Loop structures are a type of structure that controls the execution flow of a program, allowing for the repeated execution of a block of code until a specific condition is met.Python provides two main types of loops: for loops and while loops.
Types of Loops in Python
|
Loop Type |
Syntax |
Applicable Scenarios |
|
for loop |
for variable in sequence: |
Iterating over strings, lists, tuples, dictionaries, and other iterable objects |
|
while loop |
while condition: |
Looping while a condition is met, such as user input or event listening |
|
Nested Loops |
for or while loop nested |
Situations requiring multiple layers of loops, such as processing two-dimensional data |
|
Loop Control Statements |
break, continue, pass |
Controlling the flow of loops |
for Loop
The for loop is used to iterate over strings, lists, tuples, dictionaries, sets, and other iterable objects.
Syntax:
for variable in iterable:
code block # Operations performed on each element
Execution Logic:
·The for loop retrieves elements sequentially from the iterable (such as a list, string) and assigns them to the variable, then executes the code block.
·After iterating through all elements, the loop ends.
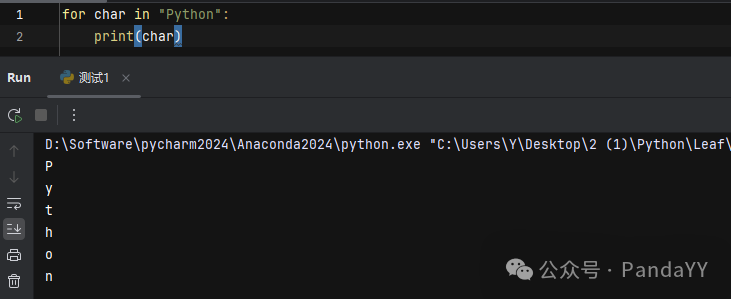
Example 1: Iterating over a string Example 2: Iterating over a list
Example 3: Generating a sequence with range()
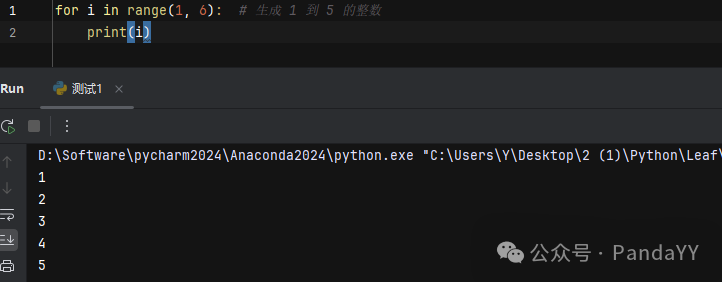 range(start, stop, step) is used to generate a sequence of integers:·start (optional): starting value, default is0.·stop (required): ending value (exclusive).·step (optional): step size, default is1.
range(start, stop, step) is used to generate a sequence of integers:·start (optional): starting value, default is0.·stop (required): ending value (exclusive).·step (optional): step size, default is1.
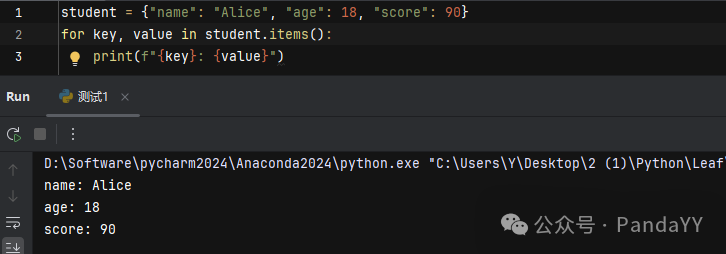
Example 4: Iterating over a dictionary
while Loop
The while loop is suitable for situations where the exact number of iterations is unknown, but the loop condition is known, such as user input or sensor data monitoring.
Syntax
while condition:
code block # Executed when the condition is True