
Common Rail Guide
The common rail system requires precise fuel injection from the injector, but due to manufacturing deviations of the injector itself, the control accuracy of the fuel volume can be affected. To overcome this impact, electronically controlled diesel engines commonly use injector correction code technology. This issue will take you into the world of injector correction codes.
Case One

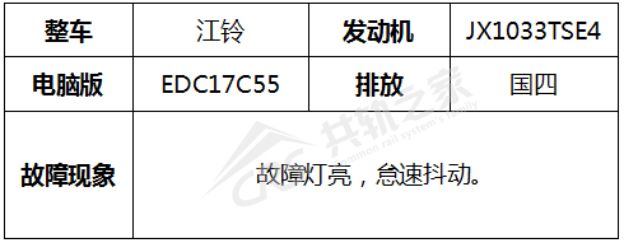
Troubleshooting
Step
One
Use a decoder to read the fault code.

The fault code indicates “Cylinder × (Physical Cylinder ×) lacks injector fuel correction code”. The logic behind this fault code is that the injector correction value (IQA code) for the engine’s injector has not been written into the ECU or has been written incorrectly.
Step
Two
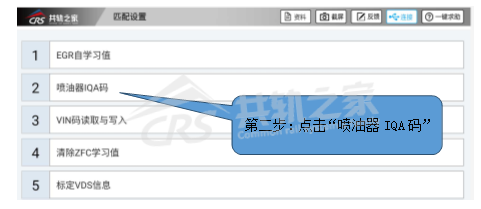
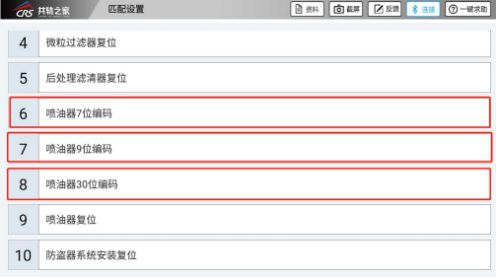
Use the decoder to read the IQA code and enter the system for “Matching Settings”.

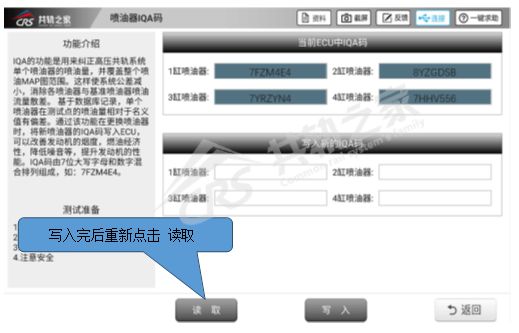
After entering the matching settings, click on “Injector IQA Code”.
After entering the injector IQA code, click “Read” to retrieve the IQA code written in the ECU.
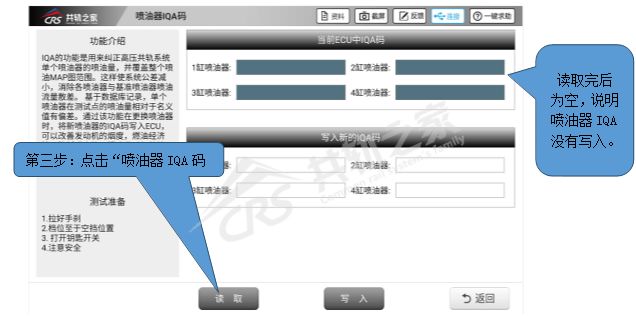
If it is empty after reading, it indicates that the injector IQA has not been written into the ECU, resulting in a fault reported by the ECU. Now you need to write the injector IQA code into the ECU.
Step
Three
Remove the cylinder cover to read the injector IQA code.
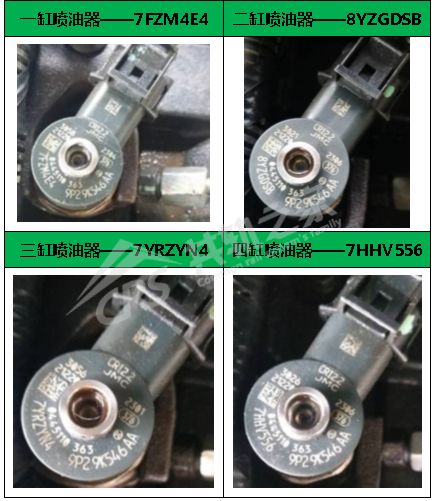

Step
Four
Write the injector IQA code into the ECU.
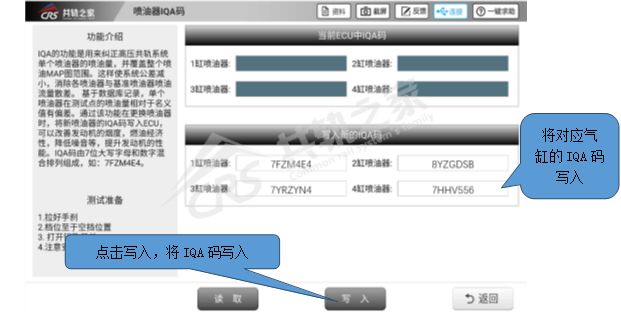
Step
Five
After writing, read the IQA code again.
Step
Six
After writing, turn off the key, then re-enter the system and read the fault code again.

The system is normal, and the fault is resolved.
Tip:
The importance of data is self-evident. When flashing the ECU, data is usually either from the decoder or a backup of the ECU, or requested from the manufacturer or friends. We decided to launch a new feature to make it easier for everyone to flash data. That is WeChat flashing. Others can send you the flashing data through WeChat, and with one click, you can flash it on the Diagnostic Master 3.0.
Case Two

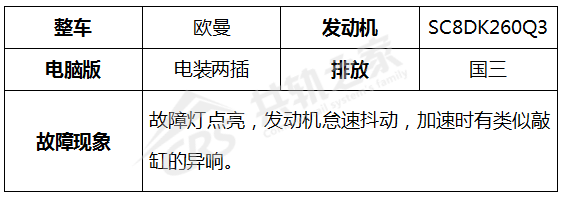
Troubleshooting
Step
One
Use a decoder to read the fault code.

The fault code indicates “QR code definition error” and “QR code error”, which means the error of the injector correction value for the specific cylinder reported by Bosch. This indicates that the injector correction value has either been written incorrectly to the ECU or not written at all.
Step
Two
Use the decoder to enter “Matching Settings” and select the corresponding cylinder’s QR code to read the original QR code in the ECU.
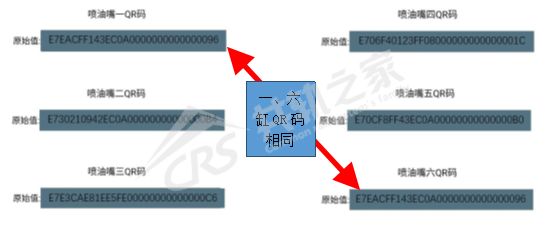
From the read QR code, it can be seen that the QR codes of cylinder one and six are the same. Each injector has its unique QR code, just like our ID card, which will not be repeated. Now that cylinder one and six are the same, it indicates that at least one cylinder’s QR code has been written incorrectly.
Step
Three
Remove the cylinder cover to read the QR code of the injector and find that the QR code of cylinder one has been written incorrectly.
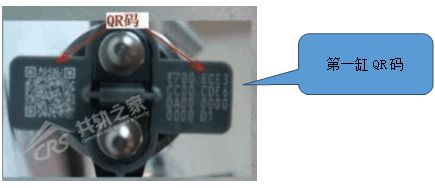
Rewrite the QR code of cylinder one and read the QR code of the injector in the ECU.
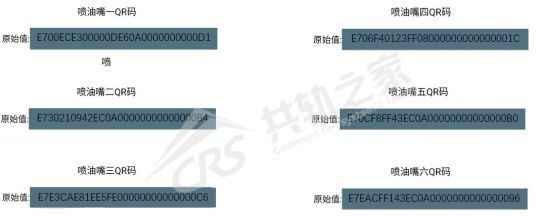
The QR codes of the injectors are all different; the change is successful.
Step
Four
Use the decoder to read the fault code.

The system shows normal, no fault codes, and the fault is eliminated.
Tip:
The injector correction codes for fuel volume are called differently in various systems; for example, in the Bosch system, it is called IQA code, in the Denso system, it is called QR code, and in the Delphi system, it is called IMA code.

Knowledge Expansion
In the common rail system, the fuel volume is determined by the rail pressure and the excitation time of the injector. In other words, for the same injector, since the number of nozzle holes, diameter of the nozzle holes, and the injection cone angle are already determined, under the same excitation time, the fuel volume should theoretically be a fixed value.
During mass production, manufacturing deviations of the injector itself are unavoidable. For example, parameters such as the diameter of the nozzle holes, the size of the metering hole, and the resistance that needs to be overcome when the solenoid valve opens all have differences between injectors. If these differences are not compensated for, the precise control of fuel volume by high-pressure common rail diesel engines will be restricted, and injector correction is the technology that achieves this fuel volume adjustment.
Taking Bosch as an example, the injector correction code (IQA) includes the deviation value of the fuel volume of this injector under five conditions compared to the standard volume.
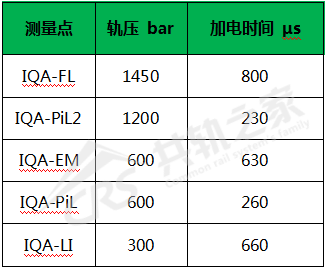
By adjusting the above injection points, precise control of the injector’s fuel injection can be achieved. However, when the injector correction code is incorrect, it may lead to the following faults:
l Engine knocking
l Engine idle shaking
l Engine emitting black smoke
l High engine oil consumption
l Insufficient engine power
However, not all vehicles can report faults related to injector correction; this is related to the engine’s calibration. Therefore, when we replace new injectors and ECU, we need to rewrite the injector correction code to avoid faults.
Now let’s discuss the injector correction codes in detail.
01
Bosch
For Bosch large vehicles, injectors CRIN1, CRIN1.6, CRIN2, CRIN3, and CRIN3.3 do not require writing the injector correction code.

For Bosch small vehicles, such as injectors CRI2-994, CRI2-18, it is necessary to write the QR code. The Bosch QR code is generally located at the head of the solenoid valve, and the IQA code is usually 7 digits long.
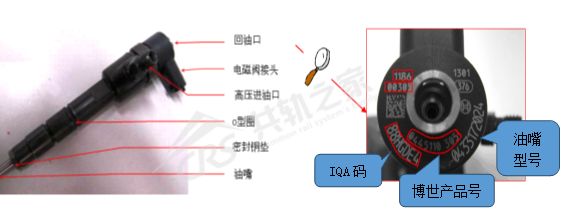
Bosch small vehicles must write the IQA code. If not written, it may lead to engine knocking, insufficient power, and shaking faults.
02
Denso
Denso injectors have signal X1, G2, G3, and it is necessary to write the IQA code. The QR code of Denso injectors is generally on the injector body, and the QR code is usually 8 digits or 30 digits, with the Denso 6222 having a 30-digit compensation code.
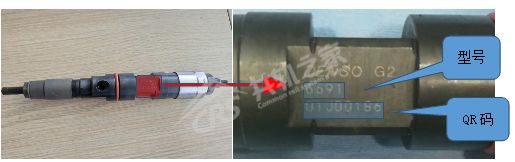

For Denso injectors with QR codes on the body, it is necessary to take a photo of the QR code before installing it in the engine cylinder head, as the QR code on the Denso injector body cannot be seen after installation.
03
Delphi
Delphi injectors must have the QR code written, and the QR code lengths vary, including 20 digits, 16 digits, and 8 digits. For example, injector 3301D has a 16-digit compensation code, and injector 5310D has a 20-digit compensation code.

04
Cummins
Cummins injector correction codes generally have 7, 9, and 30 digits, usually located on the injector solenoid valve.

When writing the Cummins injector correction code, first confirm the number of digits of the correction code, and write the correction code to the correct position.
For the Cummins system, the injector correction code avoids reading errors and does not contain the letters “I, O, S, Z”, only the Arabic numbers “1, 0, 2, 5”, which is different from Bosch and needs to be memorized distinctly.
05
Common Individual Pump System Correction Codes
The diesel engine electronic control individual pump system uses an electronically controlled individual pump with a mechanical injector. Therefore, the individual pump is the only actuator in the electronic control system. The fuel volume and timing are controlled by the ECU to actuate the fuel solenoid valve, and the injection pattern is determined by the camshaft profile of the individual pump.
To achieve precise control of the fuel volume and timing, and to eliminate manufacturing deviations of the individual pump, some electronic control individual pumps have adopted individual pump correction code technology.
Delphi Individual Pump
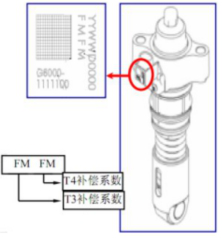
Correction Code Explanation:
FM-T3 compensation coefficient;
FM-T4 compensation coefficient.
Check the code against the compensation coefficient table to obtain the corresponding compensation coefficient. Each code corresponds to two parameters, and one can be chosen at will.
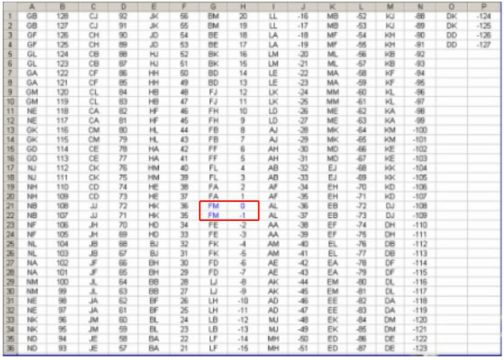
Domestic Weite Individual Pump
The fuel volume correction code for Chengdu Weite individual pump is shown in the following figure.
