Hello everyone, I am Xian Di!
The following content is a summary of my personal learning notes on microcontrollers.
Please open in the WeChat client
1. Naming Conventions of STM32
What are the differences between STM32F103 and STM32F407? How can we distinguish them?
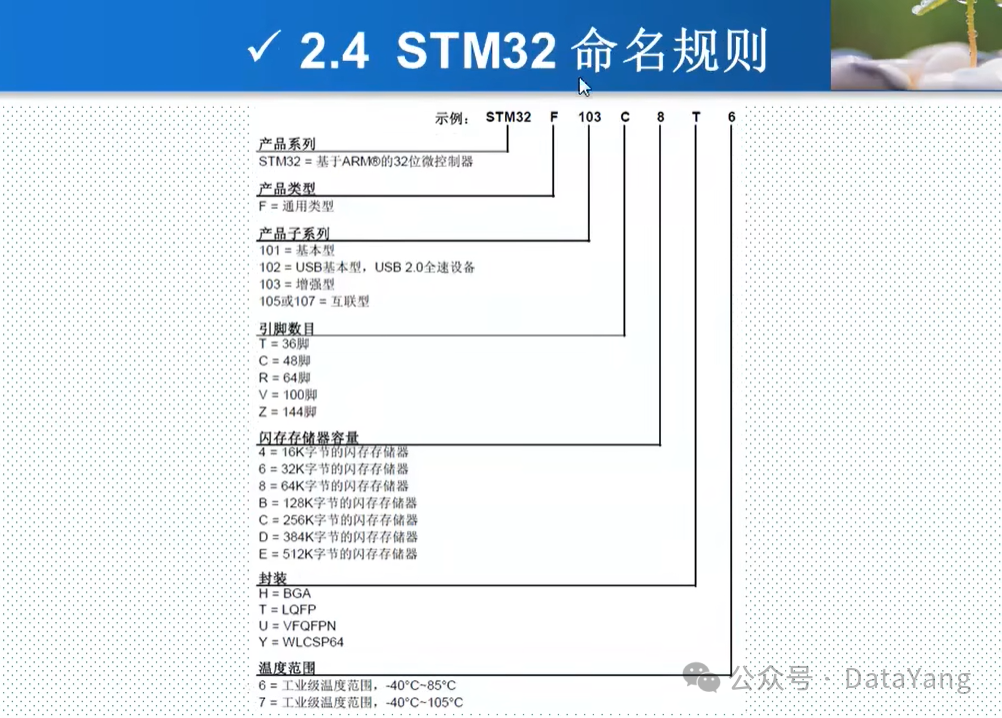
STM32 has a rigorous naming convention, for example: STM32F103ZET6
1. STM32: Indicates the product series, STM32 is a 32-bit microcontroller based on ARM.
2. F: Indicates the product type, F is for general-purpose products.
3. 103: Indicates the sub-series, where:
101: Basic type
102: USB type (USB 2.0 full-speed device)
103: Enhanced type
105 or 107: Internet type, can be connected to the network.
4. T indicates the number of pins, where:
T: 36 pins;
C: 48 pins;
R: 64 pins;
V: 100 pins;
Z: 144 pins.
5. E indicates the flash memory capacity, where:
4: 16KB flash capacity;
6: 32KB;
8: 64KB;
B: 128KB;
C: 256KB;
D: 384KB;
E: 512KB.
6. T indicates the packaging method, where:
H: BGA package;
T: LQFP package;
U: VFQFPN package;
Y: WLCSP64 package.
7. 6 indicates the operating temperature range of the chip (in degrees Celsius), where:
6: Industrial temperature range, -40 to 85 degrees;
7: Industrial temperature range, -40 to 105 degrees.
Please open in the WeChat client
2. Architecture of Cortex-M3 Chips
The Cortex-M3 chip is mainly divided into two parts based on the manufacturer: the M3 chip core and the high-level system designed by ARM, while other components such as the bus, various peripherals, timing and reset, memory, and various IO are designed and developed by the chip manufacturer.
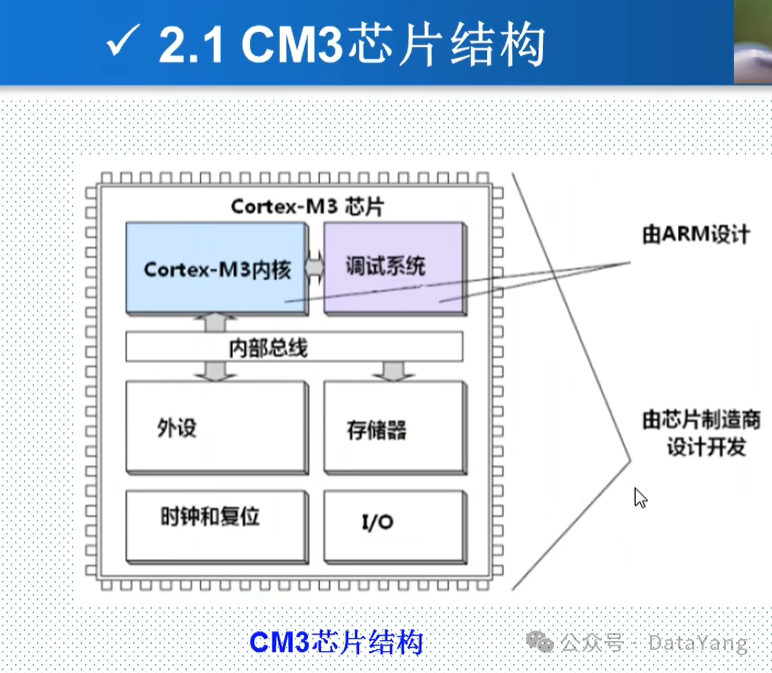
This production structure allows ARM to focus on chip design and development without spending too much effort managing the chip production process.