Introduction
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) integrates various sensing and control technologies with mobile communication and intelligent analysis into every aspect of industrial production, significantly improving manufacturing efficiency, product quality, reducing costs, and resource consumption, ultimately elevating traditional industries to a new stage of intelligence.
>
July 2015
>
November 2017
>
October 2019
The “14th Five-Year Plan” for national informatization proposes that by 2025, digital infrastructure capabilities represented by 5G, IoT, cloud computing, and industrial internet will reach an internationally advanced level. China is vigorously promoting the accelerated integration and fusion of IoT with other new generation information technologies, with the scale of IoT connections and applications continuing to grow.
The IoT is booming,security risks
are quietly arising
The perception layer is the lowest layer of the IoT network, responsible for sensing physical objects and collecting information through sensing and acquisition technologies; the network layer is built on the infrastructure of cellular networks and fiber broadband, providing data encoding, authentication, and transmission; the application layer is the fundamental goal of IoT development, utilizing analyzed sensing data to provide users with rich specific services, achieving monitoring, querying, controlling, and scanning functions.
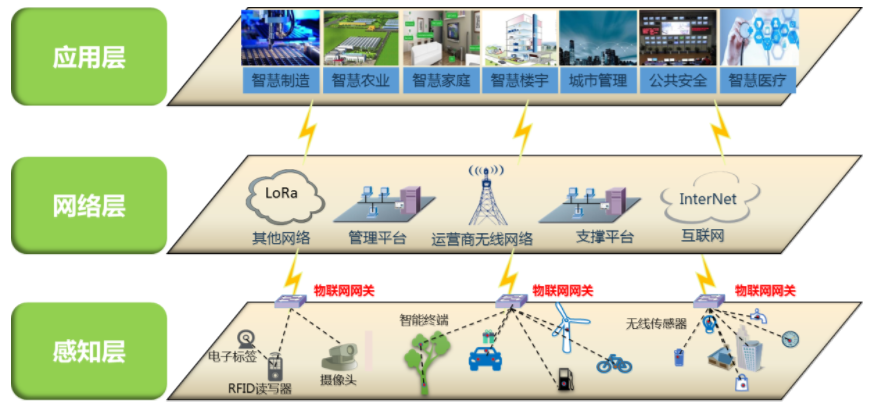
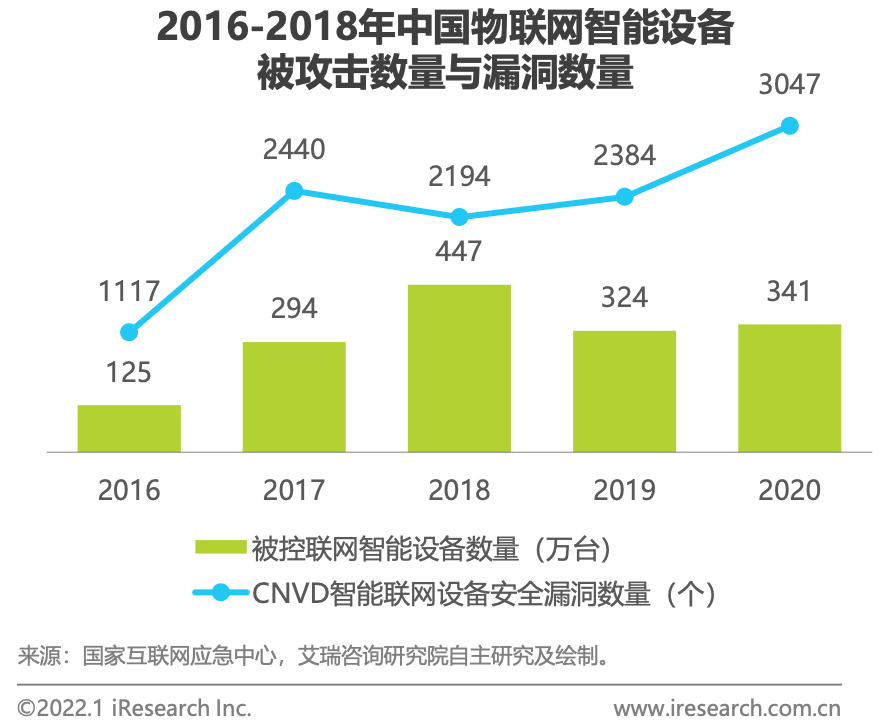
In the typical network structure of IoT, the security issues at the application layer are relatively mature and align well with existing security products. However, due to the large number of IoT devices connected, there are significant gaps in security construction at the network and perception layers, especially at the boundary connecting the perception layer and upper layers, where necessary security measures are lacking, leading to frequent IoT security incidents. According to statistics from the National Internet Emergency Center and iResearch Consulting, the number of controlled IoT devices and vulnerabilities in China remains high, and the widespread distribution of IoT devices significantly extends the coverage area of cyberspace, synchronously expanding the risk range brought by controlled devices and their vulnerabilities, highlighting the importance of boundary protection.
Needs of the IoT Network
Need 1:Address the risk of unauthorized access by terminals
Need 2:Address the risk of unauthorized communication by terminals
Terminal devices accessing the sensor network primarily need to transmit raw data to application layer servers, without the need to communicate with other devices at the application layer. However, due to the lack of access control measures at the boundary, many sensor terminals can be controlled and access application systems freely.
Need 3:Address the risk of illegal command transmission
In the Industrial IoT, the communication protocols used for data acquisition and automation control are often industrial protocols. Control commands in industrial protocols direct lower-level machines to complete specified tasks. If illegal control commands are issued, it can lead to abnormal operation of automated equipment and business losses. Moreover, due to the widespread distribution of IoT devices, locating and repairing issues can be time-consuming and labor-intensive.
Need 4:Address the risk of more frequent network attacks
In March 2022, the NSA exposed a representative cyber weapon used against targets within China—the Quantum attack platform, which has achieved complete engineering, automation, and artificial intelligence capabilities, allowing for indiscriminate automated attacks on targets on the internet. The security of public network environments is significantly challenged. The infrastructure of IoT network layers is primarily cellular networks, requiring sensors in the perception layer to connect to the internet, making industrial enterprises more susceptible to network attacks compared to closed local area networks, such as various common network scans, DDoS attacks, and malformed packet attacks.
Need 5:Address the risk of data leakage during transmission
At the end of 2020, a technology company in Shanghai was caught illegally collecting high-speed rail signal data, including IoT, cellular networks, and GSM-R spectrum data used in railways. The suspects used easily purchasable equipment for signal collection, such as antennas, SDR devices, laptops, and external hard drives. Fortunately, the railway wireless data had already been encrypted, preventing serious incidents. This incident highlights the low cost of illegally collecting IoT signals, which can easily lead to data leakage.
Need 6:Meet the need for remote wireless communication
According to IDC Consulting, IoT devices connected through cellular networks account for one-third of the total scale. In industrial settings, there are many monitoring and manufacturing stations where deploying wired networks is difficult, creating a demand for cellular network communication.
Need 7:Meet the need for high reliability in communication
For industrial scenarios, the reliability of communication is crucial. The maintenance cost of widely distributed IoT edge nodes is high, and directly debugging devices during communication failures is not feasible, while communication interruptions can negatively impact business operations.
Need 8:Meet the need for interconnectivity between distributed field stations
In industries like smart manufacturing, which require coordination among multiple factories to produce final products, there is a strong need for network transformation before achieving intelligent transformation. This interconnectivity demand among various field stations is becoming increasingly urgent.
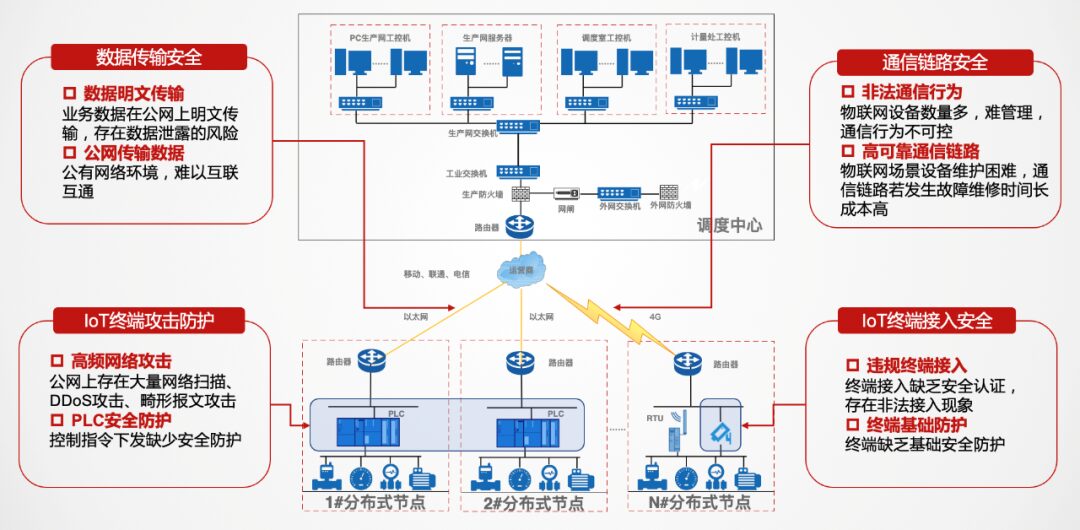
Figure 4 Pain Points in IoT Network Needs
Solutions to Industrial IoT Security Issues
Winuet IoT Secure Access Gateway
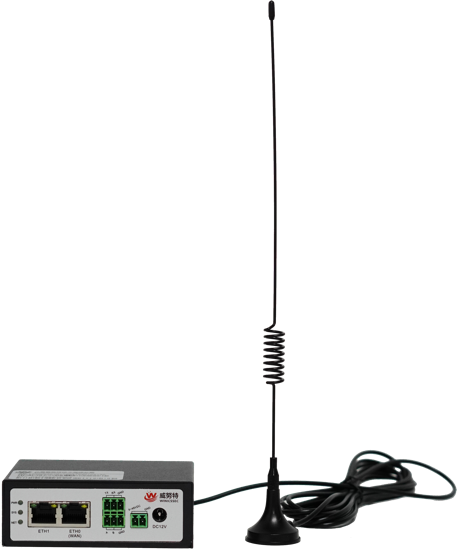

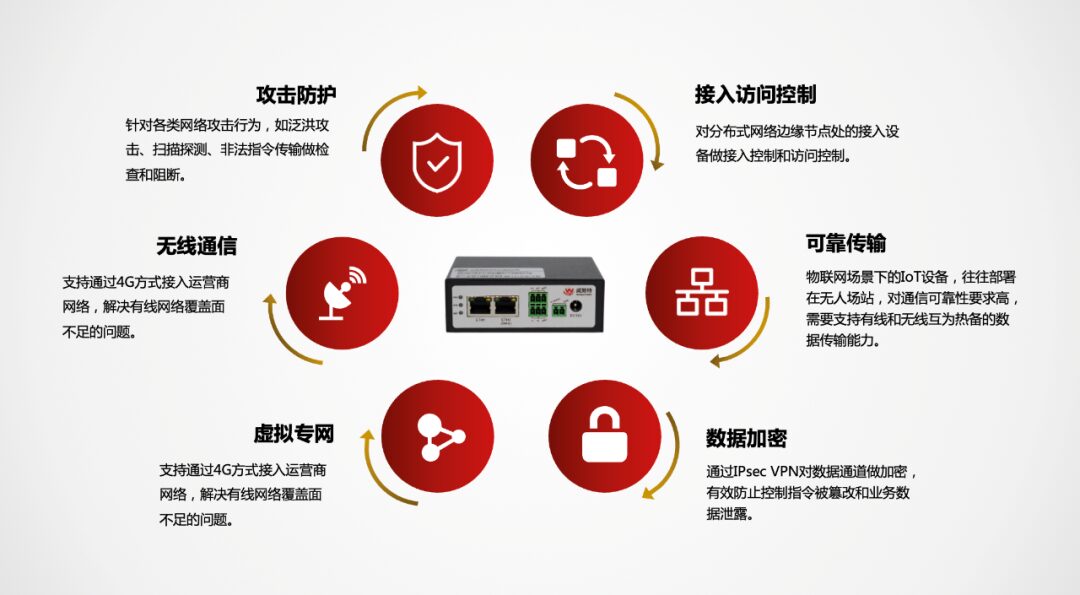
Capability 1:Access Control
The perception layer of the IoT network has many sensors and sensing devices. Due to the physical distance of the IoT network, managing unauthorized access is challenging. The IoT Secure Access Gateway has access control capabilities to effectively prevent unauthorized connections.
Capability 2:Network Attack Protection
There are numerous automated network attacks on public networks. Although the types of attacks are common, their high frequency can negatively impact normal business operations. The IoT Secure Access Gateway supports attack protection capabilities, effectively safeguarding against various network attacks and illegal command transmissions.
Capability 3:Wireless Communication
IoT sensors are widely distributed, and there are areas where wired networks cannot reach. The IoT Secure Access Gateway supports 4G full network access to solve the problem of insufficient wired network coverage.
Capability 4:Reliable Communication Link
The IoT Secure Access Gateway supports both wired broadband and wireless 4G communication capabilities. To enhance communication reliability, it supports hot backup between wired and wireless links, ensuring high reliability in data transmission.
Capability 5:Virtual Private Network Construction on Public Networks
Building a smart system first requires networking, followed by intelligent transformation. Therefore, interconnectivity in IoT networks is a significant pain point. The IoT Secure Access Gateway supports the establishment of virtual private networks to address the challenges of networking on public networks.
Capability 6:Data Transmission Encryption
The sensing data from the IoT network provides a wealth of raw data for upper-layer applications, meeting the needs of smart system construction while also posing risks of data leakage. The IoT Secure Access Gateway supports data transmission encryption to meet high confidentiality requirements for business data.
The Winuet IoT Secure Access Gateway is comprehensive, easy to deploy, and can be applied in municipal heating, municipal water management, environmental monitoring, video protection, wind and solar power, power distribution networks, smart cities, and other scenarios. It helps users build secure and reliable IoT systems with effective technical means and comprehensive security capabilities.
Conclusion


Beijing Winuet Technology Co., Ltd. (abbreviated as Winuet) is a leader in the domestic industrial control security industry and a subsidiary of China’s state-owned capital venture capital fund. With outstanding technical innovation capabilities, it is one of the six companies globally awarded the ISASecure certification by the International Society of Automation and one of the first national-level specialized and innovative “little giant” enterprises.
Winuet relies on its pioneering core technology concept of the industrial network “white environment” and a full range of self-developed industrial control security products to provide comprehensive lifecycle defense solutions and specialized security services for key national industries such as electricity, rail transportation, petroleum and petrochemicals, municipal services, tobacco, smart manufacturing, and military industry. To date, it has enabled safe and compliant operations for over 4,000 industry clients in China and along the “Belt and Road” initiative.
As a national team for industrial control security in China, Winuet actively promotes the construction of industrial clusters and ecosystem development, leads and participates in the formulation of national and industry standards in the field of industrial control security, and is committed to safeguarding the security of critical information infrastructure networks in China, striving to become a backbone force in building a strong networked nation!