
○ NVIDIA CEO Jensen Huang appeared at the GTC conference with Disney’s robot, unveiling a humanoid robot general-purpose open-source model; the National and Local Joint Innovation Center for Humanoid Robots has established an embodied intelligence simulation platform and announced an open fund; Beijing will host the world’s first humanoid robot “half marathon” competition next month…
○ In the past week, the topic of humanoid robots has remained hot. In Nanjing, the enthusiasm for technological innovation and industrial development of humanoid robots shows no signs of waning.
○ “Dexterous hands” can twist screws and pinch tweezers, with flexibility comparable to Tesla’s humanoid robot; brain-computer interface technology decodes mysterious signals from the human brain, leading to the development of a non-invasive navigation surgical robot—this is the latest achievement from the “Zhongke System” startup in Nanjing’s Qilin Science and Technology Innovation Park, backed by the “national team”.
○ Jicui Intelligent focuses on electric servo and electro-hydraulic servo systems, Shenyuan Intelligent Technology mass-produces six-dimensional force sensors, and Tianchuang Electronics has released the world’s first explosion-proof humanoid robot. The domestic industrial robot leader, Estun, is about to launch its second-generation humanoid robot—private enterprises in Nanjing are leading the charge to tackle one challenging problem after another.
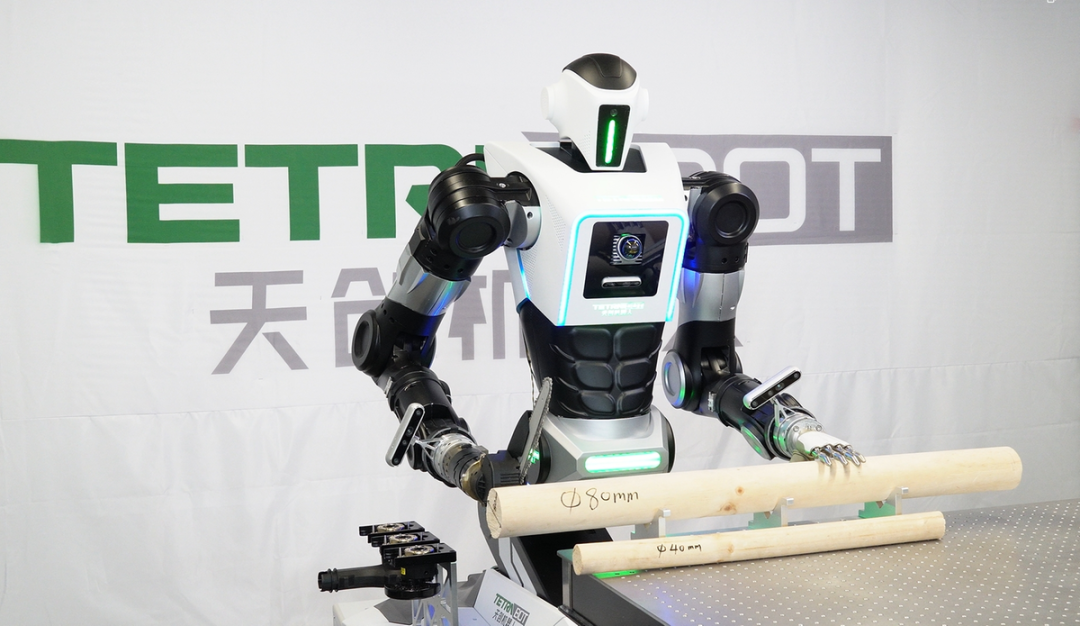

○ “Embodied intelligence” and “intelligent robots” have been included in the government work report for the first time this year. Humanoid robots are the advanced form of intelligent robots and the best carrier for embodied intelligence, attracting global attention from technology and capital. The year 2025 is seen as the “year of mass production” for humanoid robots.
○ In this trillion-level new track, many regions in China are competing to enter the market. In Nanjing, from the “brain” to the “limbs” of humanoid robots, from upstream core component research and development to downstream application by complete machine manufacturers, there are challengers and leaders throughout the entire industrial chain.
01Those Who Master Dexterous Hands Will Conquer the World
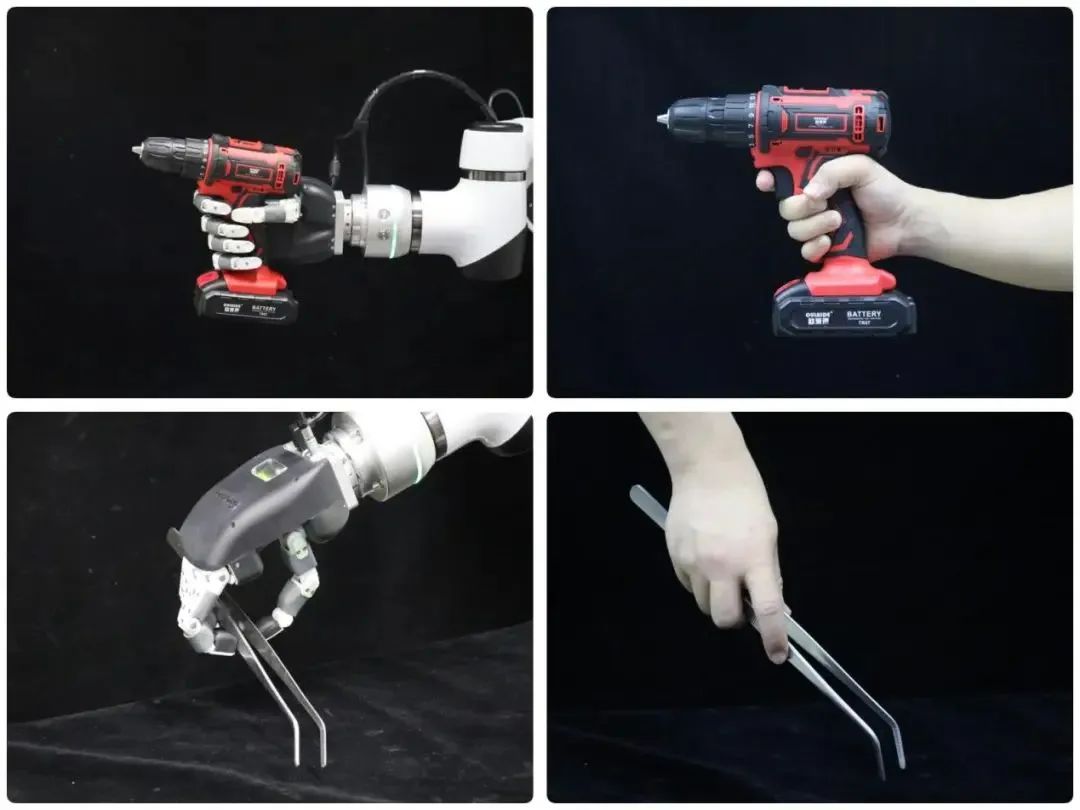
○ Picking up an egg, it neither squeezes too hard to break nor too lightly to drop. This is an innate skill for humans, but it has been a significant challenge for robots.
○ In Nanjing’s Qilin Science and Technology Innovation Park, this challenge has already been easily overcome. Visitors to the Zhongke Silicon Technology (Nanjing) Robot Co., Ltd. in the Qilin Artificial Intelligence Industrial Park are often amazed. The humanoid dexterous hand here can not only easily “grasp” an egg but can also hold a wrench to twist screws, pinch a pipette, and cut dragon fruit with a fruit knife.

○ “Human hands have 24 degrees of freedom, while this dexterous hand can achieve 25, capable of replicating over 90% of human-like dexterous operations, and the cost is far lower than similar products abroad,” said Zhang Tianyi, the company’s chairman and CEO. “For example, our humanoid dexterous hand product is fully aligned with foreign products, with many indicators at the international leading level, effectively breaking the foreign technology monopoly.”
○ “Those who master dexterous hands will conquer the world.” Dexterous hands belong to the intersection of cutting-edge technologies such as deep bionics, soft perception, micro-electromechanical systems, and high-performance materials, with research and development costs accounting for about 20%-30% of humanoid robots, representing a critical bottleneck that intelligent robots urgently need to overcome. Without years of investment and deep technological accumulation, ordinary enterprises cannot achieve this. As early as ten years ago, the Chinese Academy of Sciences, representing the “national team,” began to lay the groundwork for research on dexterous hands.
○ Zhongke Silicon Technology was registered in the park last year and is a result of the transformation of achievements incubated by the Zhongke Artificial Intelligence Innovation Research Institute. The startup’s ambition to scale technological “heights” is supported by the “national team.” The foundational research results of dexterous hands come from Professor Wang Peng’s Casia Hand embodied intelligence robot team at the National Key Laboratory of Multimodal Artificial Intelligence Systems of the Chinese Academy of Sciences. The founding team has focused on breakthroughs in the dexterous operation capabilities of robot “upper limbs” for over a decade, being among the first in the country to systematically conduct research on tendon-driven dexterous hands and “dexterous hands + embodied intelligence.” This achievement has received authoritative recognition both domestically and internationally, winning the “Gold Medal at the 49th Geneva International Invention Exhibition” and the “ISTA Global Innovation and Invention Award.” “Our company booth is often crowded with visitors,” Zhang Tianyi said.
○ “Years ago, there were already Chinese players in this track, so we can say that both domestic and international players are at the starting line simultaneously,” Zhang Tianyi metaphorically stated. Dexterous hands must be sufficiently “sensitive” to be “skillful.” The challenge lies in achieving the right balance among “rigid, soft, and flexible” aspects. In different application scenarios, it first senses information such as the material, texture, and temperature of the object’s surface, then converts it into electrical signals to transmit to the control system, and finally matches different forces and angles precisely while also being able to model, navigate, and avoid obstacles autonomously, completing human-like actions such as grasping, pinching, twisting, pulling, pushing, pressing, grabbing, and lifting.
○ The Zhongke Silicon dexterous hand is the only series product internationally that covers multiple application scenarios, with three models available: humanoid dexterous hand, general-purpose intelligent dexterous hand, and high-speed adaptive dexterous hand. From software to hardware, from the core embodied intelligence algorithm for dexterous operations to the structure, tendons, drives, and sensors, all hardware is self-developed by the team, with 100% localization of core components. Additionally, there are wearable data gloves, motion capture systems, and bionic arms for remote control of dexterous hands, with the company’s core competitiveness focused on the upper limb capabilities of humanoid robots.
○ “The ultimate goal of dexterous hands is to work like humans, and the future will face a vast blue ocean market,” Zhang Tianyi explained. Focusing on special operations, life services, and industrial applications, the team has also developed three humanoid dexterous operation robots: the “Fearless” model for bomb disposal, biochemical nuclear hazard handling, or operations in dangerous scenarios; the “Worry-free” model for public service, family service, and elderly care operations; and the “Limitless” model primarily for autonomous adaptive grasping, feeding, sorting, and assembly of diverse industrial components.
○ Having settled in Nanjing for less than a year, Zhongke Silicon has developed rapidly. Currently, the company has received millions in investment from several institutions, including Qilin Venture Capital, Shengjing Jiacheng, and Mingchuan Capital. Some products have already achieved small-batch production and are being sold to humanoid robot manufacturers. The next step for the company is to launch new products priced at around a thousand yuan and actively explore international markets.

02Upstream and Downstream Enterprises Crowd the “Starting Line”
○ High current detected, pull the switch! In the early hours of March 15, in a factory’s power distribution room, the “Tian Kui No. 1” robot, detecting high current, decisively used its dexterous fingers to operate the switch and turn the knob, performing like a skilled professional.
○ This is the world’s first humanoid robot to receive IIC T6-level explosion-proof certification, released by Nanjing Tianchuang Electronics Technology Co., Ltd. It is known as the explosion-proof “Iron Man.” This robot stands 2.2 meters tall, operates with dual arms, and can easily carry objects weighing 25 kilograms. Its lower body uses a more mature and stable wheeled walking mechanism, making it more suitable for industrial applications. Equipped with a high-performance core chip and a full-space perception radar system, it can receive commands for motion control, achieving an absolute motion accuracy of ±0.1 millimeters.

○ “Nanjing has a national-level new type of electric power (smart grid) equipment cluster. As long as we make our products well, we can quickly open up the market right in our ‘backyard,'” said Liu Shuang, chairman of Tianchuang Electronics. This product can be used for human-replacement operations and maintenance in industries such as electricity, offshore wind power, thermal power, nuclear power, and petrochemicals, as well as in emergency rescue scenarios. It has become a “hot item” right after its launch, with customer orders already lining up.
○ The humanoid robot industry chain can be divided into three core modules: “brain,” “limbs,” and scene implementation, each of which has multiple technological high grounds. In the past two to three years, it has been like hearing the starting gun, with many Nanjing enterprises already geared up and ready to start on various sub-tracks.
○ Teams specializing in core components of robots often have academic backgrounds. Dai Zhendong, a doctoral supervisor and professor at Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, founded Nanjing Shenyuan Intelligent Technology Co., Ltd. The six-dimensional force sensors developed by the team are known as the “force perception nerves” of robots. These sensors can be used for testing giant equipment weighing up to hundreds of tons or as small as 10 grams for testing the six-dimensional force on insects, covering the needs of humanoid robots, automobiles, aviation, new energy, and scientific research. The company is also the leading unit of the Ministry of Science and Technology’s key research and development project on “Key Technologies and Industrialization of Intelligent Six-Dimensional Force and Tactile Sensors for Robots,” having received angel round financing from the Ministry of Science and Technology’s Zhongke Haichuang Fund.
○ The reducer is the most costly component in the robot body. Nanjing Inks Intelligent Technology Co., Ltd. focuses on robot reducer motors, with a team composed of master’s graduates from Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics and Huazhong University of Science and Technology. Their joint module integrates reducers, motors, drivers, and encoders, suitable for complex motion control systems in bipedal robots, quadrupedal robots, and robotic arms. The company has received millions in financing from leading institutions like Oasis Capital. “Our products have already achieved mass production, and this year we will add 2,000 square meters of factory space to expand production capacity,” the company representative stated.
○ At Jiangsu Jicui Intelligent Manufacturing Technology Research Institute Co., Ltd., they just secured an order for 100 welding robotic arms from Russia. Chairman Luo Minzhou and his team are focusing their research and development on electro-hydraulic servo humanoid robots. Electro-hydraulic servo technology has high technical content and barriers, and the high-explosive electro-hydraulic servo system is a significant obstacle to the development of bipedal robots in China. Jicui Intelligent Manufacturing expects to launch the country’s first high-dynamic ultra-realistic humanoid bipedal robot within this year, overcoming the “bottleneck” of electro-hydraulic servo technology.
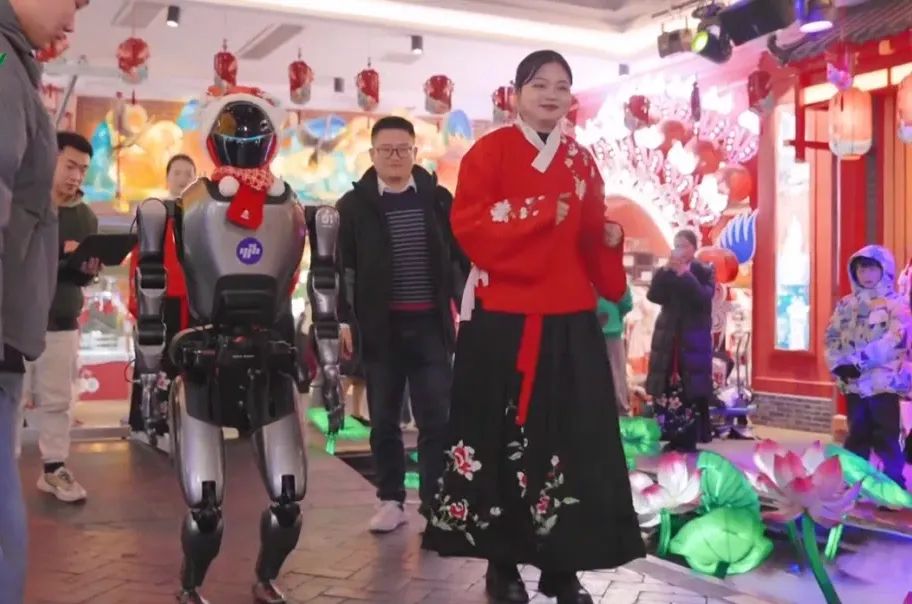
○ Humanoid robots for life services are also beginning to appear among Nanjing citizens. During the Qinhuai Lantern Festival, the Yijia and RK100 humanoid robots made appearances at the Confucius Temple; the “coolest robot” dressed in a T-shirt and jeans, wearing smart sunglasses and a mech helmet, frequently stole the spotlight on the streets. The latter is produced by Huaxia Robotics (Nanjing) Co., Ltd., and the team claims it is the world’s first mass-produced upright walking humanoid robot with a human-like face. They use bionic silicone skin that feels realistic, with precise facial and neck expressions, capable of recognizing user tones and responding accordingly. It can be used in six application scenarios: exhibition explanation, reception guidance, smart health care, smart homes, children’s education, and bionic dolls. “Some have questioned whether interactive service robots are just a gimmick, as they are not as ‘useful’ as industrial robots,” said the company’s general manager Dai Peng. “What we aim to do is to incubate more practical scenarios based on technological innovation, allowing people to see its prospects, gradually dismantling the technical dependencies from the expected form, and getting closer to the imagination step by step.”

03Must Robots Be “Humanoid”?
○ Must robots be “humanoid”? Is the development of humanoid robots inevitable? This question has puzzled many enterprises in the industry.
○ Industrial robots are usually designed for specific industrial production tasks, with relatively mature standardized products and solutions available. In contrast, humanoid robots, which can perform many tasks, find it challenging to achieve economies of scale. For manufacturing powerhouses like Jiangsu and Nanjing, the development of the robot industry is early, diverse, and widely applied. According to statistics from Nanjing’s Industry and Information Technology Bureau, Nanjing’s robot industry has built a product system that features collaborative, logistics, safety emergency, public service, personal consumption, and medical health robots, with industrial robots as the main force. With the wave of “intelligent transformation and digital upgrading” in the past two years, many enterprises have achieved intelligent and digital upgrades, with robotic arms and handling robots being ubiquitous, and dark factories and unmanned factories are not uncommon. The application of industrial robots is thriving, while the application of humanoid robots remains limited.
○ “Humanoid robots still struggle to perform efficiently on real production lines, achieving only 1/10 of the efficiency of existing robotic arms,” some business owners reported during surveys conducted by relevant departments. The accuracy of data collection and model training for humanoid robots is difficult to meet actual needs, and the humanoid robots that can be used are costly and inefficient. In the consumer product sector, some well-known domestic humanoid robot companies currently rely on providing performance, companionship, and entertainment services for profit. In the industrial sector, many believe that whether robots resemble humans is not important; what matters is that they are functional and user-friendly, without blindly following trends.
○ As a new phenomenon, although the research and manufacturing of humanoid robots are not yet perfect and their practical applications are still maturing, creating a robot that can adapt to human living scenarios may be best achieved through humanoid robots. According to Goldman Sachs, by 2035, the global humanoid robot market is expected to exceed $154 billion, with even more astonishing growth in the Chinese market. This growth is driven not only by the demand for industrial automation but also closely related to changes in population structure—accelerating aging is creating a need for care and companionship scenarios, while rising labor costs in manufacturing are pushing for further “machine replacement”.
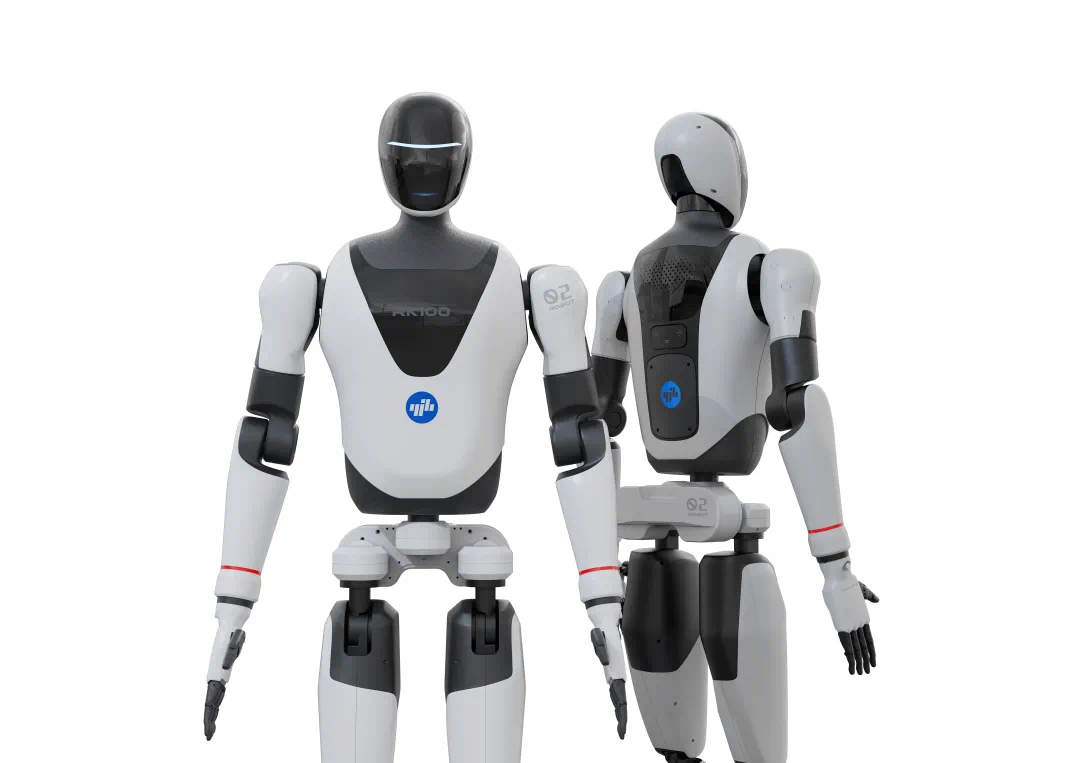

The Yijia and RK100 humanoid robots
○ The industry is opening up, technological advancements are occurring, and prices are continuously dropping, making mass production and commercial applications possible. Currently, through localization, the cost of humanoid robots is transitioning from the million-yuan level to around 200,000 yuan. Major companies like Huawei and Xiaomi are entering the market, and the path for breakthroughs in humanoid robot hardware, technological iteration, and scenario penetration is becoming increasingly clear.
○ It is essential to be “down-to-earth,” tailoring approaches based on industrial realities, while also “looking to the stars,” strategically positioning to seize opportunities, and at least preparing technologies in advance to form competitive advantages, which has become a consensus among governments and enterprises.
○ The Ministry of Industry and Information Technology issued the “Guiding Opinions on the Innovative Development of Humanoid Robots” in 2023, clearly stating that by 2025, an innovative system for humanoid robots will be initially established, cultivating 2-3 globally influential ecological enterprises and creating 2-3 industrial development clusters. At the end of last year, the “Action Plan for Promoting the High-Quality Development of the Robot Industry in Nanjing (2024-2026)” was released, proposing that by 2026, the overall development level of the robot industry will rank among the top in the country, creating a “1+N+1” complete machine system, with the last “1” being a forward-looking layout of the humanoid robot industry, comprehensively promoting the research and development of humanoid robot components such as “brain,” “small brain,” and “limbs,” and establishing a general platform for humanoid robot complete machines with initial small-batch production capabilities.
○ In various parks in Nanjing, policies and funding are also being synchronized. In Qilin Science and Technology Innovation Park, as a “regional innovation highland” co-built by the Chinese Academy of Sciences and Jiangsu Province, the park has become one of the most concentrated areas for scientific and technological innovation resources outside of Beijing’s Zhongguancun. The Qilin Venture Capital Fund insists on “investing small and early,” proactively laying out new tracks such as embodied intelligence, and has invested early in several “Zhongke System” AI enterprises, providing patient capital support for hard-core technological innovation. The newly introduced Zhongke Yixiang “brain-computer interface” team has already landed to carry out achievement transformation, completing the production of the first domestic brain-computer interface flexible electrode implantation robot and developing a non-invasive navigation surgical robot.
○ In the China (Nanjing) Software Valley, an embodied intelligence robot application center was established last week, aiming to address pain points in the development of the humanoid robot industry, such as difficulties in data acquisition and limited scenarios, and is expected to fill the gap in large-scale scene data collection for humanoid robots in China. In the Jiangning Development Zone High-tech Park, efforts are being made to promote the domestic industrial robot leader Estun to lead the creation of a future robot and artificial intelligence joint research and development experimental center, a humanoid robot and core component pilot platform, and a provincial-level robot industry benchmark incubator, among other innovative platforms, while planning to establish Jiangsu Province’s embodied intelligence industry innovation center.
○ The curtain on the humanoid robot industry has just been raised, and Nanjing has already taken its place on the track.
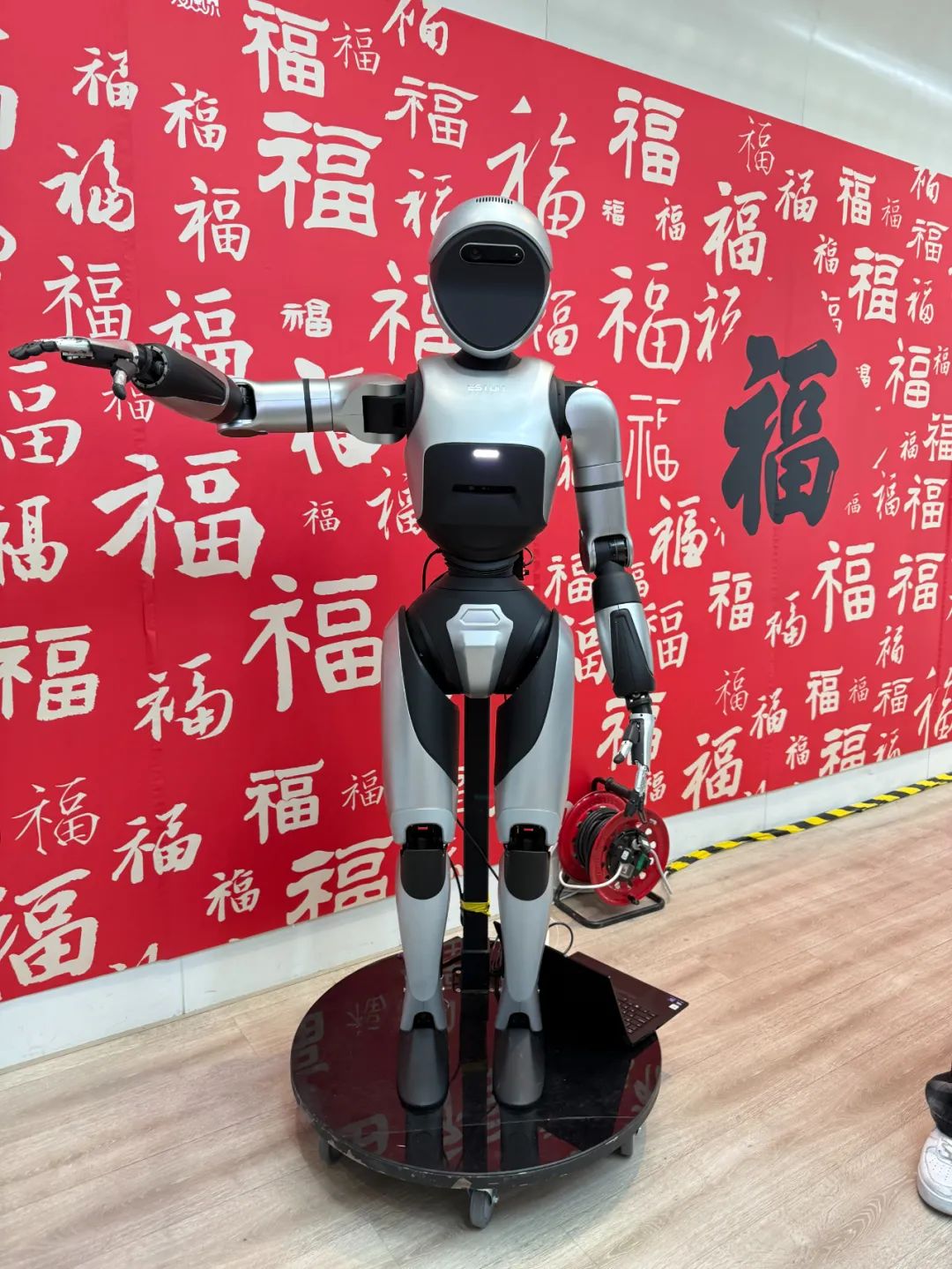

Nanjing Estun Automation Co., Ltd.’s humanoid robot Coolzhu Codroid 01
Content Source | Xinhua Daily Nanjing Observer Reporter Li Kai
Editor | Qi Cancan
Proofreader | Liu Bei, Shi Youyue
Reviewer | Nie Ying

Like + View
Share with Friends
↓↓↓