The official WeChat platform of the School of Computer Science, North China University of Science and Technology, focused on technological innovation, dedicated to resource sharing, the latest updates from the college, fashionable and fun IT news, we have everything you want to know!

Algorithms are the soul of programs and software. As an excellent programmer, only by having a comprehensive grasp of some basic algorithms can one feel at ease in the process of designing programs and writing code. This article is the second in a series of nearly a hundred C language algorithms, including classic algorithms such as the Fibonacci sequence, simple calculator, palindrome check, and prime check. They may come in handy in your graduation project or interview.
The Fibonacci sequence, also known as the Fibonacci series or the golden ratio series, refers to the sequence: 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21.
The C language implementation code is as follows:
/* Displaying Fibonacci sequence up to nth term where n is entered by user. */#include <stdio.h>int main() { int count, n, t1=0, t2=1, display=0; printf("Enter number of terms: "); scanf("%d",&n); printf("Fibonacci Series: %d+%d+", t1, t2); /* Displaying first two terms */ count=2; /* count=2 because first two terms are already displayed. */ while (count<n) { display=t1+t2; t1=t2; t2=display; ++count; printf("%d+",display); } return 0; }
Result output:
Enter number of terms: 10 Fibonacci Series: 0+1+1+2+3+5+8+13+21+34+
You can also use the following source code:
/* Displaying Fibonacci series up to certain number entered by user. */ #include <stdio.h> int main() { int t1=0, t2=1, display=0, num; printf("Enter an integer: "); scanf("%d",&num); printf("Fibonacci Series: %d+%d+", t1, t2); /* Displaying first two terms */ display=t1+t2; while(display<num) { printf("%d+",display); t1=t2; t2=display; display=t1+t2; } return 0; }
Result output:
Enter an integer: 200 Fibonacci Series: 0+1+1+2+3+5+8+13+21+34+55+89+144+
Source code:
/* C program to check whether a number is palindrome or not */ #include <stdio.h> int main() { int n, reverse=0, rem,temp; printf("Enter an integer: "); scanf("%d", &n); temp=n; while(temp!=0) { rem=temp%10; reverse=reverse*10+rem; temp/=10; } /* Checking if number entered by user and it's reverse number is equal. */ if(reverse==n) printf("%d is a palindrome.",n); else printf("%d is not a palindrome.",n); return 0; }
Result output:
Enter an integer: 12321 12321 is a palindrome.
Note: 1 is neither a prime nor a composite number.
Source code:
/* C program to check whether a number is prime or not. */#include <stdio.h>int main(){ int n, i, flag=0; printf("Enter a positive integer: "); scanf("%d",&n); for(i=2;i<=n/2;++i) { if(n%i==0) { flag=1; break; } } if (flag==0) printf("%d is a prime number.",n); else printf("%d is not a prime number.",n); return 0; }
Result output:
Enter a positive integer: 29 29 is a prime number.
Use * to create a triangle
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * *
Source code:
#include <stdio.h> int main() { int i,j,rows; printf("Enter the number of rows: "); scanf("%d",&rows); for(i=1;i<=rows;++i) { for(j=1;j<=i;++j) { printf("* "); } printf("\n"); } return 0; }
As shown below, use numbers to print half a pyramid.
1 1 2 1 2 3 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 5
Source code:
#include <stdio.h> int main() { int i,j,rows; printf("Enter the number of rows: "); scanf("%d",&rows); for(i=1;i<=rows;++i) { for(j=1;j<=i;++j) { printf("%d ",j); } printf("\n"); } return 0; }
Use * to print half a pyramid
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * *
Source code:
#include <stdio.h> int main() { int i,j,rows; printf("Enter the number of rows: "); scanf("%d",&rows); for(i=rows;i>=1;--i) { for(j=1;j<=i;++j) { printf("* "); } printf("\n"); } return 0; }
Use * to print a pyramid
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *
Source code:
#include <stdio.h> int main() { int i,space,rows,k=0; printf("Enter the number of rows: "); scanf("%d",&rows); for(i=1;i<=rows;++i) { for(space=1;space<=rows-i;++space) { printf(" "); } while(k!=2*i-1) { printf("* "); ++k; } k=0; printf("\n"); } return 0; }
Use * to print an inverted pyramid
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *
Source code:
#include <stdio.h> int main() { int rows,i,j,space; printf("Enter number of rows: "); scanf("%d",&rows); for(i=rows;i>=1;--i) { for(space=0;space<rows-i;++space) printf(" "); for(j=i;j<=2*i-1;++j) printf("* "); for(j=0;j<i-1;++j) printf("* "); printf("\n"); } return 0; }
Source code:
/* Source code to create a simple calculator for addition, subtraction, multiplication and division using switch...case statement in C programming. */ # include <stdio.h> int main() { char o; float num1,num2; printf("Enter operator either + or - or * or divide : "); scanf("%c",&o); printf("Enter two operands: "); scanf("%f%f",&num1,&num2); switch(o) { case '+': printf("%.1f + %.1f = %.1f",num1, num2, num1+num2); break; case '-': printf("%.1f - %.1f = %.1f",num1, num2, num1-num2); break; case '*': printf("%.1f * %.1f = %.1f",num1, num2, num1*num2); break; case '/': printf("%.1f / %.1f = %.1f",num1, num2, num1/num2); break; default: /* If operator is other than +, -, * or /, error message is shown */ printf("Error! operator is not correct"); break; } return 0; }
Result output:
Enter operator either + or - or * or divide : - Enter two operands: 3.4 8.43.4 - 8.4 = -5.0
Source code:
#include <stdio.h> int prime(int n); int main() { int n, i, flag=0; printf("Enter a positive integer: "); scanf("%d",&n); for(i=2; i<=n/2; ++i) { if (prime(i)!=0) { if ( prime(n-i)!=0) { printf("%d = %d + %d\n", n, i, n-i); flag=1; } } } if (flag==0) printf("%d can't be expressed as sum of two prime numbers.",n); return 0;} int prime(int n) /* Function to check prime number */{ int i, flag=1; for(i=2; i<=n/2; ++i) if(n%i==0) flag=0; return flag; }
Result output:
Enter a positive integer: 34 34 = 3 + 31 34 = 5 + 29 34 = 11 + 23 34 = 17 + 17
Source code:
/* Example to reverse a sentence entered by user without using strings. */ #include <stdio.h> void Reverse(); int main() { printf("Enter a sentence: "); Reverse(); return 0; } void Reverse() { char c; scanf("%c",&c); if( c != '\n') { Reverse(); printf("%c",c); } }
Result output:
Enter a sentence: margorp emosewa awesome program
/* C programming source code to convert either binary to decimal or decimal to binary according to data entered by user. */ #include <stdio.h> #include <math.h> int binary_decimal(int n); int decimal_binary(int n); int main() { int n; char c; printf("Instructions:\n"); printf("1. Enter alphabet 'd' to convert binary to decimal.\n"); printf("2. Enter alphabet 'b' to convert decimal to binary.\n"); scanf("%c",&c); if (c =='d' || c == 'D') { printf("Enter a binary number: "); scanf("%d", &n); printf("%d in binary = %d in decimal", n, binary_decimal(n)); } if (c =='b' || c == 'B') { printf("Enter a decimal number: "); scanf("%d", &n); printf("%d in decimal = %d in binary", n, decimal_binary(n)); } return 0; } int decimal_binary(int n) /* Function to convert decimal to binary.*/ { int rem, i=1, binary=0; while (n!=0) { rem=n%2; n/=2; binary+=rem*i; i*=10; } return binary; } int binary_decimal(int n) /* Function to convert binary to decimal.*/ { int decimal=0, i=0, rem; while (n!=0) { rem = n%10; n/=10; decimal += rem*pow(2,i); ++i; } return decimal; }
Result output:
Source code:
#include <stdio.h> int main() { int r,c,a[100][100],b[100][100],sum[100][100],i,j; printf("Enter number of rows (between 1 and 100): "); scanf("%d",&r); printf("Enter number of columns (between 1 and 100): "); scanf("%d",&c); printf("\nEnter elements of 1st matrix:\n");/* Storing elements of first matrix entered by user. */ for(i=0;i<r;++i) for(j=0;j<c;++j) { printf("Enter element a%d%d: ",i+1,j+1); scanf("%d",&a[i][j]); }/* Storing elements of second matrix entered by user. */ printf("Enter elements of 2nd matrix:\n"); for(i=0;i<r;++i) for(j=0;j<c;++j) { printf("Enter element a%d%d: ",i+1,j+1); scanf("%d",&b[i][j]); }/*Adding Two matrices */ for(i=0;i<r;++i) for(j=0;j<c;++j) sum[i][j]=a[i][j]+b[i][j];/* Displaying the resultant sum matrix. */ printf("\nSum of two matrix is: \n\n"); for(i=0;i<r;++i) for(j=0;j<c;++j) { printf("%d ",sum[i][j]); if(j==c-1) printf("\n\n"); } return 0; }
Result output:
Source code:
#include <stdio.h> int main() { int a[10][10], trans[10][10], r, c, i, j; printf("Enter rows and column of matrix: "); scanf("%d %d", &r, &c);/* Storing element of matrix entered by user in array a[][]. */ printf("\nEnter elements of matrix:\n"); for(i=0; i<r; ++i) for(j=0; j<c; ++j) { printf("Enter elements a%d%d: ",i+1,j+1); scanf("%d",&a[i][j]); }/* Displaying the matrix a[][] */ printf("\nEntered Matrix: \n"); for(i=0; i<r; ++i) for(j=0; j<c; ++j) { printf("%d ",a[i][j]); if(j==c-1) printf("\n\n"); }/* Finding transpose of matrix a[][] and storing it in array trans[][]. */ for(i=0; i<r; ++i) for(j=0; j<c; ++j) { trans[j][i]=a[i][j]; }/* Displaying the transpose,i.e, Displaying array trans[][]. */ printf("\nTranspose of Matrix:\n"); for(i=0; i<c; ++i) for(j=0; j<r; ++j) { printf("%d ",trans[i][j]); if(j==r-1) printf("\n\n"); } return 0; }
Result output: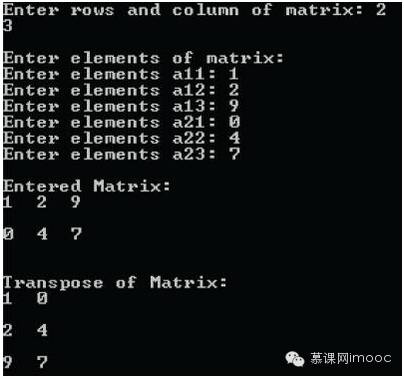
The article is reproduced from the public account: Mooc Network imooc