
Concept of ADAS:
Advanced Driving Assistance System (ADAS) utilizes various sensors installed in the vehicle (millimeter-wave radar, LiDAR, monocular and binocular cameras, and satellite navigation) to sense the surrounding environment during the vehicle’s operation, collect data, identify, detect, and track static and dynamic objects, and perform systematic calculations and analyses combined with navigation map data. This allows drivers to be alerted to potential dangers in advance, effectively enhancing the comfort and safety of driving.
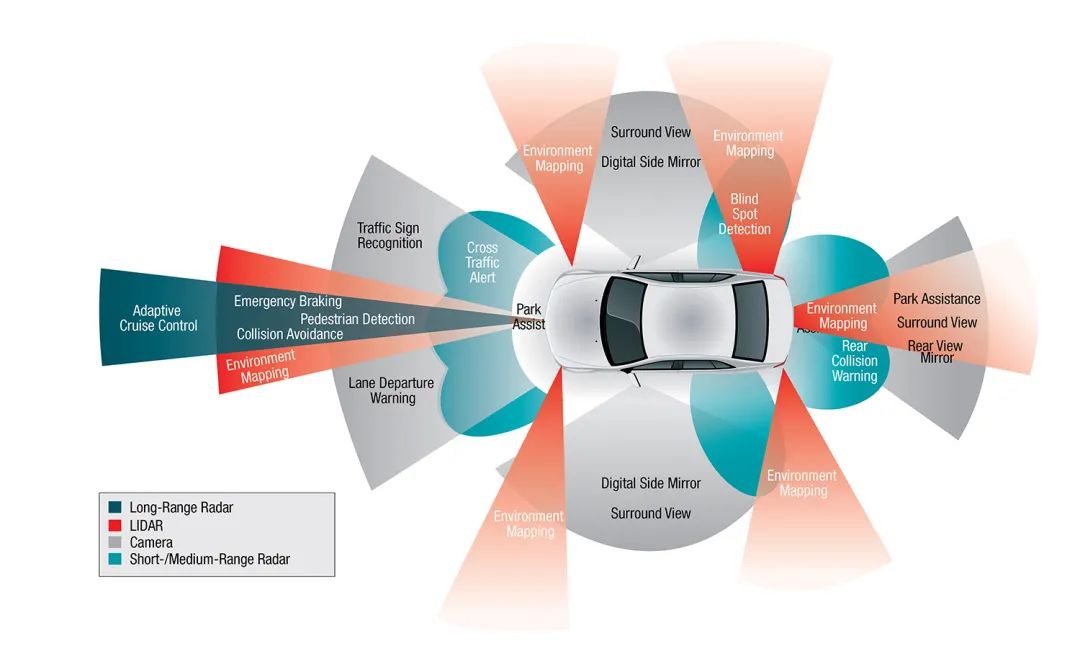
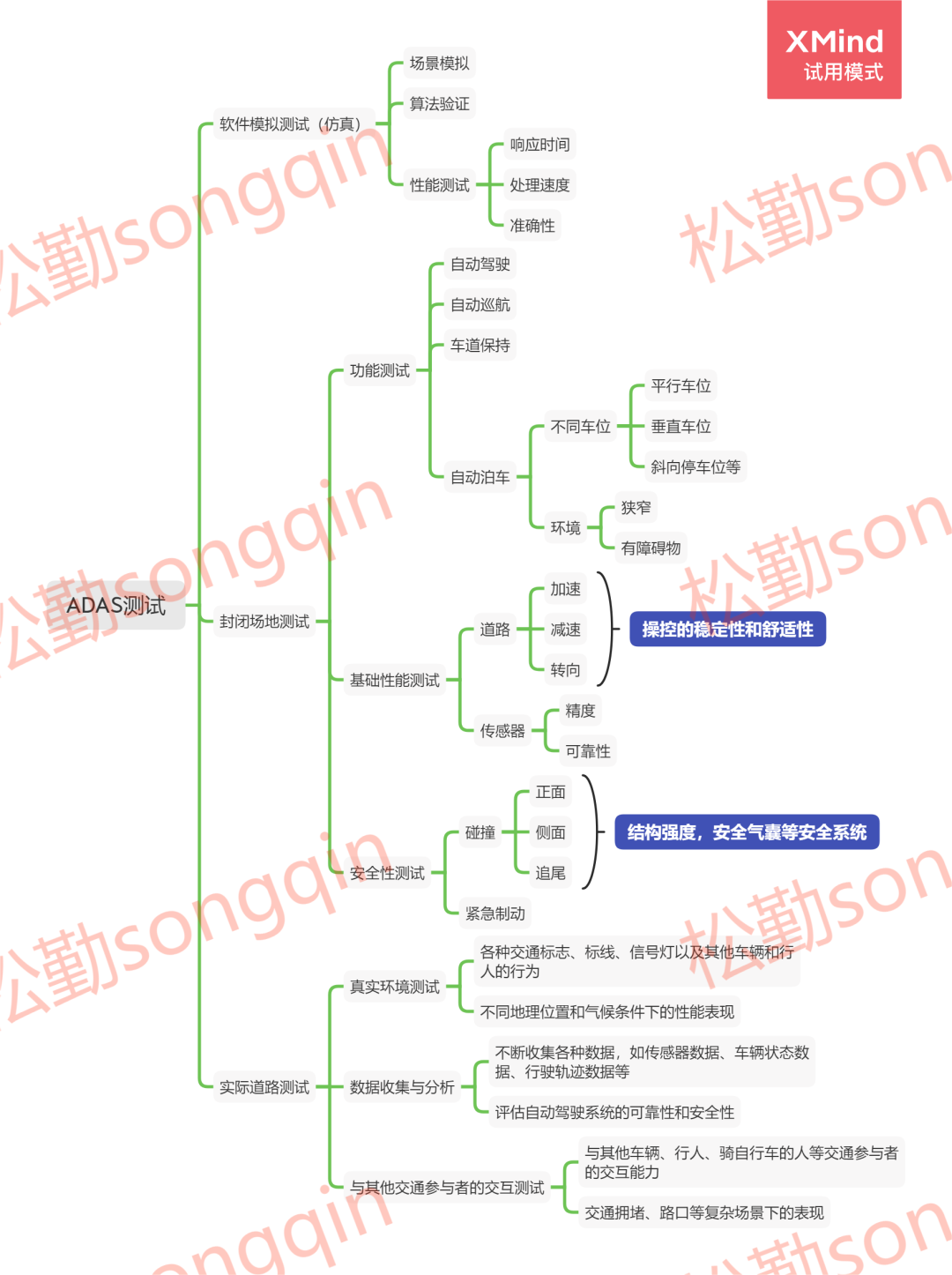
Key Analysis of ADAS Testing:
To conduct comprehensive testing of this full functionality, the features should be divided into phases, areas, and modules:
1. By Phase:
①. Components need to undergo comprehensive testing, with deeper testing of the underlying code.
②. Verification of integration/compatibility between components and the vehicle.
③. Testing of the complete vehicle with installed components in a laboratory, followed by verification in semi-closed spaces or outdoor environments, and finally in urban environments.
2. By Area:
①. The overall system should be divided into different functional areas for testing.
②. According to the example in the image above, areas should be divided into front, rear, side, etc., for relevant testing.
③. The focus and priorities of testing in each area differ; for example, the front area has more radar/sensors, so testing here will be more in-depth.