In the continuous development of Pingao virtualization technology, backend storage for virtualization has always been a focal point.
This article will trace the evolution from the initial file storage and NFS to centralized storage SAN, then to the selection of Ceph’s RBD method, and finally to the current state of backend storage supporting the vhost protocol. We will explore the development history of each type of backend storage.
The Initial File Storage and NFS
In the early stages of virtualization technology, the simplest backend storage method for virtual machines was to store virtual disk files in the local file system of the host machine. This method is simple and easy to use, suitable for small-scale deployments and testing environments.
However, as the number of virtual machines and their workloads increased, this method exposed performance bottlenecks and scalability issues.
To address these issues, we began to explore the use of network storage technologies, such as NFS (Network File System). NFS allows virtual machines to access virtual disk image files in a remote file system over the network, providing better scalability and performance.
However, NFS still has limited performance under high load and high concurrency, making it difficult to meet the demands of large-scale deployments.

Centralized Storage SAN
With the popularity of virtualization technology, the demand for higher performance and reliability has been continuously increasing.
To meet these demands, we began to adopt centralized storage technologies, such as SAN (Storage Area Network), and combine it with Logical Volume Manager (LVM) to manage the backend storage of virtual machines.
SAN provides high-performance and high-reliability storage solutions that can be connected to virtualization platforms via protocols such as Fibre Channel or iSCSI. Meanwhile, LVM offers flexible volume management capabilities, allowing dynamic resizing of volumes and supporting advanced features like snapshots. This method greatly enhances the performance and management efficiency of virtual machine backend storage, making it suitable for medium-sized enterprise deployments.
However, as the scale of virtualization continues to expand and application loads increase, the scalability and management complexity of SAN and LVM have become challenges.
Additionally, traditional storage solutions also face high costs and the risk of single points of failure.

Ceph RBD
To address the above challenges, we began to seek more flexible, scalable, and cost-effective storage solutions.
In this context, the emergence of Ceph provides an ideal choice. Ceph is an open-source distributed storage system with high availability, high scalability, and self-healing capabilities.
In Ceph, RBD (RADOS Block Device) is used as the backend storage solution for virtual machines. RBD allows virtual disk images to be stored in the Ceph cluster and accessed over the network, providing performance and functionality similar to traditional block devices. At the same time, the distributed architecture of the Ceph cluster and its automatic failover capabilities ensure the reliability and availability of storage.
The reasons for choosing the RBD method of Ceph mainly include:
-
High Performance: The distributed architecture of the Ceph cluster provides high performance.
-
High Availability: Ceph has automatic failover and data redundancy features, ensuring the reliability of storage.
-
Scalability: The Ceph cluster can be flexibly expanded according to demand, suitable for the growing scale of virtualization.
-
Open Source and Free: Ceph is open-source software, eliminating the high costs of commercial storage solutions.
Vhost Technology
Although the RBD method of Ceph has brought significant improvements to backend storage for virtual machines, as virtualization technology evolves and application scenarios change, we are still seeking further performance optimizations.
In this context, vhost technology has become a highly regarded option. By combining vhost technology with storage backends, virtual machines can achieve faster storage access speeds and lower storage latency, thereby improving the storage performance and responsiveness of virtual machines.
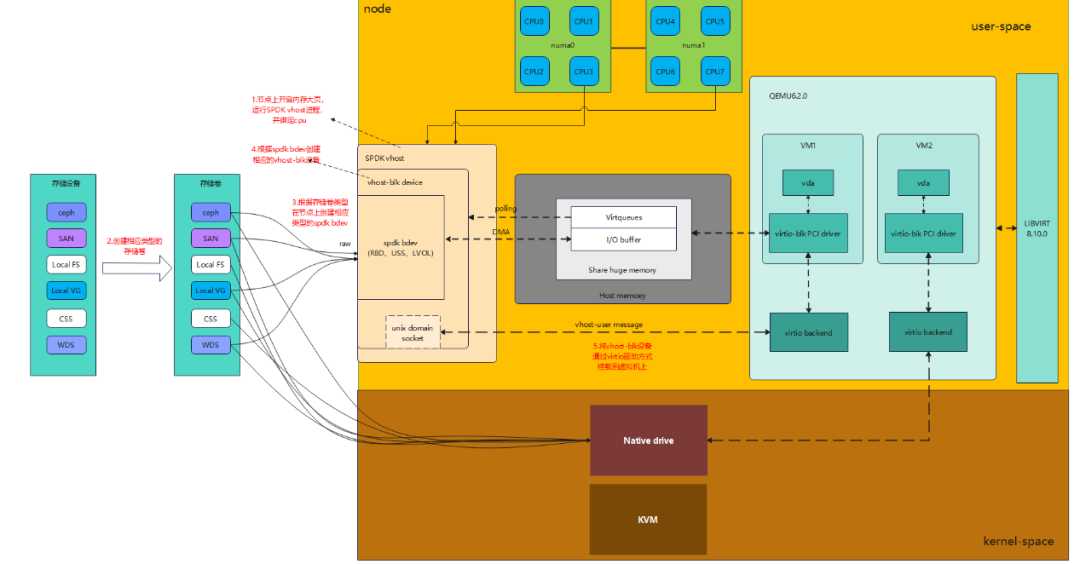
Vhost technology moves some virtual switch functions into the host kernel and uses user-space programs to communicate with the host kernel, thereby reducing the overhead of the virtual switch.
This method significantly improves the network performance and throughput of virtual machines, reducing the processing latency of network traffic by the virtualization layer.
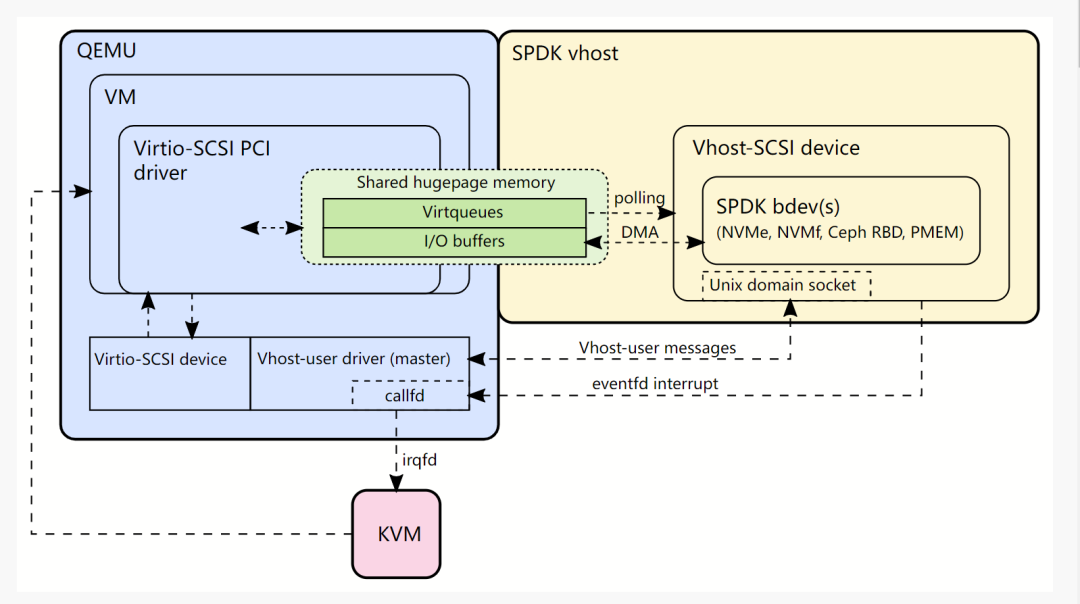
Advantages of Choosing Vhost:
-
Improved Network Performance: Vhost technology significantly enhances the network performance of virtual machines, meeting the demand for high-performance networks. When combined with RDMA networks, vhost technology can achieve astonishing performance of millions of IOPS on a single machine.
-
Reduced Network Latency: It reduces the processing latency of network traffic by the virtualization layer, improving the response speed of network communication.
-
Optimized Resource Utilization: By moving some network processing functions into the host kernel, it frees up resources in the virtualization layer, improving overall resource utilization.
Conclusion
The evolution of backend storage choices in Pingao virtualization has progressed from simple file storage to complex distributed storage. The continuous selection and change of interfacing methods are aimed at adapting to the ever-changing application demands and technological advancements.
Currently, Pingao Hyperconvergence has chosen vhost technology as a high-performance solution, bringing new possibilities to the Pingao hyperconverged virtualization environment. Pingao Hyperconvergence will continue to promote the development of virtualization storage technology, striving to provide enterprise customers with extreme speed in virtual storage.
Contact Us
If you want to know more, please call the customer service hotline: 4008-300-246