebra operators abstracted as iterators, including next
-
Next produces a data tuple each time it is called
-
The root node repeatedly calls next to obtain the complete result
-
MySQL, SqlServer, Oracle
② Advantages
-
Operator decoupling, easy to extend
-
Low resource consumption (especially memory)
③ Disadvantages
-
High overhead of virtual functions
-
Not favorable for CPU Cache
④ Optimization Solutions
-
Batch processing, SIMD
-
Reduce the number of virtual function calls
-
Improve cache hit rate
-
Multi-row processing, SIMD parallelism provides possibilities (vectorization)
4. Morsel-Driven Parallelism
As data volumes increase and single-core capabilities cannot meet demands, the execution flow is divided into multiple operators based on small data blocks. The CPU will not suffer from frequent context switching, leading to low hit rates.
NUMA: Efficient utilization of multi-core CPUs, faster memory reads, and parallel execution scheduling solutions—the system uses a fixed number of thread pools, and the data during the execution process of each query is divided into fine-grained units (morsels), which are then processed by operator pipelines encapsulated as tasks and handed over to the thread pool for execution.
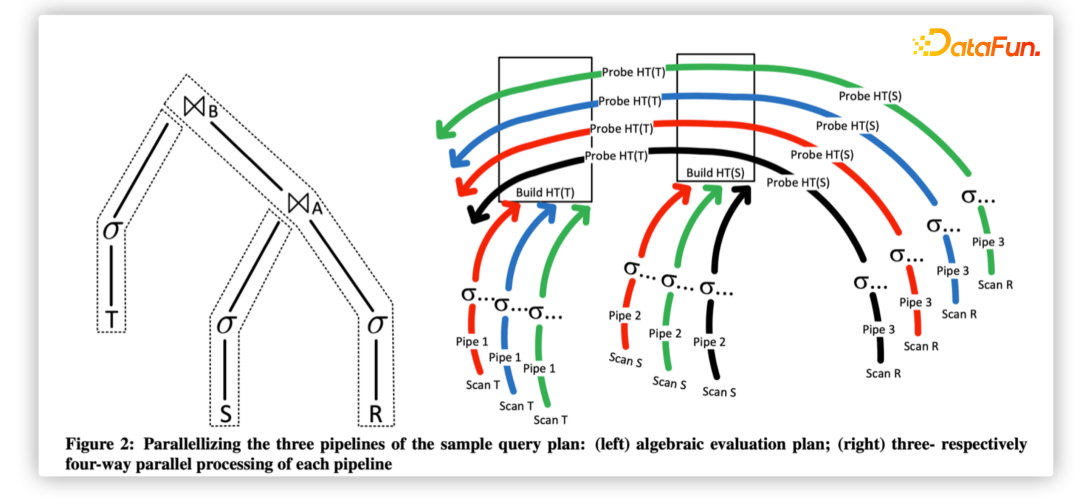
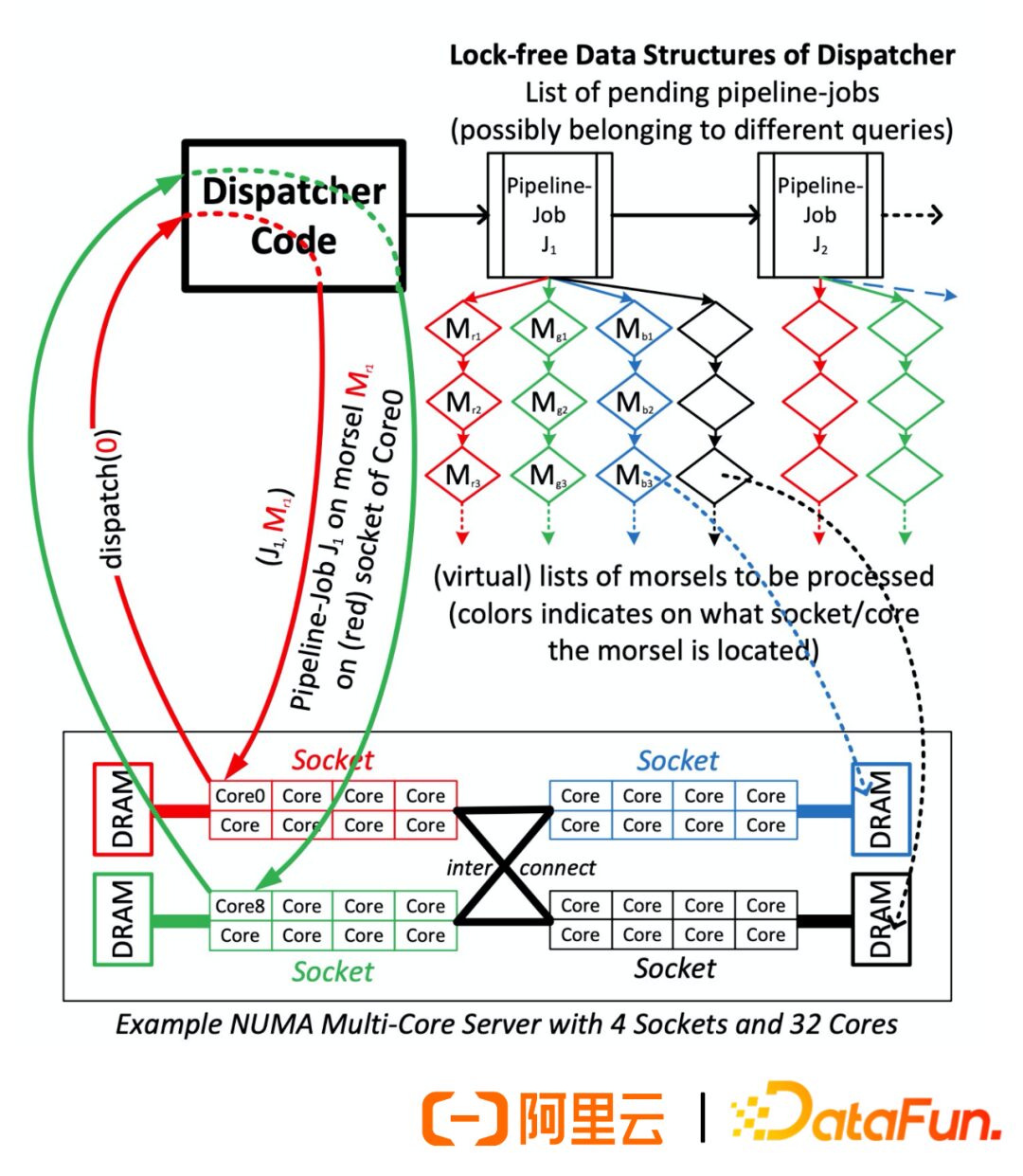
5. GDB Parallel Executor
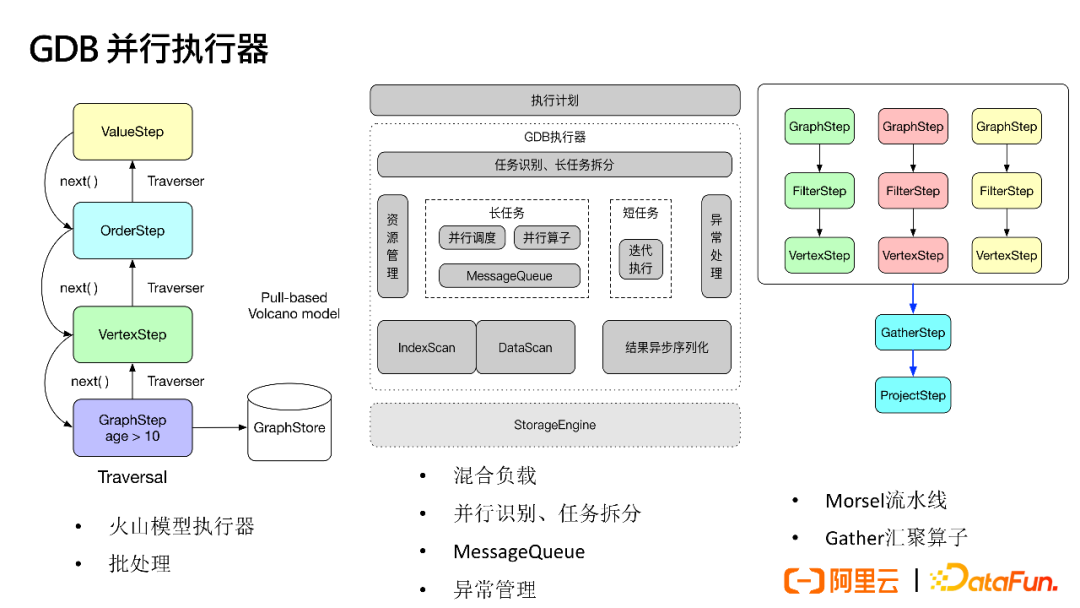
(1) Introduction to GDB Parallel Executor
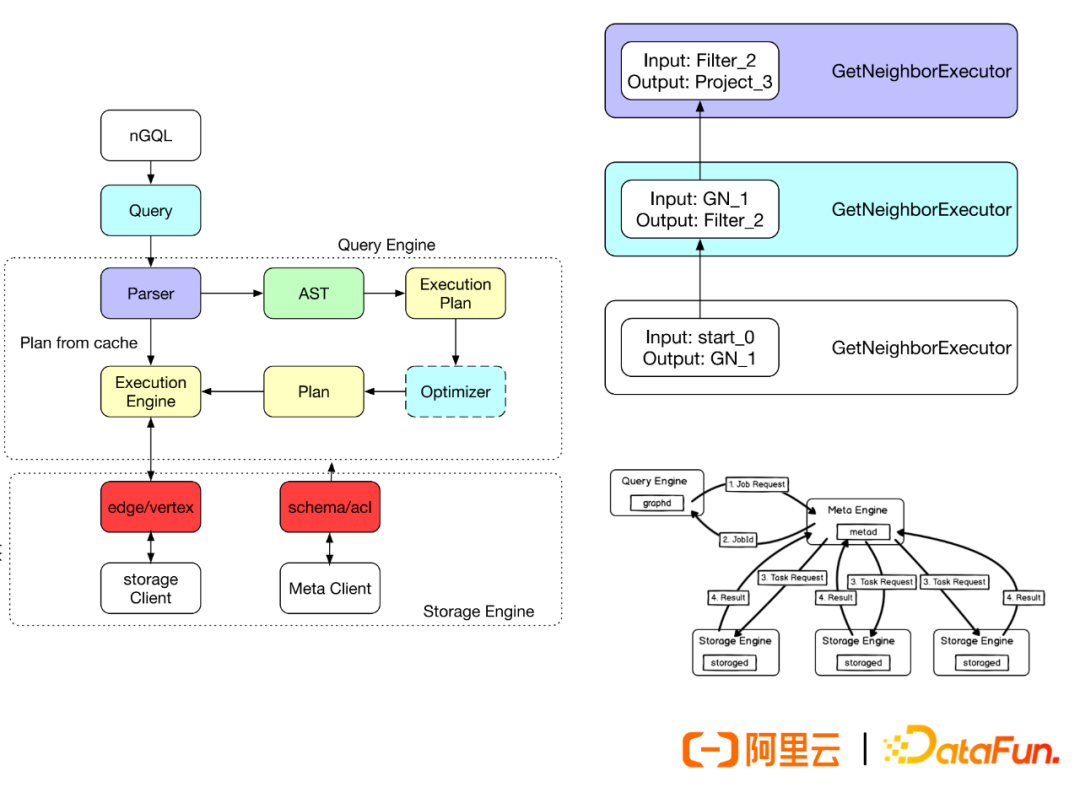
Referring to the Volcano model and NUMA’s Morsel parallel execution operator, GDB primarily adopts the Volcano model executor, returning data in batch processing formats. A traversal targets a batch of data.
The entire executor is divided into modules for task recognition and decomposition, resource management, etc., supporting mixed loads (including parallel decomposition of long tasks and iterative execution of short tasks), parallel recognition, and task decomposition. The parts interacting with storage include indexing and data iteration, result asynchronous serialization, etc.
The operator part can perform Morsel parallelization scenarios, allowing an operator to be split into multiple Morsel streams that can run on multiple CPUs. When encountering aggregation operators, they can be aggregated and returned uniformly, thus enabling mixed serial and parallel processing.
Mixed loads include short tasks running directly and long tasks being split for thread pool execution. During execution, multi-level exception handling is adopted, where Gather node exceptions are prioritized for return, and sub-task exceptions first return to the parent task, followed by batch termination and release.
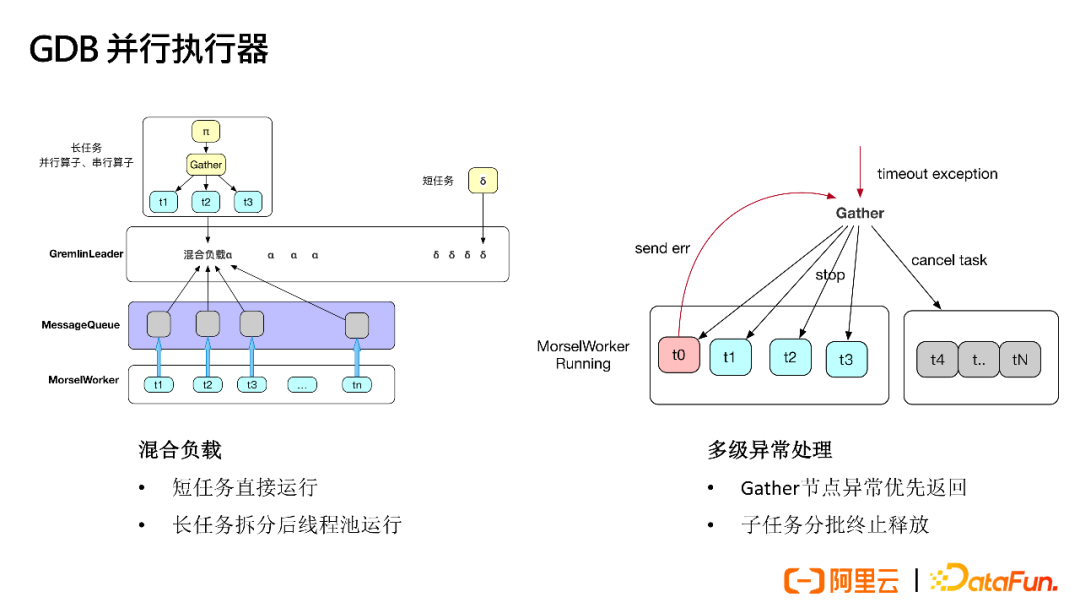
(2) Parallel Executor Case Study
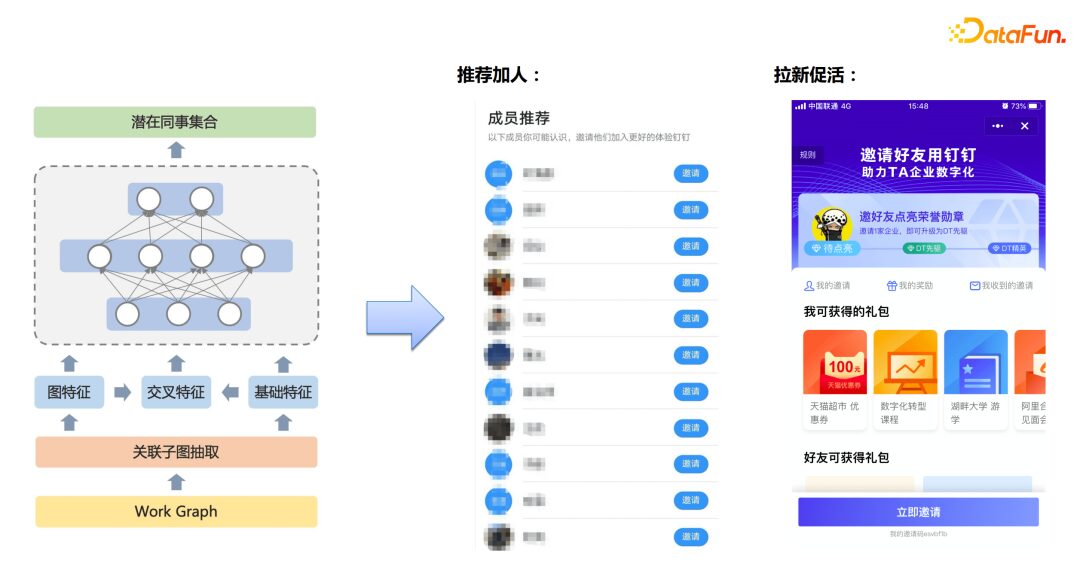
① DingTalk Friend Recommendations
a. Scenario
-
Second-degree friend recommendations
For new users coming in, find out who their friends are.
-
Batch processing of adjacent nodes
In a subsidiary with thousands of employees, Group by processing can be performed. The previous Morsel stream can be used for processing.
b. Business Value
The GDB graph database provides DingTalk with hundreds of billions of relational storage and query capabilities, managing relationships between people, between people and enterprises, and between enterprises. It provides core capabilities for functions like corporate identification, user intimacy calculation, executive predictions, and colleague relationship predictions.
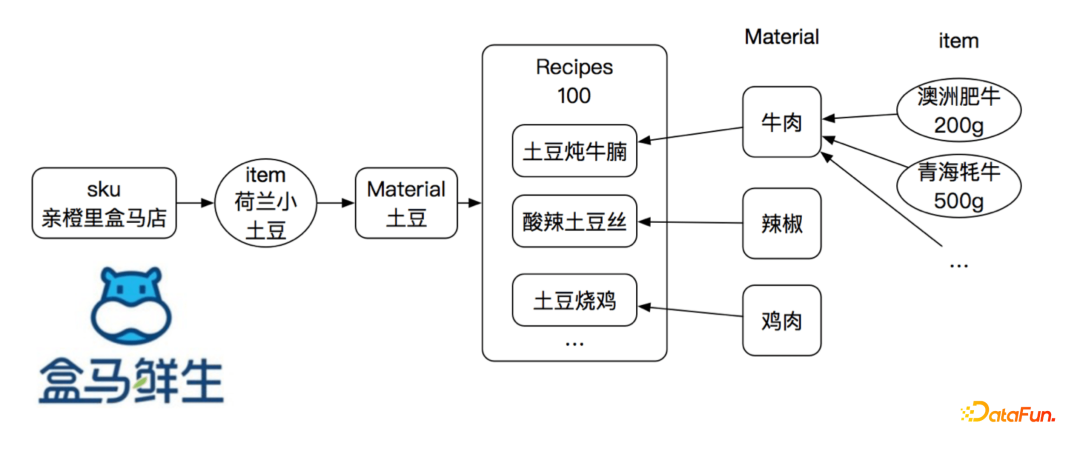
② Hema Fresh
a. Scenario: Hema Fresh Online Recommendations
-
Associated dish recommendations
-
Multiple path queries for recipes
The DSL request response time for Hema’s business was reduced from 210ms to under 100ms; before optimization, the flatMap took 140ms, and the total DSL time was 210ms. After optimization, the flatMap took 33ms, and the total DSL time was 82ms.
6. Other Database Product Executors
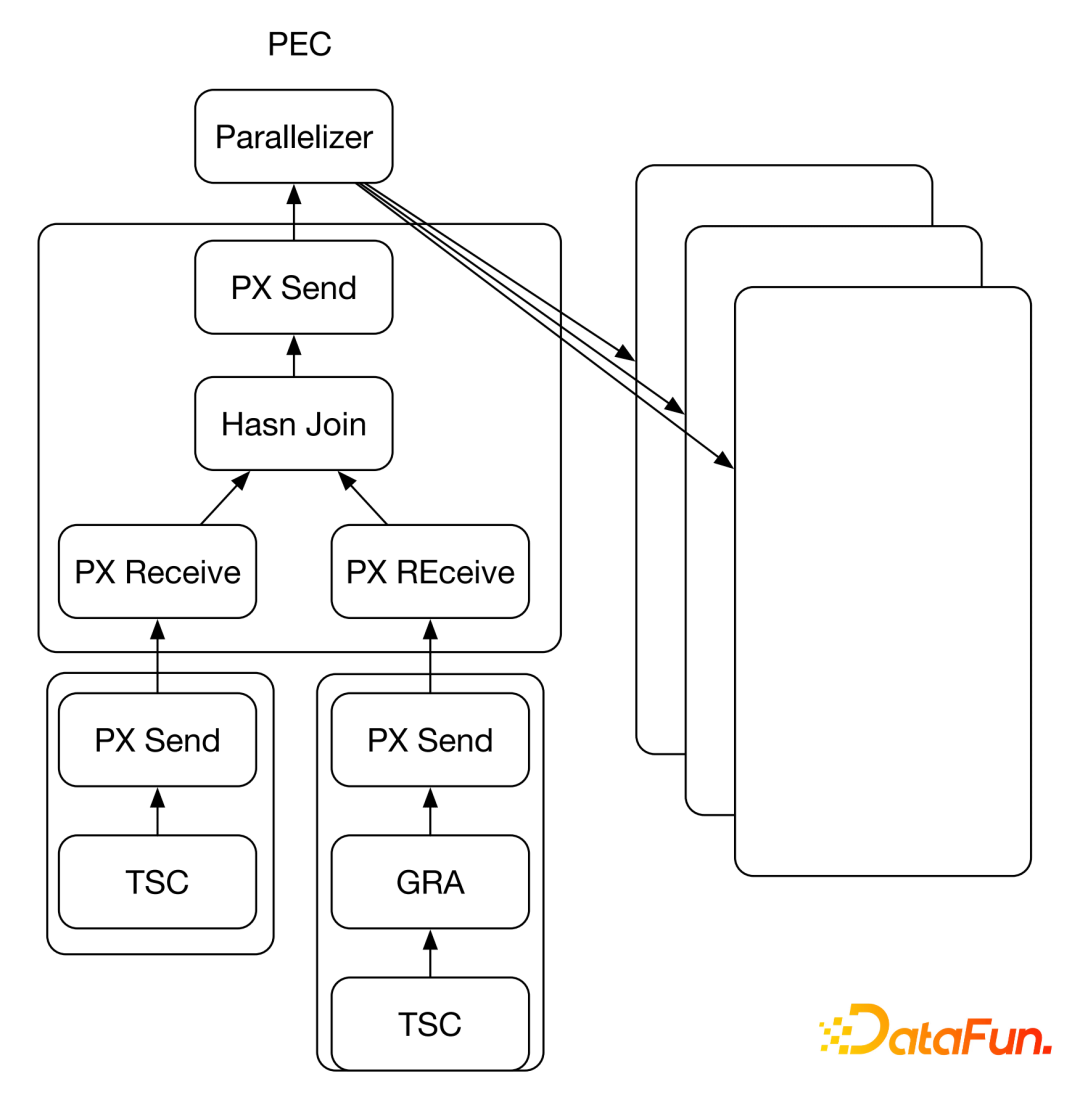
(1) Oracle 10g
Based on Oracle7, parallel optimization was performed. There are multiple Oracle data execution nodes, each with full data, stored in a shared disk. The PSC mechanism is adopted, with each execution point sharing the plan tree, and PX distributes the load across the nodes. Different execution operators run on different nodes. Serial execution on a single machine and parallel execution across multiple machines can be combined. After execution, results are aggregated and returned uniformly.
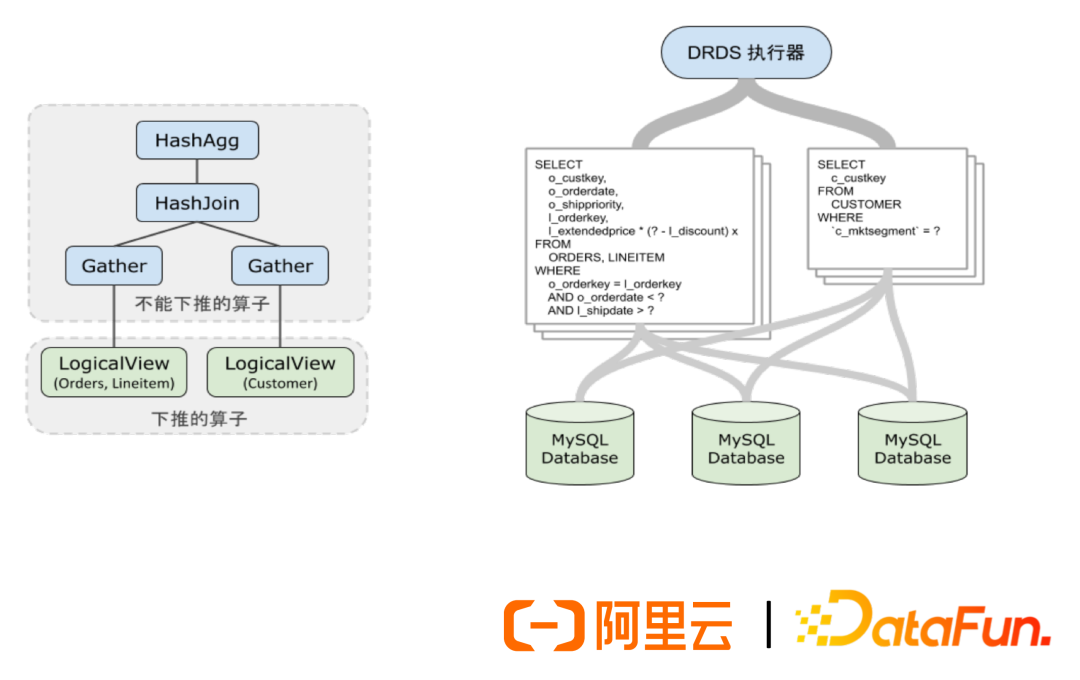
(2) PolarDB-X Parallel Executor
Alibaba’s PolarDB-X is based on the Volcano model, with multiple MySQL nodes in the storage layer. The aggregation operators above can parallelly send execution plans to the MySQL database.
-
Simple statements pushed down to the storage layer for MySQL execution
-
Volcano executor, Gather
-
DataChunk batch pulling
(3) Nebula Graph Query Engine
Nebula, as an open-source graph query engine, has the following characteristics:
① Storage and computation separation
② Volcano execution engine
③ Optimizer + Plan Cache
④ Execution plan optimization, filtering pushdown
⑤ Scheduler + Executor
⑥ Each Executor goes through four stages: create-open-execute-close
⑦ Nebula parallel implementation
-
Query engine scheduling
-
Parallel jobs sent to the storage engine
04
Application Scenarios
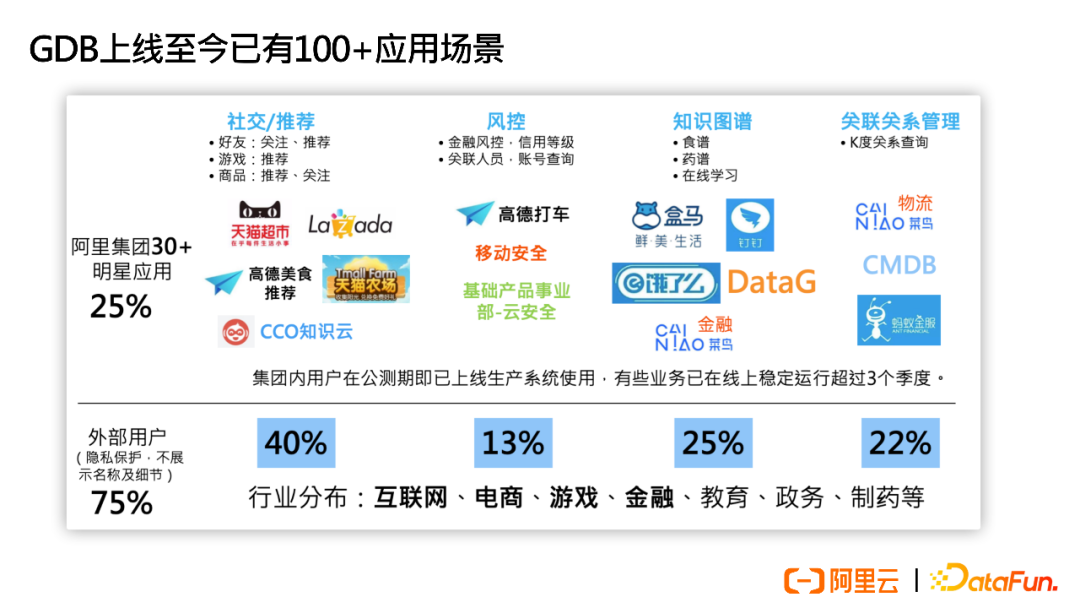
Since GDB’s launch, there have been over 100 application scenarios, with more than 30 star applications within Alibaba Group, including social/recommendation, risk control, knowledge graphs, and relationship management; among external users, it covers industries such as internet, e-commerce, gaming, finance, education, government, and pharmaceuticals.
That’s all for today’s sharing, thank you, everyone.
Please share, like, and give a three-hit combo at the end of the article~
01/Guest Speaker

Dou Chao
Alibaba Technical Expert
Master’s graduate from Xi’an University of Electronic Science and Technology, previously engaged in TFS storage development at Tencent, now mainly responsible for the development of the GDB graph database.
02/ Free Download of Materials

03/Sign Up for Live Broadcast and Get PPT for Free

04/About Us
DataFun: Focused on sharing and communication of big data and artificial intelligence technology applications. Launched in 2017, it has held over 100 offline and 100 online salons, forums, and summits in cities like Beijing, Shanghai, Shenzhen, and Hangzhou, inviting over 2000 experts and scholars to share. Its WeChat public account, DataFunTalk, has produced over 700 original articles, with over a million readings and 140,000+ precise followers.
🧐 Share, Like, and Watch, give a three-hit combo!👇