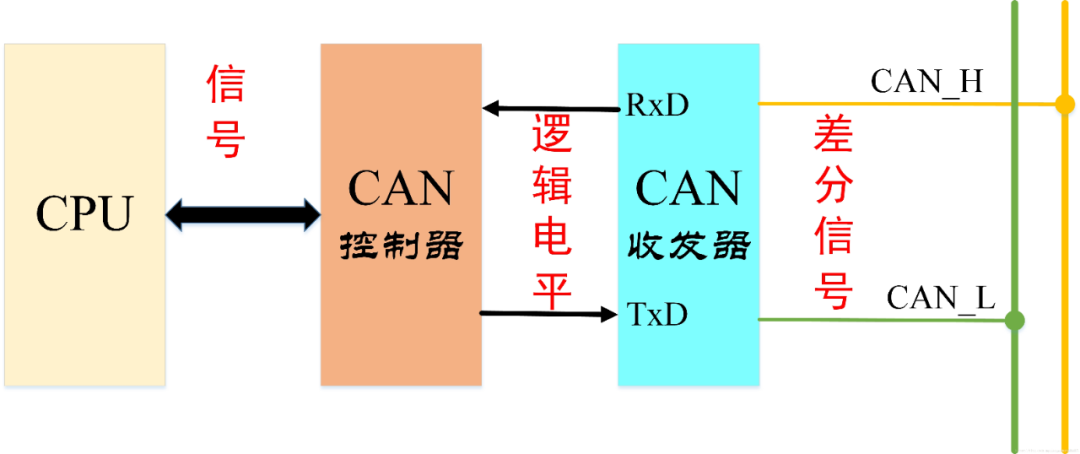
CAN (Controller Area Network) bus protocol is a serial communication bus based on a message broadcasting mode, invented by BOSCH. It was initially used to achieve reliable communication between ECUs in automobiles and has since been widely applied in industrial automation, shipping, and medical fields due to its simplicity, practicality, and reliability. Compared to other network types such as LAN (Local Area Network), WAN (Wide Area Network), and PAN (Personal Area Network), CAN is more suitable for applications in the field control domain, hence the name.
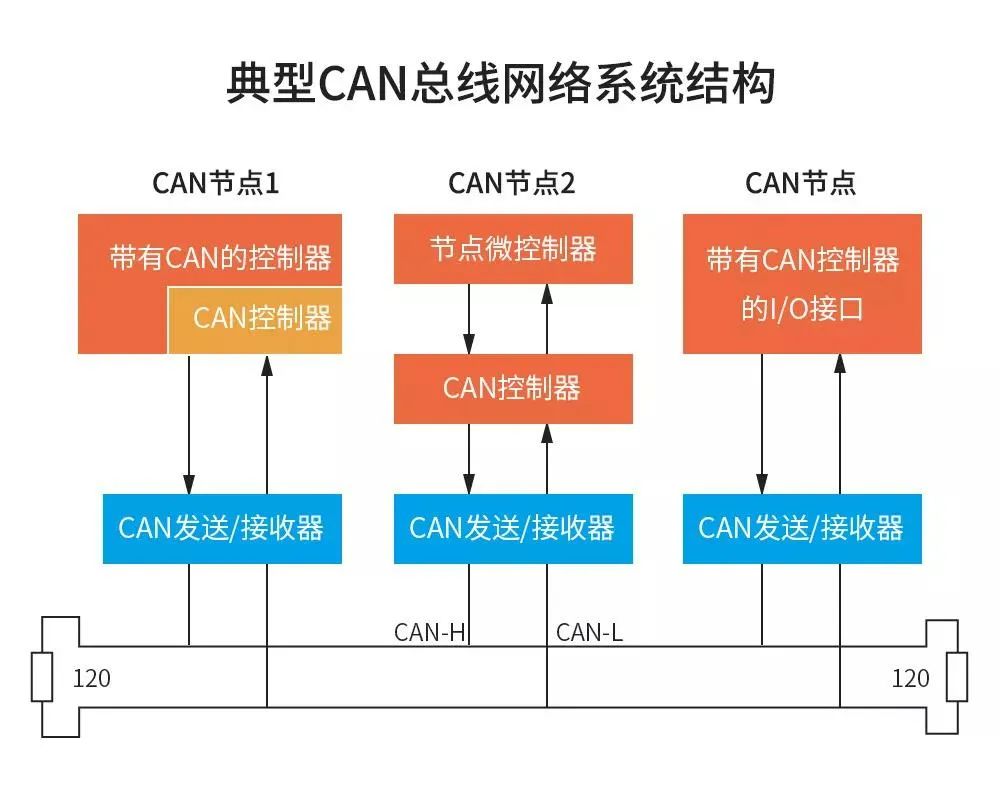
The CAN bus is a multi-master bus system. Unlike traditional bus systems such as USB or Ethernet, which rely on a bus controller to coordinate the transmission of large amounts of data from node A to node B, the messages on a CAN network are broadcasted. This means that all nodes on the network detect consistent data at the same time, making it more suitable for transmitting short messages such as control, temperature, and speed.
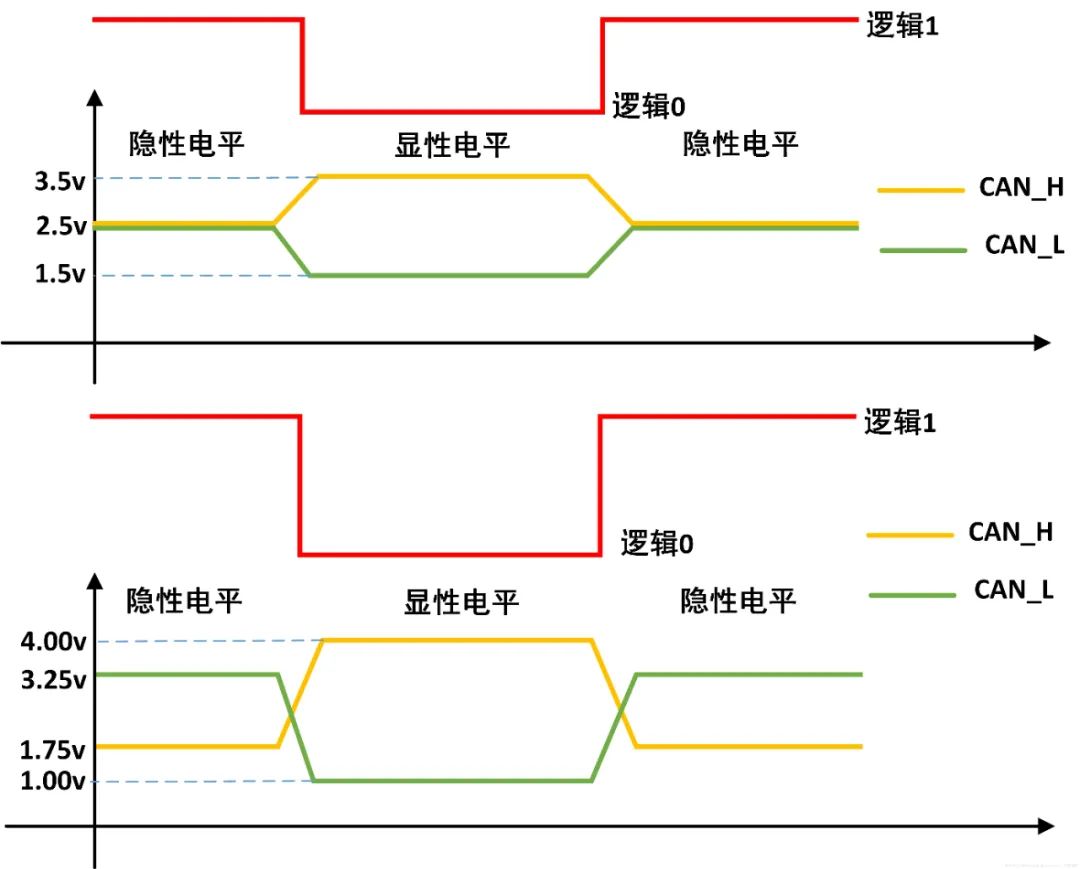
CAN was initially proposed by BOSCH and later confirmed as an international standard by the ISO organization. It is divided into different sub-standards based on characteristic differences. The CAN international standard only involves the physical layer and data link layer of the OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) reference model. Upper-layer protocols are defined as application layers based on the CAN standards, and there are different application layer standards available in the market.