USB Host Application Development Based on BeagleBone Green
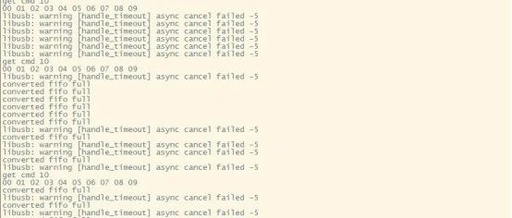
USB Development 1. Introduction This article demonstrates the process of using libusb for USB host application development on embedded platforms. Finally, a case study is shared, which involves real-time video stream collection through a custom protocol using bulk transfer. Refer to other articles on this development board https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/5gDfX__U8-F4MVqn92KtLw Playing Board Series II: Setting Up Samba … Read more