
Introduction
The interconnection of computers has led to the internet, allowing people to access various shared information online. The development of wireless communication technology and the convenience of smartphones have formed the mobile internet. The connectivity of networks extends beyond computers and smartphones, connecting an increasing number of devices to the internet, enabling people to use and manage devices and services more conveniently, thus gradually forming the Internet of Things (IoT).
In the era of the internet and mobile internet, data primarily comes from computers and smartphones, usually requiring human operation. In the IoT era, more data will be generated from IoT devices, which will automatically produce data and upload it to cloud computing platforms for automatic analysis and processing. The IoT is changing our work and lifestyles, and the integration of reality and the network is deepening. The rapid development and application of integrated circuits and new technologies are also promoting the growth of the IoT. Is your next project also preparing for the IoT?
1. What is IoT?
As the name suggests, the Internet of Things consists of three components: “Things”, “Connection”, and “Network”. The “Things” refer to intelligent devices or sensor terminals, “Connection” refers to the communication, and “Network” refers to the internet. When these three components are combined, they form a basic IoT system. This system collects, transmits, stores, and processes data regarding the location, time, and status of objects, while the cloud computing platform needs to clean, analyze, and visualize the collected data. Various applications and services can extend from the IoT system.
Through the deployment of IoT systems, reasonable decisions can be made in real-time, improving operational efficiency and discovering new business value. The IoT is the infrastructure of the digital economy era and plays a significant role in promoting industrial upgrading and transformation.

2. Trends in IoT
The IoT is being widely applied across various industries, with new IoT technologies continuously emerging, driving its development. Due to different application demands, the IoT is often perceived as fragmented. We can observe the trends in IoT development from a structural perspective.
Power Supply. Power supply is a converter of electrical energy. No electronic product can do without a power supply. From the perspective of how power is supplied to electronic products, it can be roughly divided into power supply, batteries, and energy harvesting methods. Large-scale IoT deployments are increasingly leaning towards battery or energy harvesting methods, avoiding the issues of on-site wiring or maintenance. Of course, this also requires low-power integrated circuits, such as ultra-low-power microcontrollers (MCUs).
Network Communication Connection. Local area wireless access technologies, represented by Wi-Fi and Bluetooth, make IoT connections simple and convenient. However, as the scale of IoT deployment increases, local area wireless access technologies cannot meet the demand for wide-area connections due to their limited coverage and high deployment costs. Low-power wide-area wireless access technologies, represented by NB-IoT, LoRaWAN, and ZETA, are gaining increasing attention. In IoT practice, a combination of local and wide-area wireless access methods may become a promising direction for IoT applications.
Intelligence, Networking, and Edge Computing. With the development of microcontroller (MCU) products, device terminals are becoming increasingly intelligent, and the demand for data collection, management, and control is promoting the development of connectivity. The connection of devices is evolving from a few devices to a large-scale network. The networking of device terminals is an important direction for the future development of the IoT. As more device terminals are connected, a large amount of data will be uploaded to cloud computing platforms, where much of it may be unnecessary, leading to network latency. Edge computing can significantly enhance the efficiency of data transmission and processing.
Additionally, as the IoT becomes more interconnected, IoT security will also become a topic of concern.
3. Applications of IoT
-
Industrial IoT: Industrial IoT refers to the application of IoT in the industrial sector. It focuses on machine-to-machine (M2M) communication, big data, and machine learning to achieve higher efficiency and reliability in operations. Industrial IoT is the integration of information computing and operational technology. Operational technology refers to the networking of operational processes and industrial control systems, including human-machine interfaces, monitoring and data acquisition systems, distributed control systems, PLCs, etc.
-
Agricultural IoT: Agricultural IoT technology can measure environmental indicators affecting agricultural crops, such as temperature, humidity, and soil conditions, and precisely regulate them through IoT technology to ensure a suitable growing environment for crops. It can also track livestock health indicators, using technology for monitoring physiological indicators and improving livestock health levels while reducing losses. Agricultural IoT can significantly enhance agricultural efficiency, reduce environmental impact, and minimize costs.
-
Smart Home: Thanks to sensors and IoT technology, continuous data collection can achieve automation of lighting, heating, and appliances, maximizing energy efficiency and enhancing convenience and comfort.
-
Smart City: Smart cities encompass the management and services of all aspects of urban life, relying on data. The IoT supports data collection and transmission functions, connecting various urban services such as lighting, parking, waste management, building monitoring, and metering, further optimizing management and services, thus saving time and costs.
-
Smart Vehicles: Computing has endowed vehicles with greater intelligence, integrating perception, information processing, communication, control, execution, automated driving assistance, and entertainment systems. Through cellular networks and C-V2X technologies, vehicles are connected to the network, enabling information exchange among people, vehicles, roads, and services.

4. How Does IoT Assist Digital Transformation?
Different people have different understandings of digitalization, leading to various definitions. According to Baidu Encyclopedia, “Digital transformation is a high-level transformation based on digital conversion and upgrading, further touching the core business of the company, aiming to establish a new business model. Digital transformation is about developing digital technologies and support capabilities to create a vibrant digital business model.”
Driven by technology, digital transformation redefines business, achieving automation, intelligence, and secure services through data-driven decision-making.
The development of new technologies such as IoT, blockchain, cloud computing, and artificial intelligence has become the main driving force behind digital transformation, allowing people to access and manage information more conveniently in new ways.
IoT device terminals connect to the internet through network communication technology, and data is uploaded to cloud computing platforms, which provide powerful computing support for IoT applications, while big data and AI applications offer automated operations and decision-making for data analysis.
The IoT is the foundational infrastructure for digitalization. The IoT network connects not just the two ends (cloud and terminal) but also connects businesses. The digital construction of the IoT is redefining social products and services.
5. STMicroelectronics – Focusing on Automotive, Energy, and IoT Goals to Assist Customers in Seizing Smart Business Opportunities
IoT
The IoT can be broadly divided into two types of networks: one based on IP (Internet Protocol) networks and the other non-IP networks. IP networks are those that operate using internet protocols, while non-IP networks generally refer to networks operating on protocols like Matter, LoRaWAN, and Bluetooth. The IoT is unlocking tremendous potential for the interconnection of billions of smart devices using different protocols. The IoT enables almost any system to innovate using the internet and cloud computing ecosystem, making various objects smarter and more aware. The growth of internet-connected devices is driven by the availability of high-quality, reliable wireless connections and the widespread availability of low-cost, low-power embedded components. Although IoT devices come in many different forms, they all require common functional building blocks, such as processing and security, sensing and actuation, connectivity, signal conditioning, protection, power, and energy management.
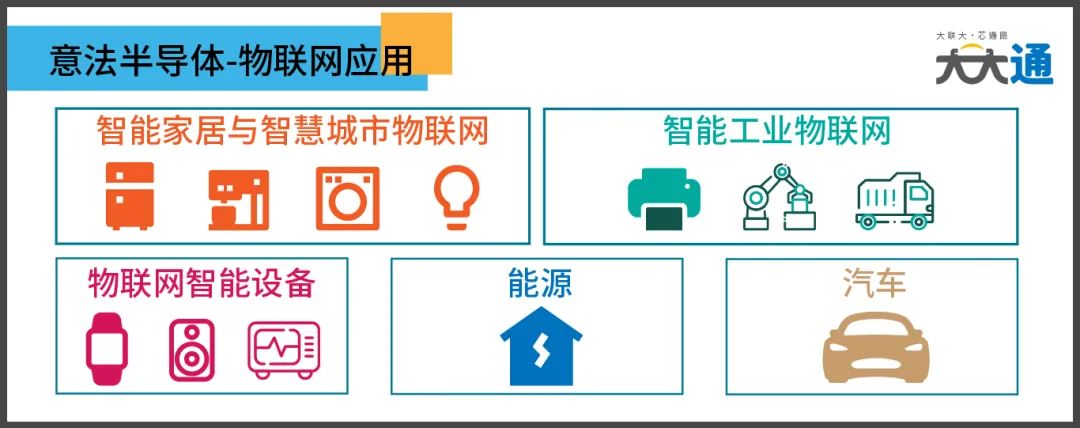
ST’s Applications in IoT Include:
Smart Home and Smart City IoT
-
Large Appliances: Refrigerators and freezers, kitchen range hoods, indoor air conditioning (RAC), dishwashers, washing machines, dryers, induction cookers,
-
Small Appliances and Kitchen Tools: Coffee machines, multifunction food processors and blenders, microwaves, robotic vacuum cleaners, cordless and corded vacuum cleaners, air quality monitoring systems
-
Gas, Heat, and Water Metering: Heating metering, gas metering, water metering
-
Logistics: NFC HF readers, RAIN UHF readers, portable data terminals, pallet and container tracking, barcode scanners, electronic shelf labels, goods assurance
-
Energy Metering: Three-phase meters, single-phase meters
-
Garden Robots and Tools: Lawnmowers, gardening tools, pool cleaners
-
Bank Automation: USB NFC dongles, bill counters
-
Point of Sale: ePOS, ECRs, cash registers, payment dongles, mobile POS
Smart Industrial IoT
-
Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs): IO-link modules, PLC control units, human-machine interfaces, digital I/O modules, fieldbus and industrial Ethernet
-
Industrial Sensors: Position and motion monitoring, process and environmental monitoring
-
Industrial Tools: 3D printers, forklifts, industrial printers, industrial drones, CNC machines, pumps, welding, textiles, valve control, fans
-
Industrial Robots
-
Industrial Drives: AC drives, servo drives, forklifts, pumps, fans
-
Industrial Communication: Industrial gateways, IO-link gateways, fieldbus and industrial Ethernet, contactless communication (RFID/NFC)
-
Condition Monitoring/Predictive Maintenance: Edge processing, smart sensor nodes
IoT Smart Devices
-
Wearable Devices: Fitness trackers, smartwatches
-
Therapeutic Devices: CPAP and ventilators, pill dispensers, electric beds, dialysis machines
-
Diagnostic Devices: Digital thermometers, patient monitoring, blood pressure monitors, blood glucose meters
-
Audio and Video: Remote controls, speakers
Energy
Energy provisioning (usually in the form of electricity or natural gas) relies on a complex infrastructure that connects power plants to end-user devices through distribution networks. Besides ensuring availability and energy quality reliably, the integrated system must also operate as efficiently as possible. New renewable energy sources like solar and wind are increasingly integrated with traditional power generation systems, not only to meet the growing demand and promote carbon dioxide reduction but also to help lower costs for suppliers and consumers. Renewable energy is also driving innovation in many ways, including energy storage technology, which is key to integrating traditional and renewable energy, as energy availability can be unpredictable, especially during peak times.
ST’s Applications in Energy Production and Distribution Include:
-
Distributed Solar Power Generation: Power optimizers, micro-inverters
-
Concentrated Solar Power Generation: Solar inverters (string and centralized), smart junction boxes, smart string combiner boxes
-
Energy Distribution: Commercial battery storage systems, home battery storage systems, DC fast charging stations
Automotive
It is estimated that 80% of innovations in the automotive industry today are achieved directly or indirectly through electronic devices. With the continuous improvement of automotive functions in each new model, the number of semiconductor devices in each vehicle is constantly increasing.
From ICE powertrains, chassis and safety, body and convenience to telematics and infotainment, ST is able to support a wide range of automotive applications, paving the way for the new era of automotive electrification, advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS), and automotive connectivity and safety.
Network connectivity and telematics are fundamentally changing vehicles on the road. Through wireless software upgrades and preventive maintenance connected to cloud-based services, this brings numerous benefits to occupants and manufacturers. As the number of electronic control units (ECUs) involved in safety, engine management, motor control, infotainment, etc., continues to grow, these units need to be connected to ensure timely upgrades and safety. The connectivity required by occupants, including Wi-Fi or Bluetooth, must seamlessly integrate with other networks.
Consumers expect to use personal electronic products in their vehicles, and this user experience drives the development of in-car infotainment systems, making it a rapidly growing segment in the automotive industry. In-car occupants expect to use entertainment facilities, connect to networks, and seamlessly access information and content from multiple sources. Since the launch of ST’s first automotive radio IC, we have been committed to developing innovative integrated circuits for in-car infotainment systems. Our latest IC solutions for complex infotainment dashboards integrate advanced audio and video capabilities, smartphone and multimedia device mirroring, and applications, while quickly and securely transmitting data inside and outside the vehicle. Enhanced processing power, greater in-car bandwidth, secure external communication links, and world-class audio amplifiers ensure you can build infotainment systems that meet all market demands. Our extensive infotainment product portfolio covers high-end integrated platforms, digital broadcasting, and outstanding AB and D class audio power amplifiers, among others.
As the degree of vehicle connectivity increases, mobile services are rapidly growing. Strong processing power, vehicle connectivity, and innovative sensors provide new possibilities for software service developers and offer rich application functionalities for vehicle owners. Enhanced services related to automotive safety (such as “emergency calls” in the event of an accident) rely on sensors to detect accidents, using telematics and GNSS positioning to transmit the accident location, employing cameras to record events, and providing preemptive information services for imminent emergencies. Insurance boxes can record events before they happen, and with the activation of driver monitoring functions, they can collect data, analyze driver behavior, and customize reasonable traffic fee tables, thus subtly changing the entire market. Other mobile services include fleet management, car sharing, free parking detection, and tolling, all of which rely on automotive sensors, processors, and communication modules provided by ST. As cars evolve from personal vehicles to shared services provided by autonomous fleets in smart city environments, the level of services offered by vehicles will significantly increase. ST’s products are widely used in various advanced driving systems, and the successful experience gained in safety connectivity and sensor technology provides us with a platform for building mobile services.
-
Telematics and Connectivity: Smart antennas, smart gateways, firmware over-the-air upgrades, remote communication and connectivity control units, vehicle-to-everything (V2X)
-
In-Vehicle Infotainment Systems (IVI): Digital clusters, infotainment modules, infotainment hosts, automotive audio systems
-
Mobile Services: Emergency calls, automatic billing systems, fleet management on-board units, telematics devices
6. Essential Knowledge and Skills in the IoT Era
[ST MCU Empowers IoT] Industry or Market Information
-
Introduction to Microcontrollers – To understand IoT, one must first understand the essence of MCUs!
-
Graphical User Interface (GUI) Market Brief – Entering IoT, first determine market orientation!
-
KNX-RF – Wireless Intelligence for Longer Distances – Key technology for IoT in home automation, a must-learn selection!
-
Sub-1GHz RF Transceiver Market Brief – Essential Technology for IoT (1) Radio technology meets the connection needs of ubiquitous IoT!
-
Graphical User Interface (GUI) Market Report – Essential Technology for IoT (2) Making intelligence visible and tangible!
-
Wearable Device Market Shipment Growth Slows, Headphone Products Expected to Grow Significantly – Human-device interaction that “understands” and devices that “listen” make human-machine communication a reality!
-
Looking at LoRa Development from LoRa Alliance Certified Products – Opening the door to large-scale wireless applications of IoT.
-
Overview of the Smart Lock Market in China – Entry-level products for smart homes.
-
Overview of IoT Industry Alliances and Organizations – Industry market information at a glance.
-
The IoT Era is Reshaping the New Ecology of MCU Applications – STM32 makes the development of IoT projects easier and simpler.
-
Overview of Open Source Real-Time Operating Systems (RTOS) in IoT – Security, energy efficiency, and better communication management.
-
Wireless RF Chips in Low Power Wide Area Networks (LPWAN) – LPWA technology operating in unlicensed frequency bands allows enterprises to build their networks, activating their innovative capabilities and driving the development of innovative applications.
7. Future Developments in IoT
[ST MCU Empowers IoT] Product Introduction
-
STEVAL-BCN002V1B: BlueTile – Sensor node development kit supporting Bluetooth LE
-
STM32 Graphical User Interface
-
STM32L4R9I-EVAL Evaluation Board Introduction
-
STM32L4R9I-DISCO Discovery Kit Introduction
-
STM32H743I-EVAL Evaluation Board Introduction
-
New Opportunities for Short-Range Wireless Connections ST60 60 GHz RF Transceiver
-
Small Low-Loss Smart Molding Module Simplifying Motor Control Solution Design
-
STKNX Embracing New Changes in Smart Buildings
-
ST Launches STM32WL LoRa SoC Products, Opening New Markets for Sub-1GHz IoT Wireless Connections
-
IOTA DLT Technology Enables STM32 to Build IoT Foundation Security
-
STM32Cube.AI Simplifying Design of Artificial Neural Networks
-
Photovoltaic Converters Using STM32 High-Resolution Timers to Extract More Energy from Sunlight
-
ST IO-Link Products Empowering Smart Factories
-
From “Preventive” Maintenance to “Predictive” Maintenance, ST’s Predictive Maintenance Solutions Assist Smart Factories in Digital Transformation and Upgrading
-
MCUs and MPUs Together Continue the Successful Story of STM32
8. How to Contact Us?
Contact me: (Taiwan) [email protected]
Contact me: (China) [email protected]
