
In applications such as CAN and RS-485, it is generally recommended to use shielded twisted pair cables for networking and wiring to reduce external interference on bus communication. Many engineers understand this recommendation but do not know the underlying reasons. This article will briefly introduce the principle of interference resistance in twisted pair cables.
1Differential Signal Transmission
CAN and RS-485 interfaces use differential signal transmission. Differential signal transmission is a method of transmitting information using two complementary electrical signals. For example, in high-speed CAN, different logic states are transmitted through two signal lines, CANH and CANL, and the receiving circuit only identifies the signal difference between the two lines. Under ideal conditions, the waveform of the CAN bus is shown in Figure 1.
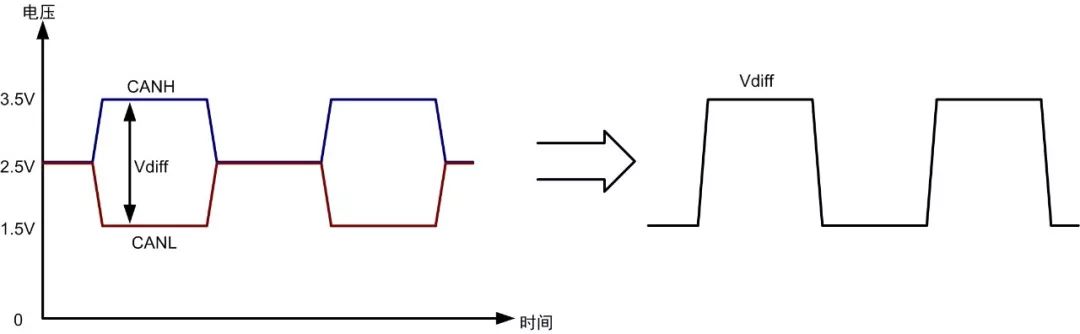
Figure 1
Interference signals generally exist in the form of common mode. When the bus is disturbed, both lines are simultaneously affected, but their differential voltage remains unaffected, as shown in Figure 2. Compared to single-ended signal transmission, differential signal transmission has better interference resistance.
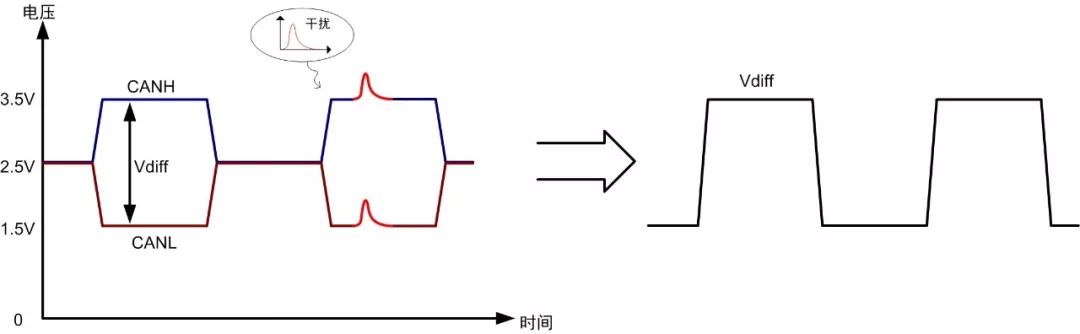
Figure 2
However, using differential transmission does not mean one can be complacent. CAN and RS-485 buses are often used for long-distance communication. As the length of the cable increases, various interferences couple onto the bus, significantly increasing the likelihood of external interference affecting bus communication. If the cable selection and usage are improper, it can easily lead to communication anomalies. For applications such as CAN and RS-485, we generally recommend using twisted pair cables.
2Noise Coupling Mechanisms
To understand the advantages of twisted pair cables, one must first understand how interference affects useful signals. Interference (noise) typically impacts a system through coupling mechanisms, which include conduction coupling, capacitive coupling, inductive (or magnetic) coupling, and radiative coupling.
In conduction coupling, the interference source has an electrical connection with the disturbed circuit, such as a common ground. The current flowing from the interference source creates a current in the common part, generating interference voltage that affects the signal of the disturbed circuit. Figure 3 illustrates conduction coupling, where Es is the signal source, Zs is the internal resistance of the signal source, Zc is the common part impedance, Zl is the load impedance, En is the interference source, and Vl is the load voltage. The current generated by the interference source En flows through Zc, causing a voltage drop across Zc, which results in a change in Vl voltage, thus affecting the signal on the load side.
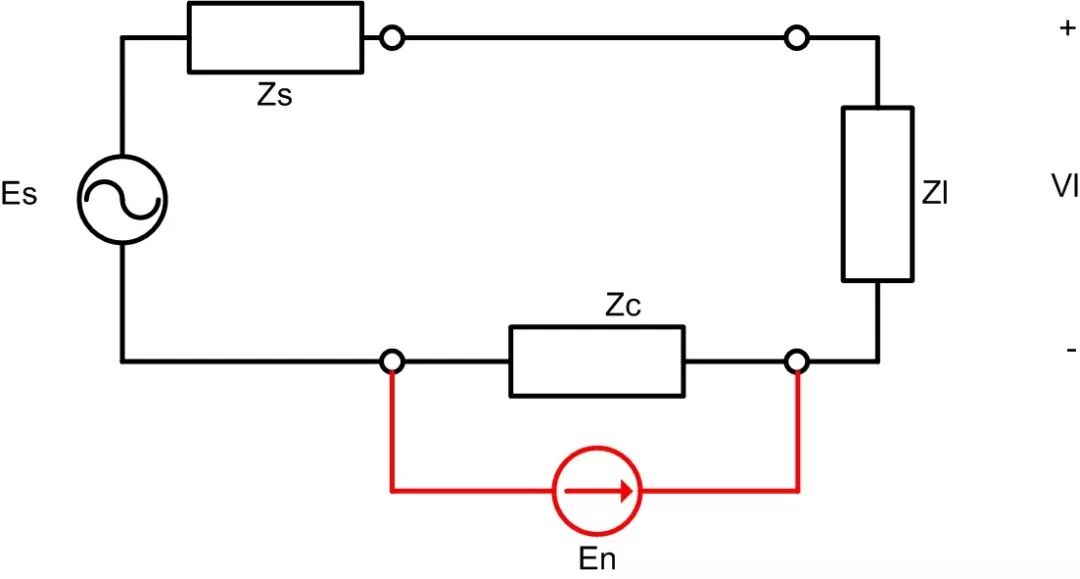
Figure 3
Capacitive coupling occurs when there is a varying electric field between two adjacent conductors. The interference current flows into the disturbed circuit through the coupling capacitance between the conductors. Because the coupling capacitance is generally small and has high impedance, the interference source can be viewed as a constant current source for the disturbed circuit, especially when the signal circuit has high impedance. Figure 4 illustrates capacitive coupling, where Es is the signal source, Zs is the internal resistance of the signal source, Cm is the coupling capacitance, Zl is the load impedance, En is the interference source, and Vl is the load voltage. The interference current flows through Cm into Zl, affecting Vl.
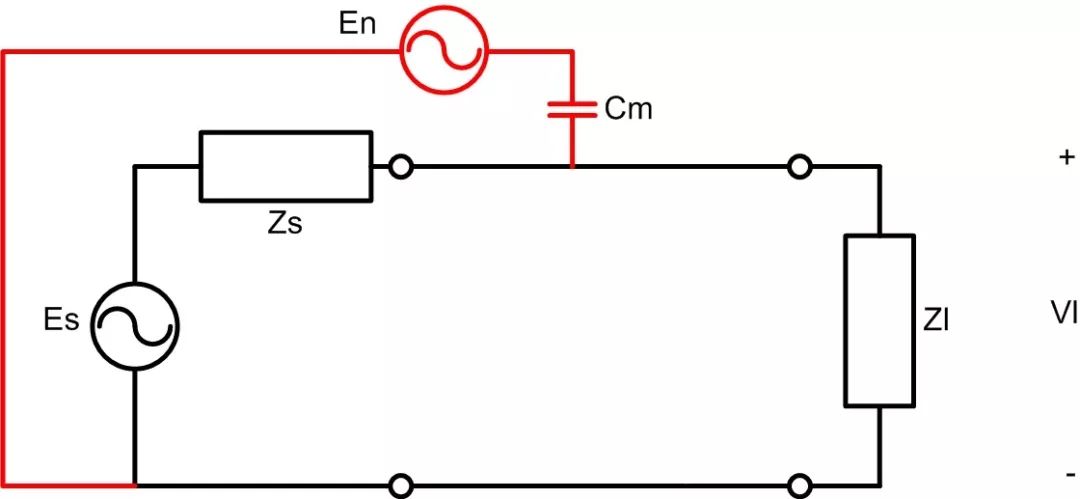
Figure 4
Inductive (or magnetic) coupling occurs when there is a varying magnetic field between two parallel conductors. The current flowing through the conductor from the interference source generates magnetic flux, which induces electromotive force in the conductor of the disturbed circuit, thus affecting the disturbed signal. In this case, noise can be viewed as a constant voltage source, and the noise impact increases in low impedance circuits. Figure 5 illustrates inductive coupling, where Es is the signal source, Zs is the internal resistance of the signal source, Lm is the mutual inductance, Zl is the load impedance, En is the interference source, and Vl is the load voltage. The current from the interference source En flows through the mutual inductance Lm, inducing a voltage in the disturbed circuit and affecting Vl.
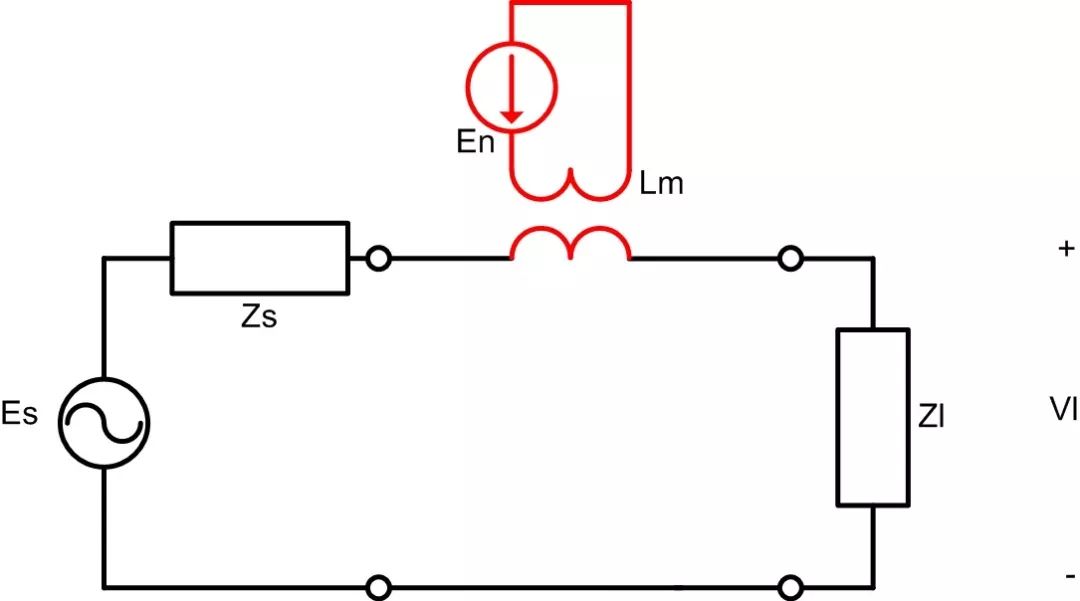
Figure 5
Radiative coupling occurs when the interference source is far from the disturbed device. Both the interference source and the disturbed device act as wireless antennas, with the interference source emitting electromagnetic waves that are received by the disturbed device.
3Advantages of Twisted Pair Cables
Twisted pair cables consist of two insulated wires twisted together, making them particularly suitable for differential signal transmission. Compared to parallel wires, they can more effectively suppress interference.
1. Eliminate Capacitive Coupling
Compared to parallel pairs, the coupling capacitance values of each wire in a twisted pair cable are closer to the interference source or ground, resulting in more balanced impedance, as shown in Figure 6.
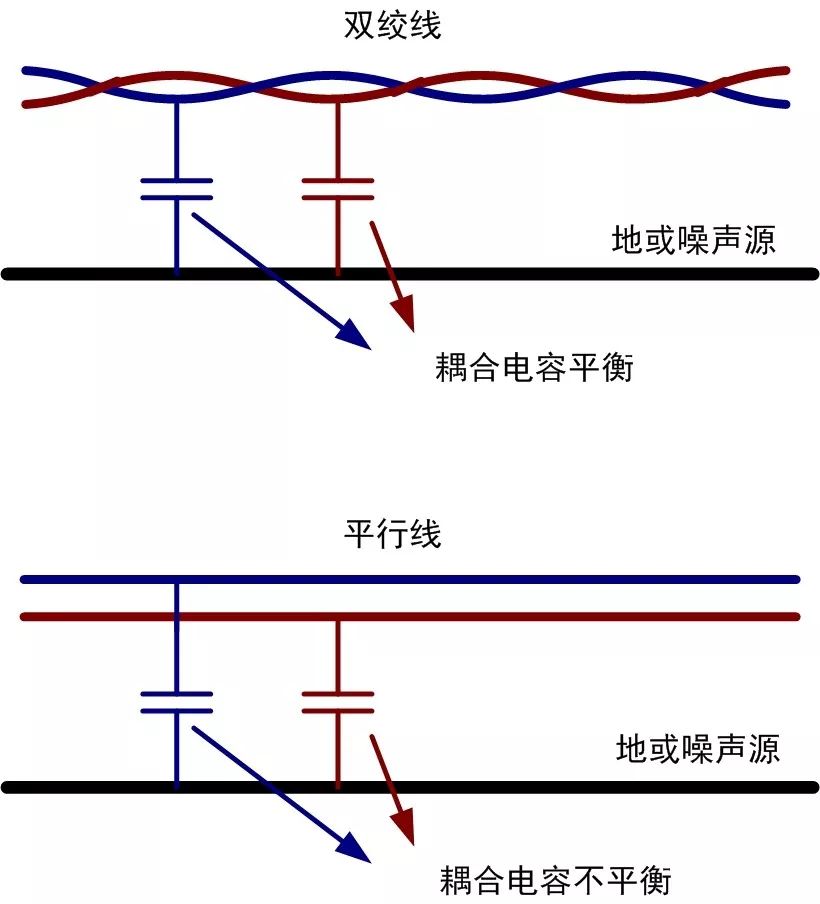
Figure 6
Due to the tight twisting of the wires, the coupling capacitance between the two signal wires and the noise source, as well as the impedance to the ground, are essentially the same. The interference current flowing into the two signal wires is approximately equal, and the difference between the two signal wires remains unchanged, converting the coupling capacitance current into common-mode interference. As shown in Figure 7, coupling capacitances C1=C2, Z1=Z2, and the current flowing into C1 and C2 from the interference source is equal, resulting in equal voltages across the two wires, thus Vn=0. Since differential signal transmission has good common-mode rejection capability, the effect of capacitive coupling can be eliminated.
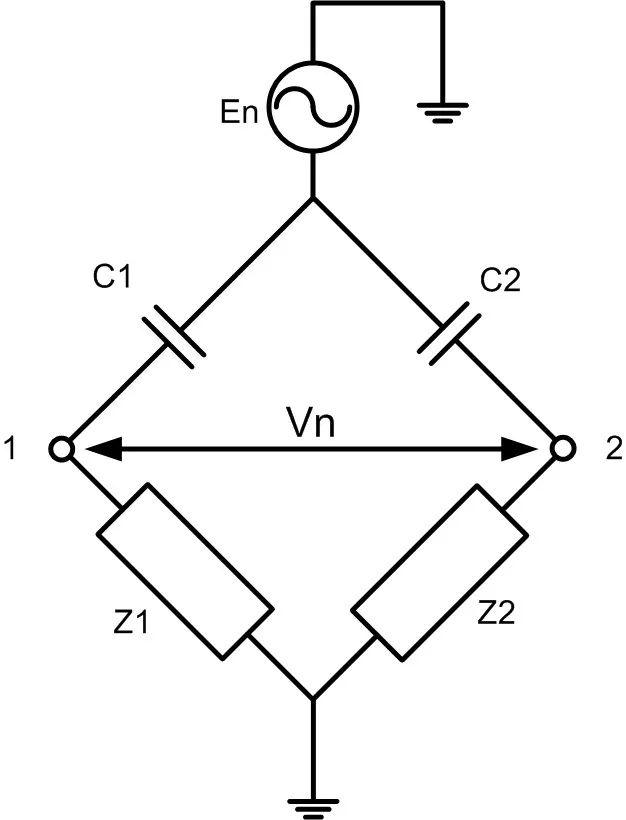
Figure 7
2. Eliminate Inductive Coupling
If parallel wires are used, the two signal wires will form a narrow loop that picks up magnetic field interference from the environment. The structure of twisted pair cables maintains a fixed spacing between the two conductors, causing the direction of the electromotive force induced by the magnetic field to reverse at each adjacent “small loop”, thus canceling each other out sequentially. From a circuit perspective, the mutual inductance at each adjacent “small loop” is one positive and one negative concerning the noise source, resulting in a total mutual inductance of zero. As shown in Figure 8, when parallel wires are affected by external magnetic field interference, the induced currents in the two wires cannot cancel each other, leading to significant induced voltage that affects signal transmission. However, the structure of twisted pair cables allows the induced currents to cancel each other, preventing induced voltage.
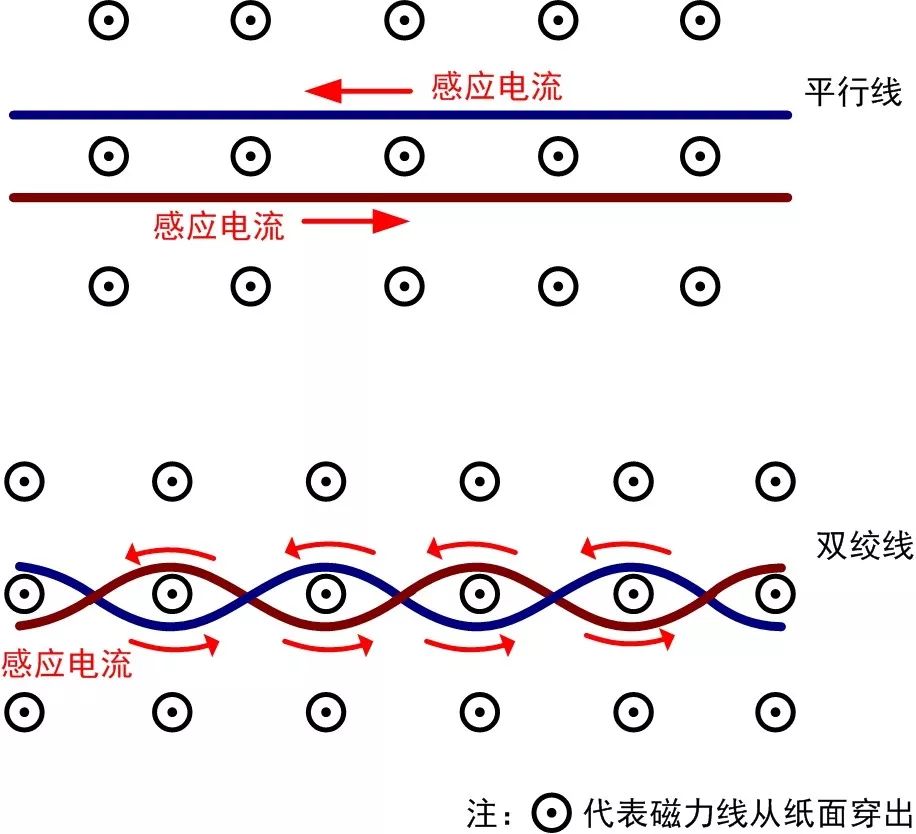
Figure 8
3. Reduce External Interference
When used for differential signal transmission, the currents in the two wires of a twisted pair cable are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction. As shown in Figure 9, ideally, the magnetic fields created by each pair of adjacent “small loops” formed by the two wires cancel each other out due to their equal size and opposite direction, resulting in reduced electromagnetic interference from the twisted pair cables compared to parallel cables.
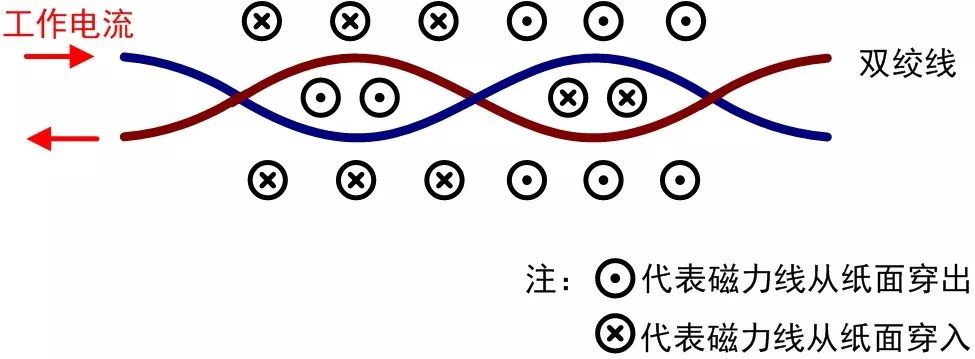
Figure 9
4Conclusion
In differential transmission applications, twisted pair cables not only reduce their own interference with the outside world but also eliminate capacitive and inductive coupling with external interference sources, achieving a dual benefit. Therefore, twisted pair cables are widely used in applications involving differential signal transmission, such as CAN and RS-485.
The above analysis is based on ideal twisted pair cables, but in practice, due to variations in twisting levels, twisting deviations, and differences in parasitic parameters of the cables, the noise suppression capability of twisted pair cables may be weakened.
Since the structure of twisted pair cables cannot eliminate conduction coupling and radiative coupling interference, in severely disturbed environments, it is still necessary to use isolation and shielding techniques to enhance the system’s resistance to interference. Isolation technology can effectively suppress common-mode interference caused by conduction coupling, while shielding technology can effectively suppress radiative interference.
In environments with severe interference, using isolated transceivers in conjunction with shielded twisted pair cables can provide excellent resistance to interference for CAN and RS-485 applications, ensuring reliable communication.
ZLG Zhiyuan Electronics Introduction
Guangzhou Zhiyuan Electronics Co., Ltd. is a subsidiary of Guangzhou Zhiyuan Electronics Co., Ltd., founded by renowned embedded system expert Professor Zhou Ligong in 2001. It is a nationally recognized high-tech enterprise and the Guangdong Provincial Engineering Technology Research and Development Center for high-end industrial control measuring instruments.
Vision:To become a leading enterprise in the industrial internet ecosystem
Using the “chip + AWorks software platform” to design high-value-added modules, boards, and high-end measuring instruments, connecting to the ZWS IoT cloud through wired and wireless interfaces for big data processing, forming an industrial internet ecosystem.
Mission:To advance the industrial internet process in China with leading technology
Values:Professionalism and focus achieve dreams
