This article was first published on WeChat public account: Thin Dragon Health,the relentless fighter against China’s obesity problem. I have entrusted “Rights Defender” to protect my article..
Disclaimer: The following text does not constitute any medical advice; it is for information sharing only. Please consult a professional for guidance.
Please feel free to share in your friend circle, for reprints, please contact the WeChat public account.
The article has a total of3427 words, estimated reading time,8 minutes.
Between 1928 and 1933, Hungarian biochemist Albert Szent-Györgyi and his colleagues first isolated Vitamin C from cabbage, paprika, and the adrenal glands of certain animals, laying the foundation for the large-scale production of Vitamin C for humans.
 Left: Albert Szent-Györgyi, image from Wikipedia
From the 1950s to 1960s, biochemist Albert Lehninger studied the biosynthesis of Vitamin C in animals.
It was found that many animals, such as cats and dogs, can synthesize Vitamin C, while humans cannot synthesize it themselves, which highlights the importance of Vitamin C intake.
Thus, humans gradually unraveled the mysteries of Vitamin C, which is no longer limited to just being able to combat scurvy.
Like humans, guinea pigs also cannot synthesize Vitamin C, so since the 1930s, they have been used multiple times in studies related to Vitamin C. Some experiments have even discovered that a lack of Vitamin C itself can lead to plaques or deposits in the aorta of guinea pigs.
Left: Albert Szent-Györgyi, image from Wikipedia
From the 1950s to 1960s, biochemist Albert Lehninger studied the biosynthesis of Vitamin C in animals.
It was found that many animals, such as cats and dogs, can synthesize Vitamin C, while humans cannot synthesize it themselves, which highlights the importance of Vitamin C intake.
Thus, humans gradually unraveled the mysteries of Vitamin C, which is no longer limited to just being able to combat scurvy.
Like humans, guinea pigs also cannot synthesize Vitamin C, so since the 1930s, they have been used multiple times in studies related to Vitamin C. Some experiments have even discovered that a lack of Vitamin C itself can lead to plaques or deposits in the aorta of guinea pigs.
 Image from Giphy
Is there a connection between Vitamin C and arterial blockage? Before revealing the answer, it is necessary to understand atherosclerosis.
Healthy arteries are flexible and elastic, but due to certain factors, plaques can gradually form and accumulate in the arteries, causing the arterial walls to thicken and harden, known as atherosclerosis.
The presence of these plaques can make the arteries narrow and congested, affecting blood flow and impacting the health of organs such as the brain, limbs, and kidneys.
Atherosclerosis is also the main cause of cardiovascular diseases (CVD), and potential diseases it may induce include but are not limited to heart failure, coronary heart disease, myocardial infarction, and more.
So, can Vitamin C resist atherosclerosis?
A related study in 2010 mentioned that Vitamin C can prevent atherosclerosis caused by cigarette smoke in guinea pig models. ①
Conclusion: Exposure of guinea pigs to cigarette smoke causes the development of atherosclerosis, which can be prevented by vitamin C supplement.
Image from Giphy
Is there a connection between Vitamin C and arterial blockage? Before revealing the answer, it is necessary to understand atherosclerosis.
Healthy arteries are flexible and elastic, but due to certain factors, plaques can gradually form and accumulate in the arteries, causing the arterial walls to thicken and harden, known as atherosclerosis.
The presence of these plaques can make the arteries narrow and congested, affecting blood flow and impacting the health of organs such as the brain, limbs, and kidneys.
Atherosclerosis is also the main cause of cardiovascular diseases (CVD), and potential diseases it may induce include but are not limited to heart failure, coronary heart disease, myocardial infarction, and more.
So, can Vitamin C resist atherosclerosis?
A related study in 2010 mentioned that Vitamin C can prevent atherosclerosis caused by cigarette smoke in guinea pig models. ①
Conclusion: Exposure of guinea pigs to cigarette smoke causes the development of atherosclerosis, which can be prevented by vitamin C supplement.
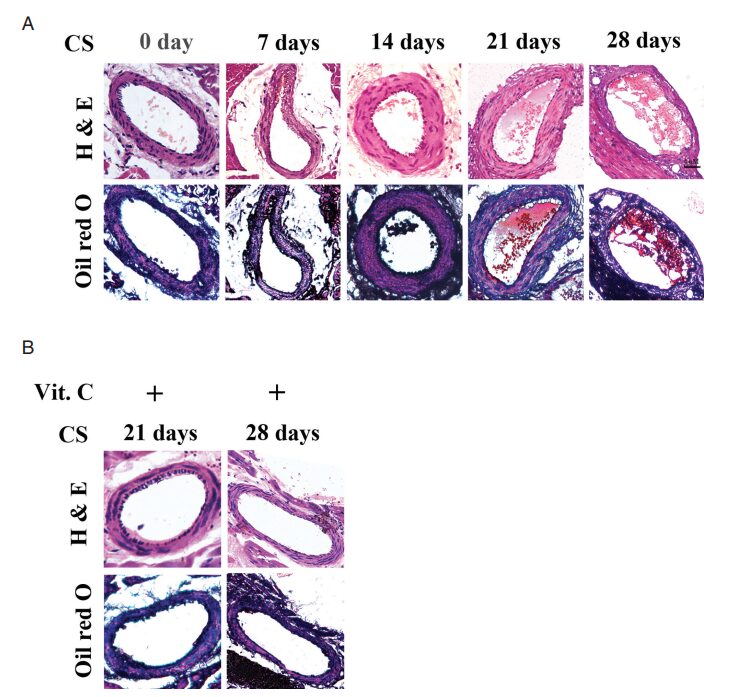 A: Guinea pigs exposed to cigarette smoke (CS) over time develop atherosclerosis. B: Feeding guinea pigs Vitamin C can reverse atherosclerosis.
In fact, not only guinea pig experiments, but also many similar findings have emerged in recent human trials. For example, in 2016, a study published in the International Journal of Molecular Sciences proposed that Vitamin C deficiency is associated with a higher risk of mortality from cardiovascular diseases. ②
Furthermore, as early as 1998, a study mentioned that Vitamin C can reduce the risk of angina and heart attacks. ③
So, what role does Vitamin C play in preventing arterial blockage?
A: Guinea pigs exposed to cigarette smoke (CS) over time develop atherosclerosis. B: Feeding guinea pigs Vitamin C can reverse atherosclerosis.
In fact, not only guinea pig experiments, but also many similar findings have emerged in recent human trials. For example, in 2016, a study published in the International Journal of Molecular Sciences proposed that Vitamin C deficiency is associated with a higher risk of mortality from cardiovascular diseases. ②
Furthermore, as early as 1998, a study mentioned that Vitamin C can reduce the risk of angina and heart attacks. ③
So, what role does Vitamin C play in preventing arterial blockage?
7 Reasons Why Vitamin C Prevents Arterial Blockage
Vitamin C fights against arterial blockage in multiple dimensions, including but not limited to the 7 aspects I want to share with you:
→ Antioxidant, Reducing Oxidative Damage and Inflammation
The human body is made up of cells, and cells need energy to function normally. The process of generating energy in the body is like a factory producing products, which will create products and also produce waste.
 Factory producing smoke, image from Giphy
When these wastes become excessive and the cleaning ability is insufficient, it can cause a lot of damage (such as oxidative stress).
Vitamin C is one of the many “cleaners” for these wastes, and it plays an important role in maintaining balance in the body, effectively reducing the impact of oxidative stress and peroxidative damage on the body.
You might wonder how this relates to arterial blockage. It is important to know that atherosclerosis is a state of promoting inflammation and promoting oxidation, and the opposing role Vitamin C plays in this is evident.
→ Preventing Cholesterol from Being Oxidized, Reducing Vascular Damage
Cholesterol is very important for humans; you could say that without it, there would be no humanity. Increasing evidence from modern research has found that the real culprit of cardiovascular diseases is not cholesterol; on the contrary, many people have taken cholesterol-lowering medication for most of their lives and still cannot avoid cardiovascular diseases.
One of the elements we really need to be cautious about is oxidized and glycated cholesterol, which means this type of cholesterol has been “damaged” by the external environment.
Many people ask me how to resist oxidized cholesterol. Vitamin C can play a role in this.
A 1997 review study proposed that the oxidation of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) in the vascular wall plays an important role in the occurrence and development of atherosclerosis, and antioxidants (including Vitamin C) can enhance the antioxidant capacity of low-density lipoprotein. ④
→ Repairing Collagen, Restructuring Vascular Vitality and Resilience
A lack of Vitamin C leads to scurvy, which is common knowledge.
Damage to the inner wall of arteries may increase the likelihood of plaque formation, further developing into cardiovascular diseases.
Vitamin C helps increase collagen production, thereby repairing damaged tissues, including vascular damage.
Factory producing smoke, image from Giphy
When these wastes become excessive and the cleaning ability is insufficient, it can cause a lot of damage (such as oxidative stress).
Vitamin C is one of the many “cleaners” for these wastes, and it plays an important role in maintaining balance in the body, effectively reducing the impact of oxidative stress and peroxidative damage on the body.
You might wonder how this relates to arterial blockage. It is important to know that atherosclerosis is a state of promoting inflammation and promoting oxidation, and the opposing role Vitamin C plays in this is evident.
→ Preventing Cholesterol from Being Oxidized, Reducing Vascular Damage
Cholesterol is very important for humans; you could say that without it, there would be no humanity. Increasing evidence from modern research has found that the real culprit of cardiovascular diseases is not cholesterol; on the contrary, many people have taken cholesterol-lowering medication for most of their lives and still cannot avoid cardiovascular diseases.
One of the elements we really need to be cautious about is oxidized and glycated cholesterol, which means this type of cholesterol has been “damaged” by the external environment.
Many people ask me how to resist oxidized cholesterol. Vitamin C can play a role in this.
A 1997 review study proposed that the oxidation of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) in the vascular wall plays an important role in the occurrence and development of atherosclerosis, and antioxidants (including Vitamin C) can enhance the antioxidant capacity of low-density lipoprotein. ④
→ Repairing Collagen, Restructuring Vascular Vitality and Resilience
A lack of Vitamin C leads to scurvy, which is common knowledge.
Damage to the inner wall of arteries may increase the likelihood of plaque formation, further developing into cardiovascular diseases.
Vitamin C helps increase collagen production, thereby repairing damaged tissues, including vascular damage.
 Image from Giphy
Research has found that a lack of Vitamin C can slow down the rate of collagen formation, leading to slower wound healing. ⑤
A 1999 study also mentioned that after supplementing Vitamin C, the healing degree, strength, and elasticity of wounds and scars in guinea pigs improved. ⑥
→ Protecting Endothelial Cells, Preventing or Delaying Endothelial Dysfunction
From large arteries to tiny capillaries, endothelial cells line every blood vessel in the body. They can regulate blood flow, prevent clotting, and affect the immune system, among other functions.
Therefore, when these cells are damaged, it can lead to cardiovascular problems.
In fact, in the early stages of atherosclerosis formation, endothelial cell dysfunction can trigger a series of pre-atherosclerotic conditions, such as reduced vascular dilation, formation of pro-inflammatory mediators, and activation of platelets, which can put the vascular system in a state of promoting thrombosis.
Vitamin C has been found to reduce the adhesion of monocytes to the endothelium, improve endothelial dependency, and reduce the apoptosis of vascular smooth muscle cells, thereby preventing the instability of atherosclerotic plaques.
A 2021 study even found that oral Vitamin C can restore endothelial function during acute inflammation in both young and older adults. ⑦
In conclusion, our data suggest that oral vitamin C exerts beneficial effects and restores endothelial function during acute inflammation in young and older adults.
→ Enhancing and Maintaining the Bioavailability of Nitric Oxide
A lack of nitric oxide can lead to endothelial dysfunction, and nitric oxide can suppress the toxicity of pro-inflammatory cytokines and adhesion molecules, which may lead to endothelial dysfunction and ultimately promote plaque formation.
Image from Giphy
Research has found that a lack of Vitamin C can slow down the rate of collagen formation, leading to slower wound healing. ⑤
A 1999 study also mentioned that after supplementing Vitamin C, the healing degree, strength, and elasticity of wounds and scars in guinea pigs improved. ⑥
→ Protecting Endothelial Cells, Preventing or Delaying Endothelial Dysfunction
From large arteries to tiny capillaries, endothelial cells line every blood vessel in the body. They can regulate blood flow, prevent clotting, and affect the immune system, among other functions.
Therefore, when these cells are damaged, it can lead to cardiovascular problems.
In fact, in the early stages of atherosclerosis formation, endothelial cell dysfunction can trigger a series of pre-atherosclerotic conditions, such as reduced vascular dilation, formation of pro-inflammatory mediators, and activation of platelets, which can put the vascular system in a state of promoting thrombosis.
Vitamin C has been found to reduce the adhesion of monocytes to the endothelium, improve endothelial dependency, and reduce the apoptosis of vascular smooth muscle cells, thereby preventing the instability of atherosclerotic plaques.
A 2021 study even found that oral Vitamin C can restore endothelial function during acute inflammation in both young and older adults. ⑦
In conclusion, our data suggest that oral vitamin C exerts beneficial effects and restores endothelial function during acute inflammation in young and older adults.
→ Enhancing and Maintaining the Bioavailability of Nitric Oxide
A lack of nitric oxide can lead to endothelial dysfunction, and nitric oxide can suppress the toxicity of pro-inflammatory cytokines and adhesion molecules, which may lead to endothelial dysfunction and ultimately promote plaque formation.
 Sweet peppers rich in Vitamin C, image from Giphy
Interestingly, a 1999 study proposed that Vitamin C can enhance the synthesis of nitric oxide in endothelial cells, and this mechanism can protect blood vessels from changes in muscle-derived tension (vasoconstriction), atherosclerosis, and coagulation abnormalities. ⑧
Additionally, Vitamin C has been found to enhance the bioavailability of nitric oxide.
→ Strengthening the Endothelial Barrier, Resisting Damage from Harmful Substances
You can think of the endothelial barrier as a “wall” formed by endothelial cells tightly linked together, which is crucial for maintaining the internal environment and stability of blood vessels.
Thus, there is a close connection between the formation of arterial plaques and the destruction of the endothelial barrier, and Vitamin C can play an active role in this.
Sweet peppers rich in Vitamin C, image from Giphy
Interestingly, a 1999 study proposed that Vitamin C can enhance the synthesis of nitric oxide in endothelial cells, and this mechanism can protect blood vessels from changes in muscle-derived tension (vasoconstriction), atherosclerosis, and coagulation abnormalities. ⑧
Additionally, Vitamin C has been found to enhance the bioavailability of nitric oxide.
→ Strengthening the Endothelial Barrier, Resisting Damage from Harmful Substances
You can think of the endothelial barrier as a “wall” formed by endothelial cells tightly linked together, which is crucial for maintaining the internal environment and stability of blood vessels.
Thus, there is a close connection between the formation of arterial plaques and the destruction of the endothelial barrier, and Vitamin C can play an active role in this.
 Image from Giphy
A 2015 study found that Vitamin C can prevent the increase in permeability caused by thrombin (an inflammatory stimulant). ⑨
Another study also mentioned that Vitamin C can reverse the endothelial permeability leakage induced by high blood sugar and advanced glycation end products receptors. ⑩
→ Dissolving Calcium, Preventing Vascular Calcification
One very good effect of Vitamin C is its involvement in calcium metabolism, dissolving calcium, which for many friends with vascular calcification, high doses of Vitamin C may give you a feeling of finding light in the dark.
Image from Giphy
A 2015 study found that Vitamin C can prevent the increase in permeability caused by thrombin (an inflammatory stimulant). ⑨
Another study also mentioned that Vitamin C can reverse the endothelial permeability leakage induced by high blood sugar and advanced glycation end products receptors. ⑩
→ Dissolving Calcium, Preventing Vascular Calcification
One very good effect of Vitamin C is its involvement in calcium metabolism, dissolving calcium, which for many friends with vascular calcification, high doses of Vitamin C may give you a feeling of finding light in the dark.
 Image from the book “The Invisible Killer Calcium Supplement”
Vascular calcification is a pathophysiological process associated with coronary atherosclerosis and is a prognostic marker for cardiovascular morbidity and mortality.
Image from the book “The Invisible Killer Calcium Supplement”
Vascular calcification is a pathophysiological process associated with coronary atherosclerosis and is a prognostic marker for cardiovascular morbidity and mortality.
 Image from Giphy
The process of calcification in arterial walls is triggered and accompanied by the promotion of osteogenic phenotype changes in resident smooth muscle cells (the most abundant cell type in larger muscular arteries), and Vitamin C plays an active role in preventing smooth muscle cells from forming calcium deposits.
A 2020 study found that supplementing Vitamin C can actively and beneficially interfere with the process of arterial wall calcification, with potential implications for human health. ⑪
We conclude that ascorbic acid supplementation can actively and beneficially interfere with the process of arterial wall calcification, with potential implications for human health.
All friends with arterial calcification are advised to seriously consume enough Vitamin C.
Image from Giphy
The process of calcification in arterial walls is triggered and accompanied by the promotion of osteogenic phenotype changes in resident smooth muscle cells (the most abundant cell type in larger muscular arteries), and Vitamin C plays an active role in preventing smooth muscle cells from forming calcium deposits.
A 2020 study found that supplementing Vitamin C can actively and beneficially interfere with the process of arterial wall calcification, with potential implications for human health. ⑪
We conclude that ascorbic acid supplementation can actively and beneficially interfere with the process of arterial wall calcification, with potential implications for human health.
All friends with arterial calcification are advised to seriously consume enough Vitamin C.
Key Insights from Thin Dragon
Vitamin C is the cheapest nutrient, and it is the most basic and useful supplement.
Of course, this does not mean that taking 100mg of Vitamin C will have these effects; 100mg is used to prevent scurvy.
To achieve other effects, such as improving resistance, combating oxidation, reducing inflammation, and even unclogging blood vessels, high doses are required.
I personally take about 10 grams daily, while some people inject hundreds of grams at once for better results, but it is recommended to do so under the guidance of professionals.
The exploration of Vitamin C is like a long scroll of painting being slowly unfolded, and you will discover different surprises as your eyes flow.
The discovery and research history of Vitamin C can repeatedly shock and delight people. On the road to combating arterial blockage, it actually has effects and can play important roles in the 7 aspects mentioned in the article.
While expressing my amazement, I also want to mention something particularly important: in daily life, high blood sugar, especially for diabetics, should pay more attention to Vitamin C supplementation.
This is because diabetes is recognized as one of the risk factors for atherosclerosis, and those in a high blood sugar state need Vitamin C more than normal people: ↓
High blood sugar can increase oxidative stress in the body and promote the occurrence of inflammation;
Vitamin C and glucose have similar structures, and high blood sugar can inhibit cellular uptake of Vitamin C;
Vitamin C deficiency caused by high blood sugar can promote endothelial dysfunction and the process of plaque formation;
It has been found that glucose can inhibit the transport of Vitamin C in various mesenchymal cells (such as endothelial cells, monocytes, fibroblasts, etc.). ⑫
——Thin Dragon Mall’s Spring Fan Festival has begun——
In the name of love, pampering you madly

(Click the image to participate in the event)
①https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/jat/17/8/17_2881/_article
②https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5000725/
③https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/1998/06/980623044903.htm
④https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0952327897904324
⑤https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17921406/
⑥https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10553546/
⑦https://physoc.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.14814/phy2.15104
⑧https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10075731/
⑨http://www.jbc.org/content/290/35/21486.abstract
⑩https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3955275/
⑪https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7364280/
⑫https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S002191500100569X
How to Nourish Your Skin without Eating Fruits, How to Supplement Vitamin C?
Who Needs Vitamin C Supplementation the Most? – Diabetics!
The Relationship Between Vitamin C and Wound Healing…
Besides this public account, where else can you find me?
My personal blog: www.chinalowcarb.com
Toutiao, Baijiahao, Netease: Thin Dragon Health
Weibo, Bilibili: Thin Dragon Low Carb Ketogenic Diet
This article was first published: http://www.chinalowcarb.com/overeating-immunity/
ClickRead the Original, enter the Thin Dragon Weishop
 Left: Albert Szent-Györgyi, image from Wikipedia
Left: Albert Szent-Györgyi, image from Wikipedia Image from Giphy
Image from Giphy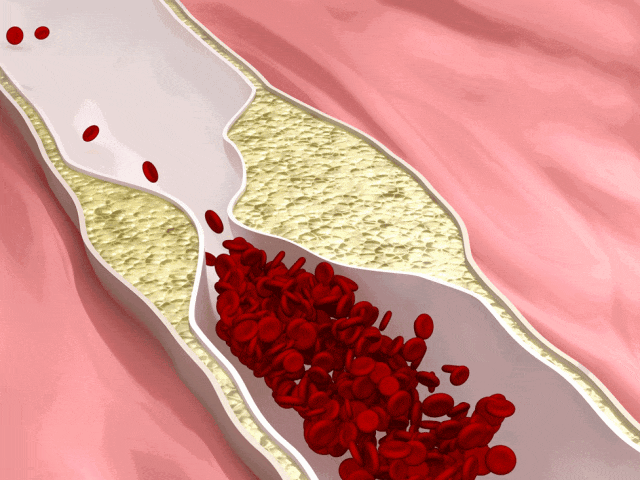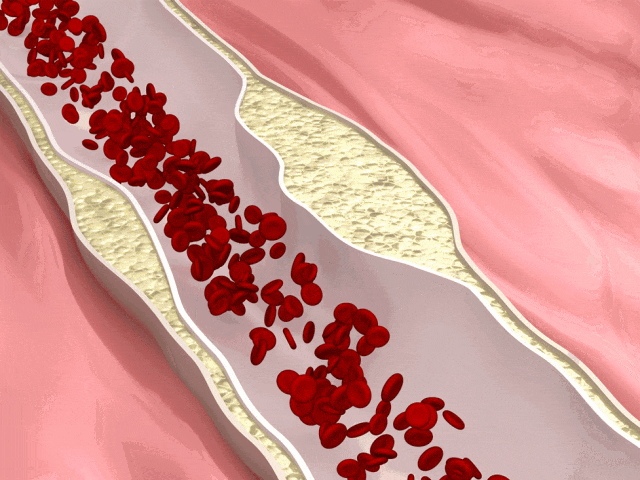
 A: Guinea pigs exposed to cigarette smoke (CS) over time develop atherosclerosis. B: Feeding guinea pigs Vitamin C can reverse atherosclerosis.
A: Guinea pigs exposed to cigarette smoke (CS) over time develop atherosclerosis. B: Feeding guinea pigs Vitamin C can reverse atherosclerosis. Factory producing smoke, image from Giphy
Factory producing smoke, image from Giphy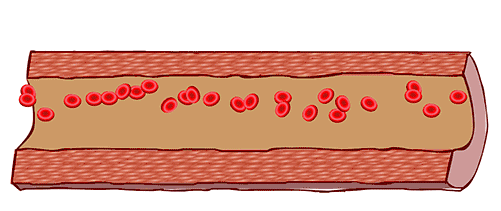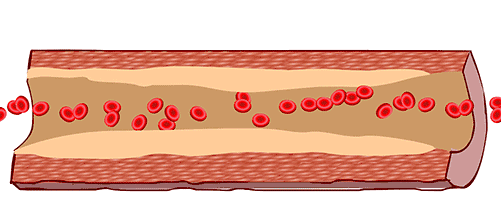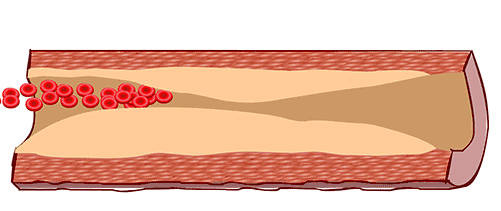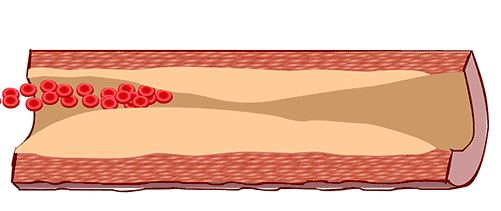
 Image from Giphy
Image from Giphy
 Sweet peppers rich in Vitamin C, image from Giphy
Sweet peppers rich in Vitamin C, image from Giphy Image from Giphy
Image from Giphy Image from the book “The Invisible Killer Calcium Supplement”
Image from the book “The Invisible Killer Calcium Supplement” Image from Giphy
Image from Giphy