Nanobodies(Nanobody, Nbs) are a new member of the antibody family, characterized by their relatively small molecular weight, ease of humanization, high affinity, high stability, microbial expression capability, low immunogenicity, strong penetration ability, and good solubility. They have attracted significant attention in basic medical research as well as disease diagnosis and treatment.
Introduction to Nanobodies
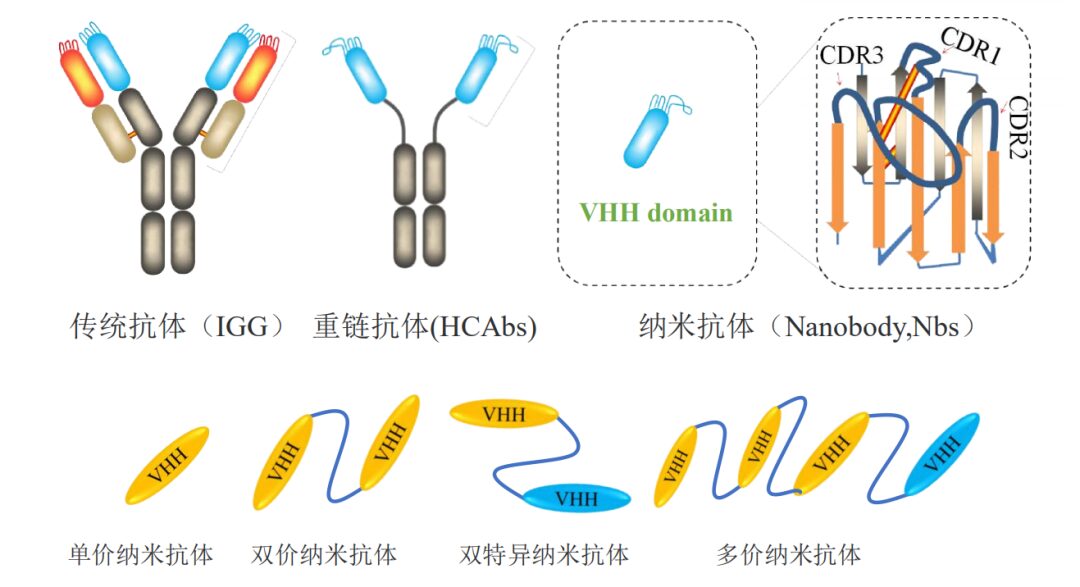
1. Small Molecular Weight: Traditional IGG antibodies have a size of 150KD, while nanobodies are only 15KD, which is one-tenth the size of traditional antibodies.
2. Simple Humanization: The sequence homology between heavy-chain antibody VH and single-domain antibody VHH is relatively high, allowing for easy humanization of nanobodies with appropriate modifications to the VHH region.
3. High Affinity: The structure of VH and VHH shows that the CDR3 region of VHH is longer, facilitating specific binding with antigens, resulting in tighter and more stable interactions.
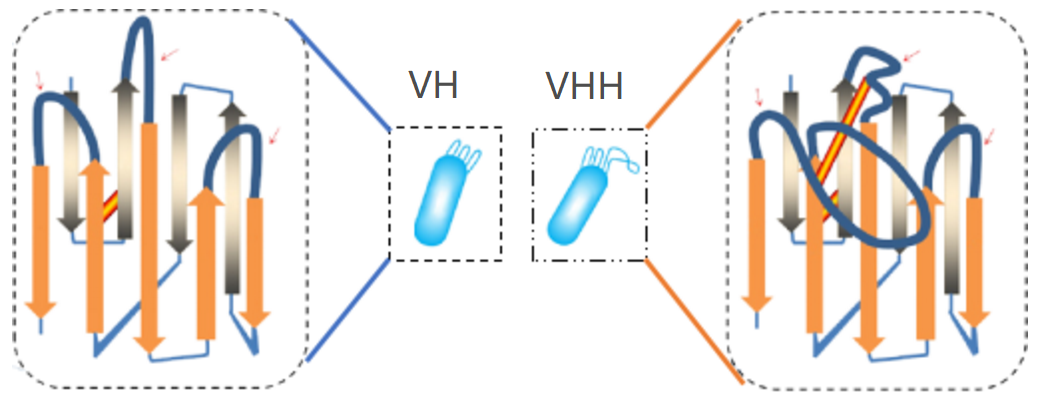
Image source: International Journal of Nanomedicine 2016:11 3287–3303
4. High Stability: Conventional single-chain antibodies have poor thermal stability, while nanobodies contain disulfide bonds that greatly enhance their heat resistance, allowing them to remain active at high temperatures (90℃) for extended periods. Additionally, they exhibit strong tolerance to harsh denaturing agents.
5. Microbial Expression Capability: Nanobodies possess hydrophilicity and monomeric properties, and due to the absence of glycosylation, they can be efficiently produced in bacterial expression systems, avoiding the high costs and long production cycles associated with cellular production.
6. Low Immunogenicity: VHH and VH-VL are structurally similar, but nanobodies have a smaller molecular weight and fewer surface binding epitopes, resulting in relatively low immunogenicity.

Image source: Laura S., Proteins, 2018;86;697-706.
7. Good Solubility and Strong Penetration Ability: Characterization of the FR and CDR regions of nanobodies shows that hydrophobic residues in the FR2 region are mutated to hydrophilic residues, resulting in improved solubility. Furthermore, nanobodies have a strong tissue penetration ability, allowing them to enter dense tissues (such as solid tumors) and exert their effects, even effectively crossing the blood-brain barrier.


Nanobody Preparation Scheme
The preparation of nanobodies generally involves immunizing llamas to obtain antibody genes, followed by phage display screening technology to select the most suitable antibody sequences from the llama antibody library. The entire process includes three main stages: llama immunization, phage library construction, and antibody screening.
1. Llama Immunization Process: Prepare Antigen → Immunize Llama → Blood Collection → Serum Separation → Isolate Lymphocytes
2. Phage Library Construction Process: RNA Extraction → Reverse Transcription cDNA → Amplify Antibody Fragments → Clone into Phage Plasmid → Transform SS320 → Amplify and Purify Phage Library
3. Antibody Screening and Identification Recommended Process: Coat Immuno-tubes → Block → Incubate Antigen and Phage → Wash → Elute → ELISA Identification

Pulley Medicine Nanomedicine Technology
Pulley Medicine has always adhered to the vision and mission of “leading medical research, enhancing human health” and “overcoming major diseases” to create translational medical value for society. The operational model of Pulley Medicine, which includes “research institute + translational technology platform + R&D pipeline,” continuously contributes efficient innovative power to the advancement of the medical and health fields. We warmly welcome friends from the pharmaceutical industry who are interested in collaborating to jointly develop and accelerate the clinical translation and research of new products and technologies for major disease diagnosis and treatment.
BioT Forum
