Bioprinter
A bioprinter is a device that can assemble biological materials or cell units according to the principles of additive manufacturing, driven by digital three-dimensional models, to create products such as medical devices, tissue engineering scaffolds, and organ tissues.
Working Principle of Bioprinter
Printing Process of Bioprinter
Before Bioprinting: Using software to reconstruct a three-dimensional structure from flat medical images, followed by slicing and uploading to the 3D printer. Then, the cells to be cultivated are separated and amplified, completing the preparation before printing. The cells are mixed with liquid biological materials such as hydrogels to create bio-ink.
During Bioprinting: The bio-ink will be placed in the ink cartridge of the bioprinter and printed sequentially according to the patient’s medical imaging data.
Applications of Bioprinter
01
Extrusion Dual-Head Bioprinter
The extrusion dual-head bioprinter developed by Professor Wang Jinwu and Academician Dai Kerong’s team at the 3D Printing Center of the Ninth People’s Hospital affiliated with Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine is a small-sized desktop bioprinter that can be used in cell rooms, clean cabinets, and other locations. This printer uses pneumatic feeding, is equipped with low-temperature, room-temperature, and high-temperature print heads, and employs a magnetic quick-installation method for the print heads, making replacement convenient. It can also be modified according to different needs, such as adding UV lights or replacing low-temperature print heads. This printer features easy operation and personalized design.
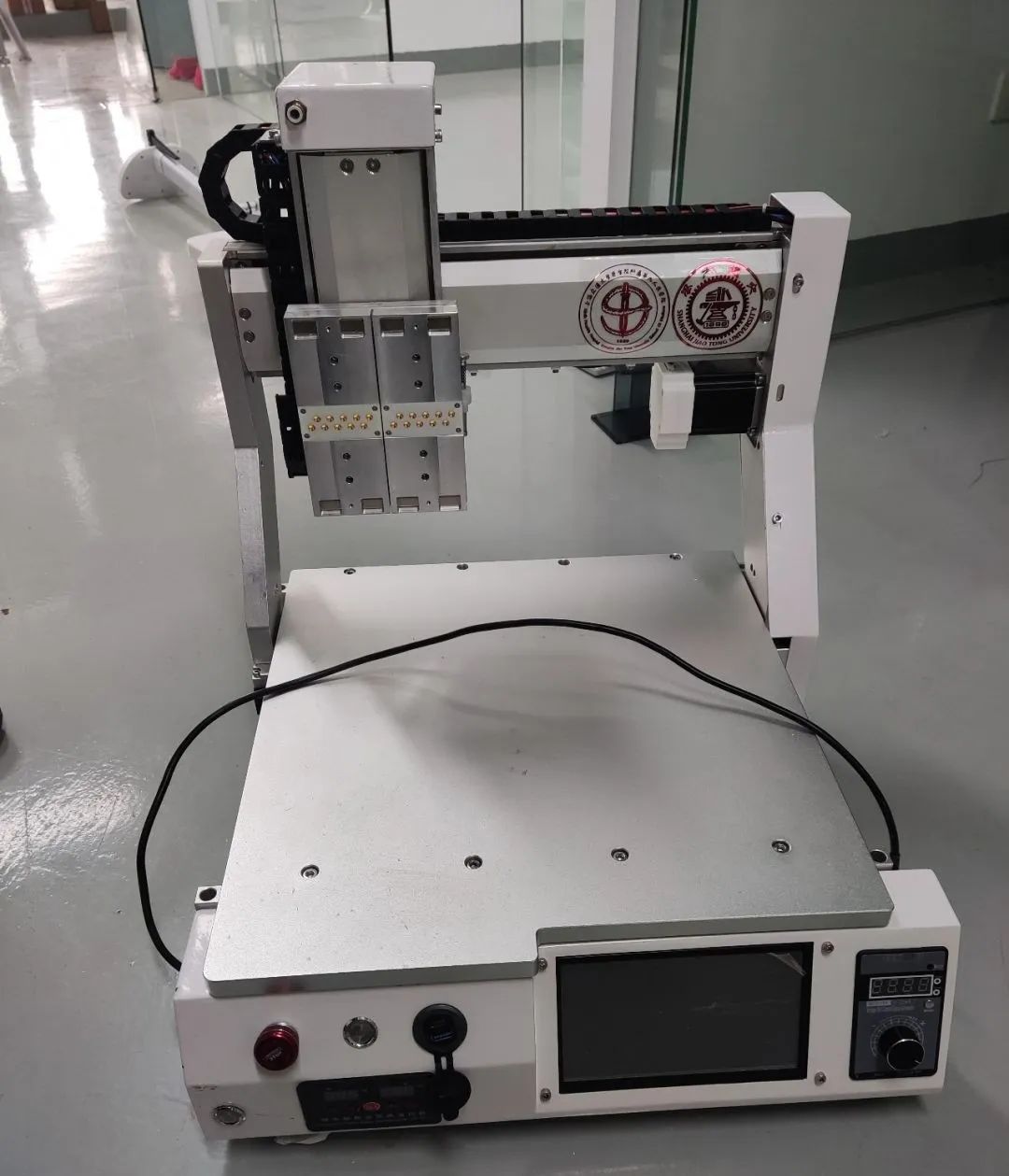
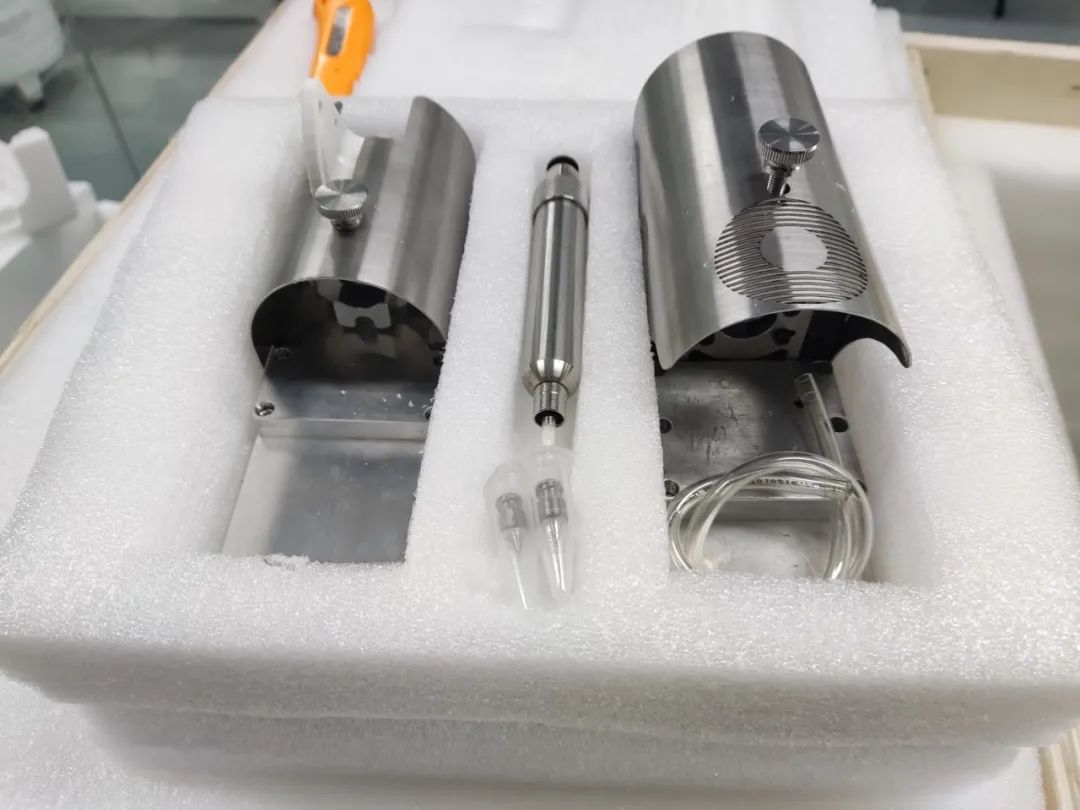


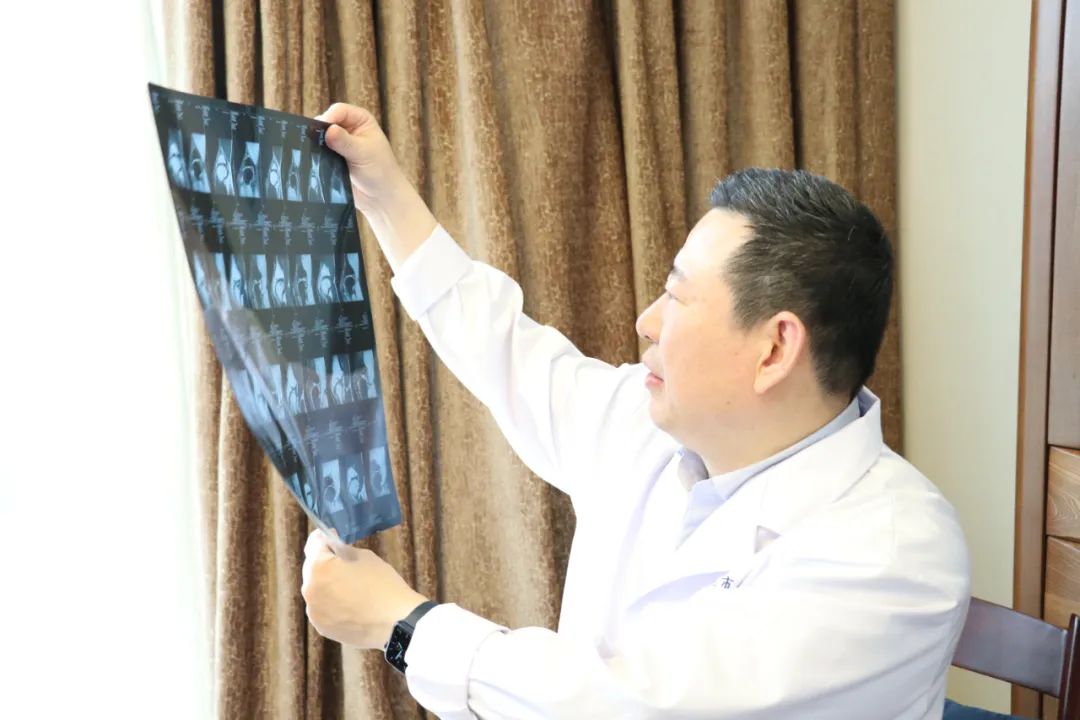
Professor Wang Jinwu’s team from the Ninth People’s Hospital with bioprinter and printing needles


Academician Dai Kerong and Professor Wang Jinwu’s team printed perfusion blood flow scaffold
02
High-Throughput Bioprinter
In drug screening, the required sample size is very large, and using ordinary bioprinters is time-consuming and labor-intensive. The high-throughput bioprinter solves this problem, as it can print multiple samples simultaneously. The high-throughput bioprinter developed by Professor Wang Jinwu and Academician Dai Kerong’s team at the 3D Printing Center of the Ninth People’s Hospital can have 24 print heads, allowing it to print up to 24 samples at once, supporting simultaneous printing of different materials, and features high resolution and sample reproducibility.


Academician Dai Kerong and Professor Wang Jinwu’s team developed high-throughput bioprinter and drug screening reactor
03
In-Situ Bioprinting Robot
In the repair of bone defects, ordinary bioprinters need to print first on their printing platform and then transplant to the bone defect site. This method not only increases the risk of surgical infection but also increases time costs. The in-situ bioprinting robot based on the UR5 robotic arm developed by Professor Wang Jinwu and Academician Dai Kerong’s team can print biological scaffolds at the site of bone defects during surgery. The designer only needs to scan the bone defect site, design a biological scaffold, and transmit it to the upper computer; the robot can then print during the surgery, thereby reducing risk.


Challenges of Bioprinter
Limits of Tissue Simulation: Although the complexity of tissues/organs can continue to be increased for a high degree of structural simulation, functionality cannot be further improved;
Scaling and Commercialization: Currently, tissue design, cell sources, and organ reconstruction are highly personalized, making it impossible to form an industrial chain;
Regulatory Challenges: The mechanisms of action are complex and the long-term effects on the host are unclear, with the mechanisms of action within the tissue structure dependent on various active components. The product characteristics are closely related to the manufacturing process, and small changes in manufacturing may lead to unpredictable effects on product characteristics.
References:
Recently, the 3D printing outpatient clinic at Rizhao Sports Hospital (Rizhao China-Canada International Health Management Center) is being prepared in an orderly manner, where the hospital collaborates with Professor Wang Jinwu’s team to provide new 3D printing technology for the citizens of Rizhao.
Consultation phone: 0633-8313311, Teacher Chang: 19963338620