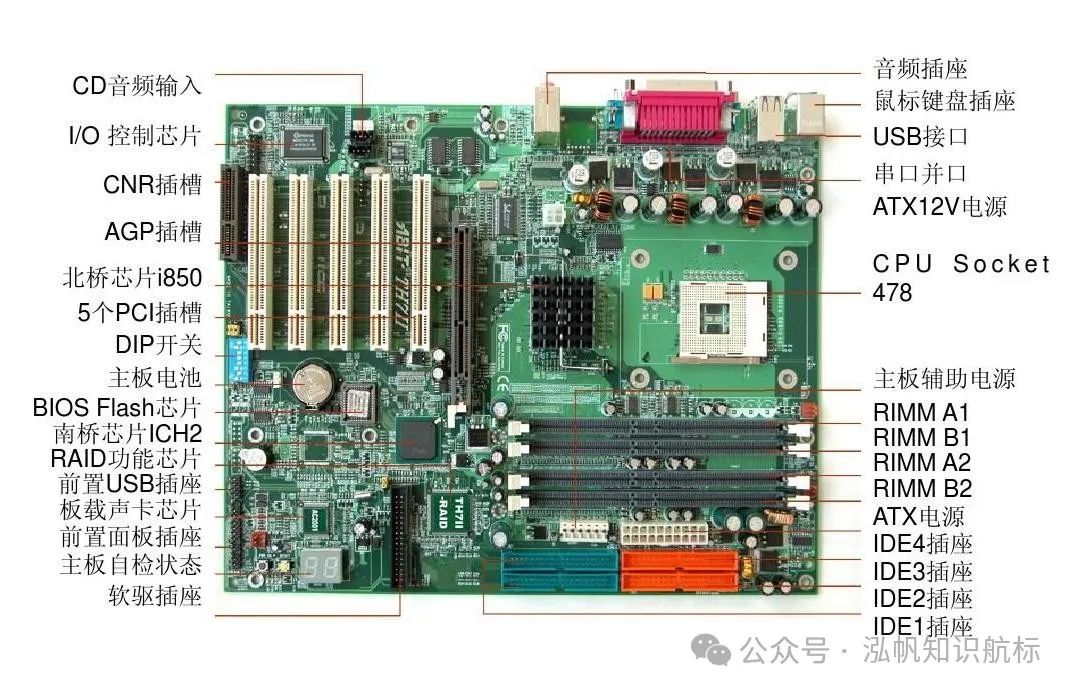
“Desktop MotherboardSelection Tips”


Clarify Usage Needs

Office Use
– If mainly used for office tasks such as document processing, web browsing, and office software, the performance requirements for the motherboard are relatively low. At this time, the stability of the motherboard and the integrity of its basic functions are the focus. Generally, choose entry-level motherboards from mainstream brands, such as Intel’s H series motherboards or AMD’s A series motherboards. These motherboards are affordable and provide enough interfaces to connect common office devices, such as USB ports for connecting mice, keyboards, and printers.
– For office computers, the integrated graphics function of the motherboard may be quite useful. Because many office scenarios do not require a dedicated graphics card, the integrated graphics on the motherboard can meet the display needs of basic office software interfaces and web content, while also saving the cost of purchasing a dedicated graphics card.
Gaming Use
– For gamers, the performance and expandability of the motherboard are crucial. First, consider the CPU and memory specifications supported by the motherboard, as gaming relies heavily on CPU and memory performance. Generally, mid-range to high-end gaming computers require motherboards that can support high-frequency memory and multi-core high-performance CPUs.
– The performance of the PCI-E slots on the motherboard is also critical. Gaming graphics cards need to connect to the motherboard via PCI-E slots, and higher version PCI-E slots (such as PCI-E 4.0 or 5.0) can provide higher bandwidth to fully unleash the performance of high-end graphics cards. For example, when using high-performance graphics cards like NVIDIA’s RTX 40 series, PCI-E 4.0 or higher slots can ensure fast data transfer between the graphics card and the motherboard, reducing frame drops during gaming.
– Additionally, gamers may need to install multiple storage devices, such as solid-state drives (SSD) for installing games to improve loading speeds, and hard drives for storing a large number of game files. Therefore, the number and types of storage interfaces on the motherboard also need to be considered. Motherboards with multiple M.2 slots (preferably high-speed M.2 slots supporting NVMe protocol) and SATA interfaces will be more suitable for gamers.

Content Creation Use (e.g., video editing, 3D modeling, etc.)
– Content creators often need to process large amounts of data and complex calculations. For video editing, the motherboard needs to support high-performance CPUs and large-capacity, high-frequency memory to handle video encoding and decoding processes. For example, when using software like Adobe Premiere Pro for 4K video editing, a multi-core CPU and over 32GB of high-frequency memory can significantly improve editing efficiency.
– The expandability of the motherboard is also important. Content creators may need to install professional graphics cards (e.g., NVIDIA’s Quadro series or AMD’s Radeon Pro series) for 3D modeling and rendering, which requires the motherboard to have enough PCI-E slots to support these high-performance graphics cards. Additionally, to store a large amount of materials and project files, the motherboard needs to provide multiple high-speed M.2 slots and SATA interfaces to facilitate the installation of large-capacity solid-state drives and hard drives.
– Moreover, during content creation, a stable network connection is also important. A motherboard with high-quality Ethernet interfaces (e.g., supporting 2.5Gbps or higher speed) can ensure efficiency when transferring large material files.

Consider Compatibility with CPU

Slot Type Matching

– Different CPU brands and models require matching specific motherboard slots. For example, Intel Core series CPUs have different slot types such as LGA1700, LGA1200, while AMD Ryzen series CPUs have AM5, AM4, etc. When purchasing a motherboard, it is essential to ensure that the CPU slot of the motherboard matches the selected CPU. If the slots do not match, the CPU cannot be installed on the motherboard.
– Additionally, slot compatibility also involves the generational issues of CPUs. For Intel, for instance, the LGA1700 slot is mainly used for the 12th and 13th generation Core processors, while earlier CPUs cannot use this slot. Therefore, when upgrading the CPU or assembling a new computer, it is crucial to carefully check the compatibility list of motherboard and CPU slots.
Chipset Support

– The chipset of the motherboard determines the CPU features it can support. For example, some Intel chipsets may only support specific CPU core counts, cache sizes, or memory frequency ranges. For users who want to fully utilize CPU performance, it is crucial to choose a chipset that matches CPU features well.
– The chipset also affects the motherboard’s support for CPU overclocking. If users have the need to overclock the CPU, they need to choose a chipset that supports overclocking features. For example, Intel’s Z series chipset motherboards (such as Z790) typically have good support for CPU overclocking, while H series chipset motherboards (such as H610) have relatively weak overclocking capabilities.

Pay Attention to Motherboard Performance Parameters
Power Supply Design
– The power supply design of the motherboard directly affects the performance of the CPU and other components. The number of power phases is an important indicator; generally, the more power phases, the more stable the power supply to the CPU. For high-end CPUs or users with overclocking needs, it is necessary to choose a motherboard with a large number of power phases. For example, some high-end Z series motherboards may have 16 or more power phases, which can provide sufficient power to the CPU during overclocking, avoiding system instability due to insufficient power.
– In addition to the number of power phases, the quality of power capacitors and inductors is also crucial. High-quality capacitors and inductors can filter out noise in the power supply, ensuring that the CPU receives clean and stable DC power. For example, Japanese solid capacitors are known for their high stability and long lifespan, and are often used in the power supply design of high-end motherboards.
Memory Support
– The motherboard’s support for memory includes memory type (such as DDR4 or DDR5), memory frequency, and maximum memory capacity. DDR5 memory has higher bandwidth and lower power consumption compared to DDR4 memory, which can enhance the overall performance of the system. If users want to use DDR5 memory, they need to choose a motherboard that supports DDR5.
– The memory frequency also greatly affects system performance. The higher the memory frequency supported by the motherboard, the faster the data transfer speed of the memory. For example, some high-end motherboards can support DDR5-6400MHz or higher frequency memory, allowing for faster data loading when running large software or games, improving system responsiveness.
– The maximum memory capacity determines the total amount of memory that users can install. For applications that require processing large amounts of data, such as content creation or server applications, it is essential to choose a motherboard that supports large-capacity memory (such as 128GB or higher).

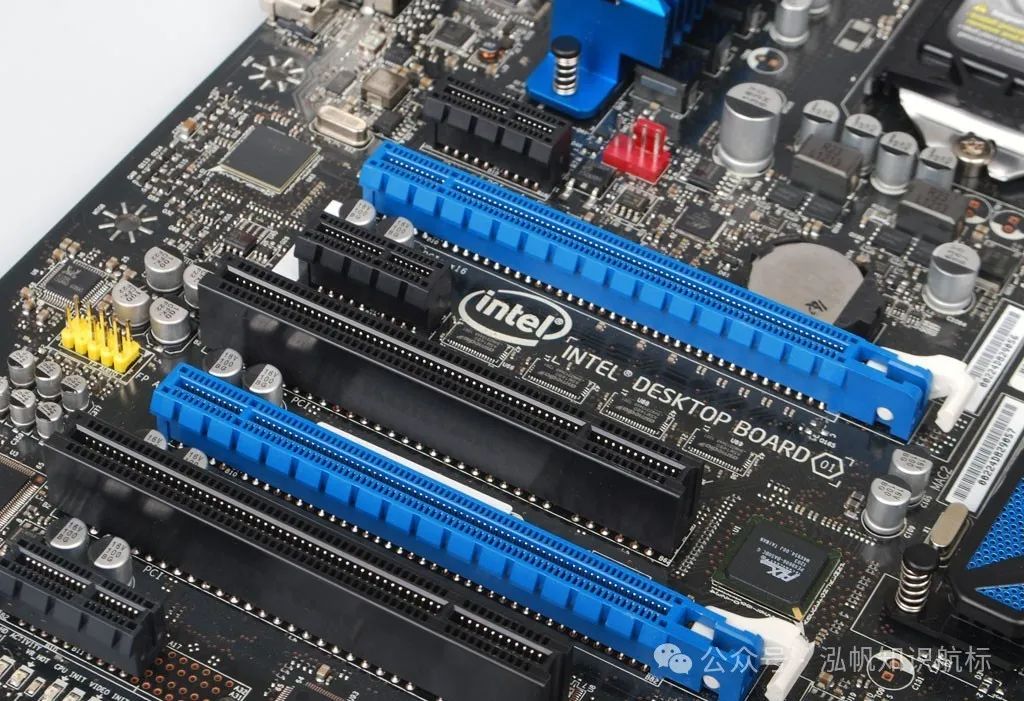
Expansion Slot Performance
– The performance of the PCI-E slots on the motherboard is mainly reflected in their version and bandwidth. PCI-E 4.0 and PCI-E 5.0 slots have higher bandwidth than PCI-E 3.0 slots, better supporting high-performance graphics cards and other high-speed expansion cards. For example, when connecting a graphics card using a PCI-E 5.0 slot, data transfer speeds can significantly increase, which is very important for gaming and professional graphics applications.
– The M.2 slots on the motherboard are also important expansion interfaces. M.2 slots have different protocols, such as SATA protocol and NVMe protocol. NVMe protocol M.2 solid-state drives have speeds far exceeding those of SATA protocol, so choosing a motherboard that supports NVMe protocol M.2 slots can achieve faster storage speeds. Additionally, the number of M.2 slots determines how many high-speed solid-state drives users can install, which is a critical factor for users who need multiple storage devices.

Motherboard Expansion Capability
Storage Interface Quantity and Type

– The motherboard’s storage interfaces include SATA and M.2 interfaces. SATA interfaces are mainly used to connect traditional mechanical hard drives and SATA protocol solid-state drives, with relatively slower transfer speeds, but still a practical choice for large-capacity storage devices. Generally, motherboards will provide 4-8 SATA interfaces, sufficient for users to connect multiple hard drives.
– M.2 interfaces are mainly used to connect high-speed solid-state drives, especially NVMe protocol M.2 solid-state drives, which can achieve speeds of several GB/s. The number of M.2 interfaces on the motherboard and the supported protocol types are crucial. For users pursuing high-speed storage, choosing a motherboard with multiple NVMe protocol M.2 interfaces is a better choice. For example, some high-end motherboards may offer 3-4 M.2 slots, allowing users to install different solid-state drives for system, gaming, and data purposes.

PCI-E Slot Quantity and Use

– The PCI-E slots on the motherboard are used to install graphics cards, network cards, sound cards, and other expansion cards. The number of PCI-E slots determines how many expansion cards users can install simultaneously. Generally, motherboards will have 1-2 PCI-E x16 slots for graphics cards and several PCI-E x1 slots for other expansion cards.
– For users with special needs, such as needing to install multiple graphics cards (for multi-screen display or dual graphics card crossfire operations) or professional expansion cards (such as capture cards, RAID cards, etc.), it is necessary to choose a motherboard with sufficient numbers and appropriate specifications of PCI-E slots. Additionally, attention should be paid to the version and bandwidth of the PCI-E slots to ensure that the performance of the expansion cards can be fully utilized.

Richness of I/O Interfaces

– The I/O interfaces of the motherboard are located at the back of the motherboard, including USB interfaces, video interfaces, audio interfaces, and Ethernet interfaces. USB interfaces have different versions, such as USB 2.0, USB 3.0, USB 3.1, and USB 3.2, with higher versions offering faster transfer speeds. Choosing a motherboard with multiple high-speed USB interfaces (such as USB 3.2 Gen2 or higher) can facilitate users connecting high-speed external devices, such as external hard drives, USB flash drives, etc.
– Video interfaces are mainly used to connect monitors, with common types such as HDMI and DisplayPort. For users using high-resolution monitors (such as 4K or 8K monitors), it is necessary to choose a motherboard that supports the corresponding high-resolution video interfaces. For example, HDMI 2.1 interfaces can support 4K 120Hz or 8K 60Hz video output, meeting the connection needs of high-end monitors.
– The quality of audio interfaces is also crucial, especially for users with audio quality requirements. Some motherboards are equipped with high-quality audio chips and independent audio circuits, providing better audio output effects. Ethernet interfaces are used for network connections; for users needing high-speed stable network connections, choosing motherboards that support high-speed Ethernet (such as 2.5Gbps or 10Gbps) interfaces can improve network performance.

Motherboard Quality and Stability

Brand Reputation
– Choosing motherboards from well-known brands can greatly ensure the quality and stability of the motherboard. Brands like ASUS, Gigabyte, MSI, etc., have many years of experience and a good reputation in the motherboard manufacturing field. These brands usually have strict quality control systems, maintaining high standards from raw material selection to production processes.
– Branded motherboards also provide better after-sales support. If issues arise with the motherboard, well-known brands’ after-sales service networks can provide timely repairs, replacements, or technical support. For example, ASUS offers a longer warranty period and nationwide after-sales service centers, making it convenient for users to receive help when motherboard failures occur.
Motherboard Workmanship
– The workmanship of the motherboard can be observed from multiple aspects. First is the quality of the PCB (printed circuit board); high-quality PCB materials usually have better electrical performance and anti-interference capabilities. For example, some high-end motherboards use multi-layer PCB designs, which can better isolate different circuit signals and reduce signal interference.
– The layout of components on the motherboard is also important. A reasonable layout can improve the motherboard’s heat dissipation efficiency, avoiding interference between components. For instance, distributing high-heat components (such as CPU power supply modules and chipsets) in well-ventilated areas of the motherboard and keeping a certain distance from other sensitive components can enhance motherboard stability.
– The quality of solder joints on the motherboard is also a factor in assessing workmanship. Neat and firm solder joints ensure good connections between components and the PCB, reducing the risk of faults caused by poor soldering.

Motherboard Heat Dissipation Design

Heat Sink Design and Material

– The heat sinks on the motherboard are primarily used to dissipate heat from high-heat components such as chipsets and power supply modules. The design of the heat sink includes its shape, size, and how well it fits with the components. Larger heat sinks can provide a greater surface area for heat dissipation, thus improving cooling efficiency. For example, some high-end motherboards have very large heat sinks for CPU power supply modules and use special fin designs to quickly dissipate heat into the air.
– The material of the heat sink is also critical. Common heat sink materials include aluminum and copper; copper has better thermal conductivity than aluminum but is relatively more expensive. Some high-end motherboards use composite heat sinks with copper bases and aluminum fins, taking advantage of copper’s high thermal conductivity while increasing the heat dissipation area with aluminum fins.
Fan Interfaces and Support

– The number and type of fan interfaces on the motherboard determine how many cooling fans users can connect and in what manner. Generally, motherboards will provide multiple 4-pin or 3-pin fan interfaces, with 4-pin fan interfaces allowing for more precise fan speed control.
– Some motherboards also support smart fan control functions, automatically adjusting fan speeds based on the temperatures of different components on the motherboard. For instance, when the CPU temperature rises, the motherboard can automatically increase the speed of the fan connected to the CPU cooler to enhance cooling efficiency.

Motherboard BIOS Features

Friendliness of BIOS Interface
– A user-friendly BIOS interface can make it easier for users to make various settings. For example, some motherboards’ BIOS use graphical interfaces, allowing users to operate by clicking with the mouse instead of using the traditional text command line interface. Graphical BIOS interfaces make operations such as overclocking settings and boot option adjustments more intuitive and easier to understand.
– BIOS language support is also important. For users in non-English speaking countries, having the motherboard BIOS support local languages can greatly facilitate user settings. For example, some motherboard BIOS support multiple languages, including Chinese, making it easier for users to set BIOS parameters.
Richness of BIOS Features
– Rich BIOS features can meet the needs of different users. For overclocking users, the BIOS needs to have detailed CPU and memory overclocking options, such as voltage adjustment, frequency adjustment, etc. For example, when overclocking the CPU, users can use the voltage adjustment option in the BIOS to ensure that the CPU receives stable power supply in overclocked states.
– The BIOS should also have hardware detection and fault diagnosis capabilities. When hardware issues arise, the BIOS can detect the fault location through self-diagnostic programs (POST) and display error codes on the screen, making it easier for users to find and resolve issues. Additionally, the boot options in the BIOS are important, allowing users to set the computer to boot from different storage devices (such as hard drives, USB drives, optical drives, etc.).
END