Previously, several showcases in this area have been posted. Unlike FPGA, this systematic design allows for a more comprehensive understanding of these things. 1. [Special Spring Festival Edition] Those Experts Who Build CPUs by Hand, Appreciating the Breathtaking Hand Wiring and Superb Skills.
2. [Build a Complete Computer System Yourself] From basic digital logic, CPU design, virtual machine implementation, assembler, compiler to operating system design, all in one go.3. To help students learn computer architecture and principles, the University of Bristol created a 16-bit computer platform consisting of more than 100 logic circuit boards.
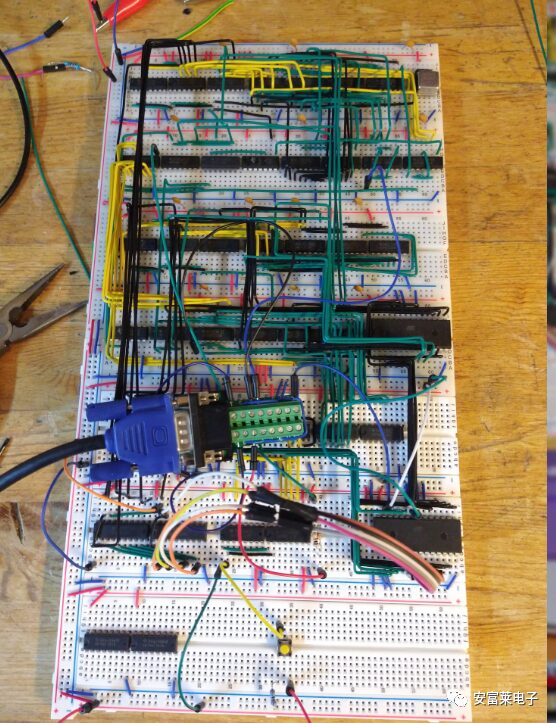
Hardware Design: GR8CPU is a fully functional computer built on a breadboard. The first version, GR8CPU Rev2, has over 600 wires, 74 integrated circuits, and 79 LEDs. It is an 8-bit architecture that considers simplicity and processing capability. The CPU can access 256 bytes of RAM and has a fully functional Tic-Tac-Toe game written for it. Currently, the second GR8CPU Rev3 is being built. There is a lot of interesting work to do: with 65536 bytes of memory, improved algorithms, and design for higher speed, this CPU is the most complex breadboard CPU ever built.
Initial Effect:
RAM Module Completed:
 Design ALU:
Design ALU:
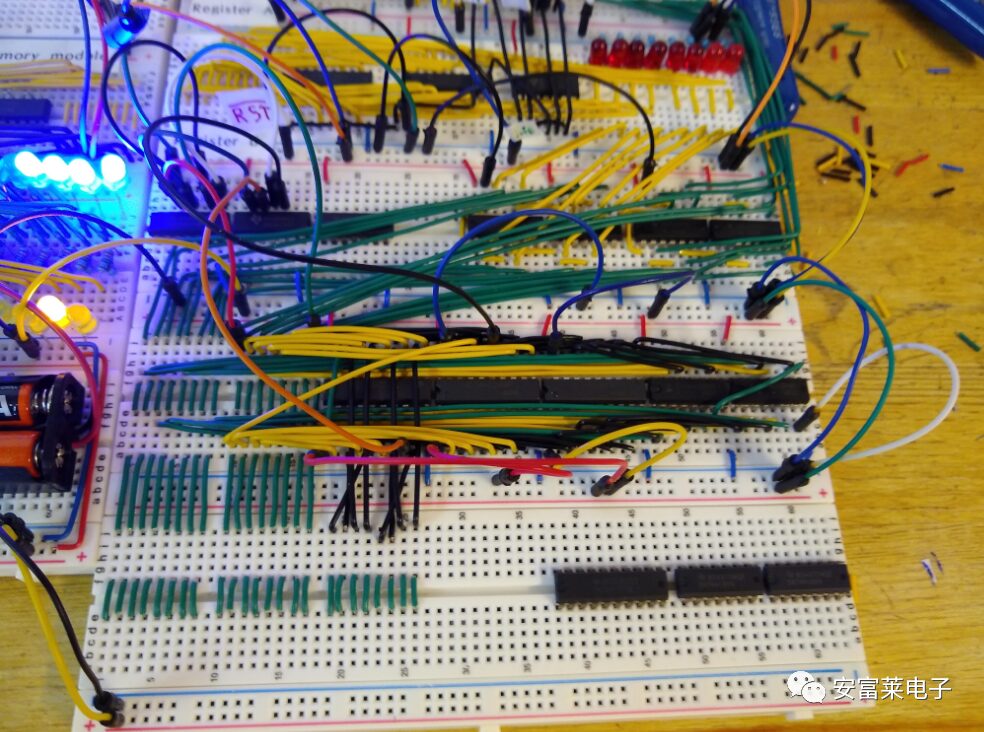 Completed ALU Design:
Completed ALU Design:
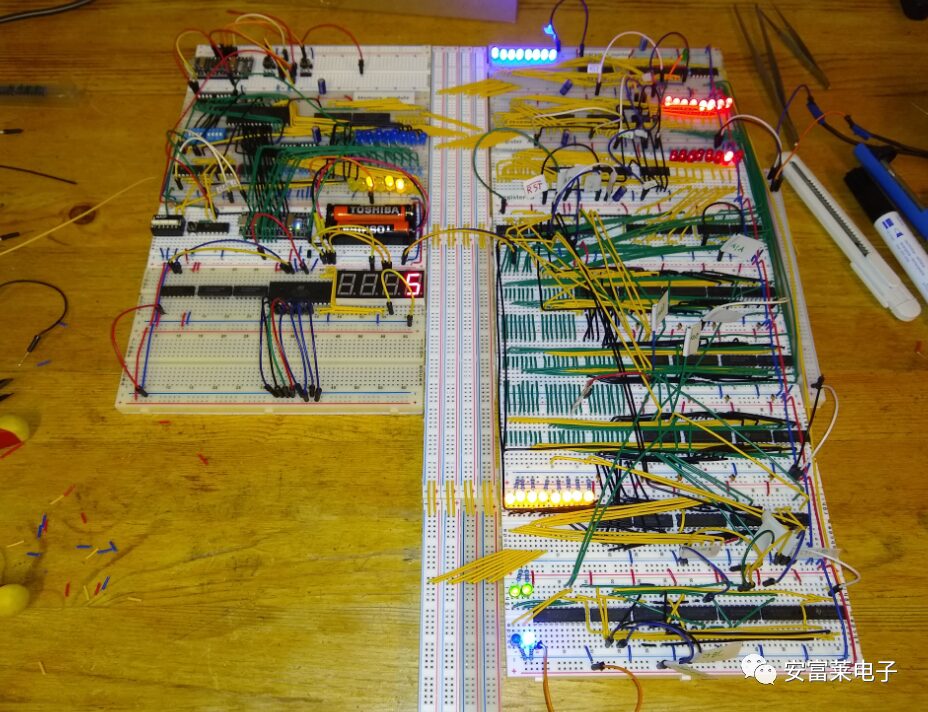 Video Card Design:
Video Card Design:
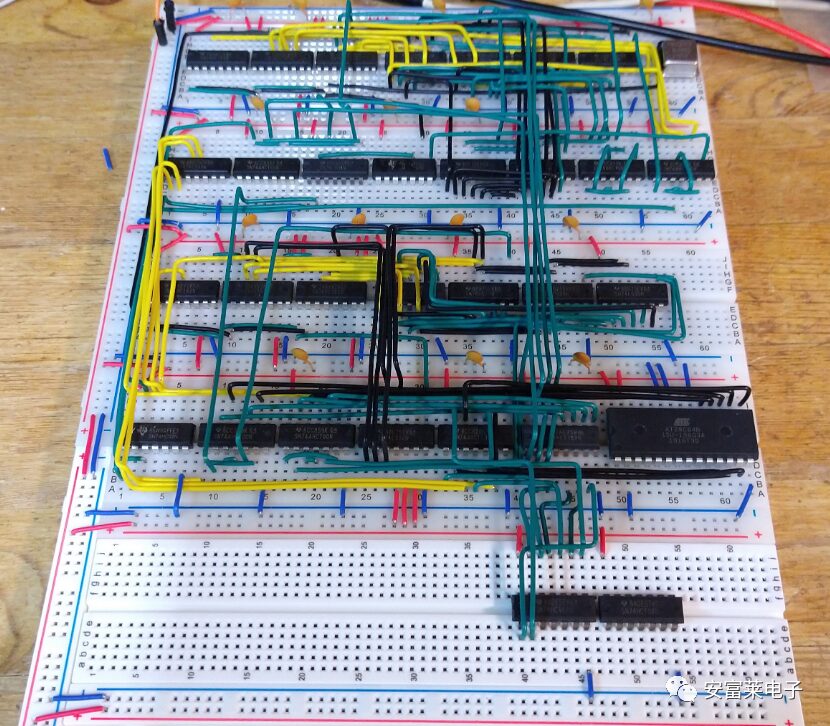 Completed Video Output Circuit:
Completed Video Output Circuit:
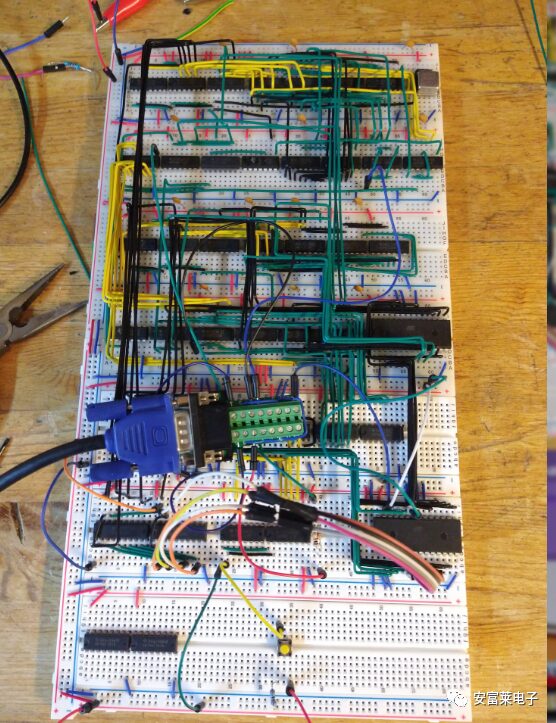
Unix-like System Design GR8NIX is an operating system inspired by Unix, which is a simple multi-user, multitasking operating system released in the 1970s. Modern operating systems based on Unix ideas include Linux, MacOS, and Android. GR8CPU Rev3 is written in assembly language, with a kernel implemented in 2000 lines of assembly code: (1) Multi-threading support for 32 concurrent threads. (2) Theoretically unlimited number of running programs. (3) Dynamic memory allocation, with a current maximum size of 8 KB. (4) True program execution is position-independent (dynamic application loading). However, GR8NIX is not perfect; due to hardware limitations, GR8NIX cannot: (1) Protect memory from process interference. (2) Recover from attempts to execute invalid instructions. (3) Reliably prevent memory leaks after process exit. After implementing dynamic memory management, the file system is being developed to load files from disk:
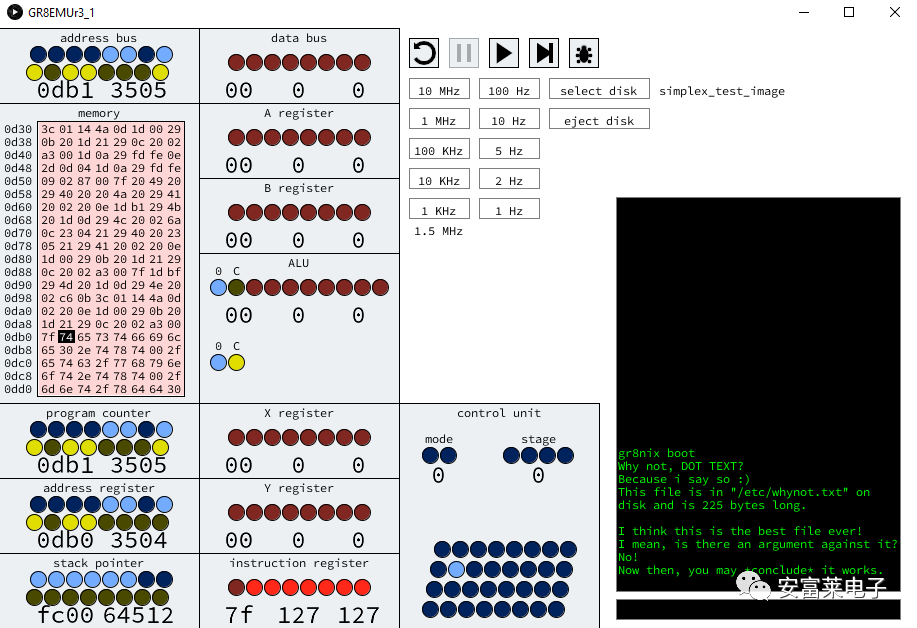
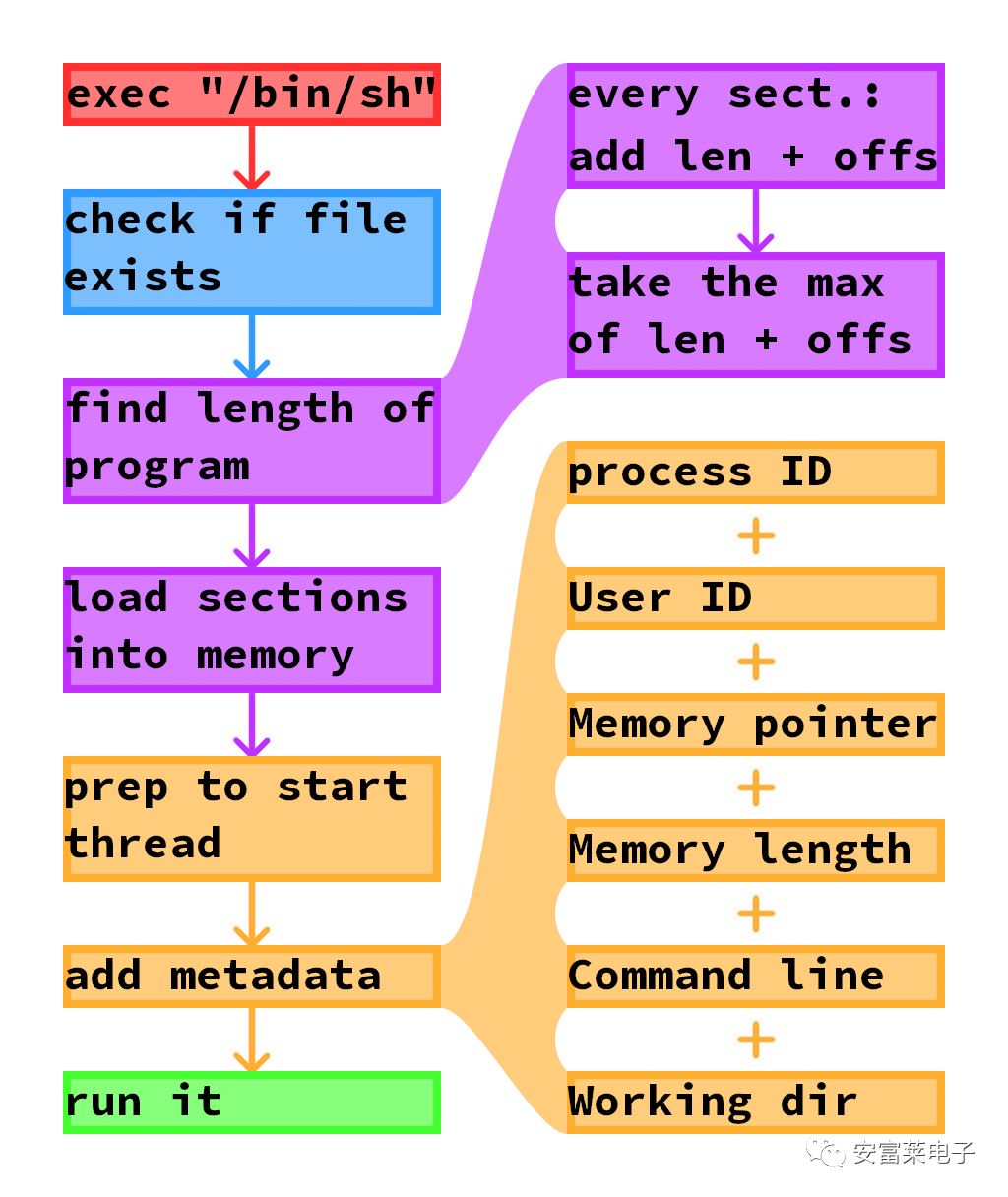
First, Exec is responsible for loading and running programs. Exec performs some integrity checks first: Does the file exist? Is it a program file? Is it valid? Next, Exec finds the length of the executable file by checking each entry and adding its offset to its length. The length found by Exec is the computed maximum length. After that, Exec calls thread_launch, a method used to prepare for starting threads. Exec completes this by adding some raw data to the process: user ID, pointer to allocated memory, command line being run, working directory, etc.