1. Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW)
Principle: An arc is generated between the flux-coated electrode and the base metal, and the electrode and the base metal are melted by the heat of the arc. The flux coating on the outside of the electrode melts when heated and functions to stabilize the arc, form slag, deoxidize, and refine.
Welding Power Supply: An AC or DC arc welding machine with a drooping characteristic is used. Generally, an AC arc welding machine is commonly used, and a DC arc welding machine is used when special requirements for arc stability are needed.
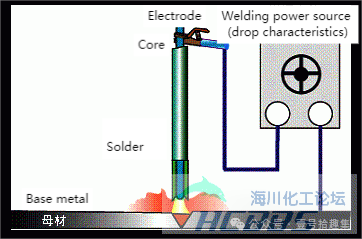
Characteristics: The welding operation is simple, the electrode holder is lightweight, easy to move, and suitable for a wide range of applications.
2. Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW)
Classification and Principle
MAG Welding (Metal Active Gas Welding): Uses CO₂ or a mixture of CO₂ or oxygen in argon (active gas). An arc is generated between the fine-diameter consumable electrode (welding wire) and the base metal, and the surrounding area is sealed with shielding gas to melt the base metal and the welding wire.
MIG Welding (Metal Inert Gas Welding): Uses inert gases such as argon and helium.
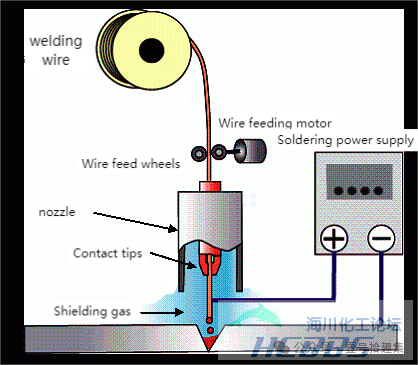
Characteristics
CO₂ Welding: High welding speed, high arc initiation efficiency, deep molten pool, high deposition efficiency, one welding wire can be used for multiple plate thicknesses, good welding quality, small post-welding deformation, and suitable for multiple base metals.
MAG Welding: Besides the advantages of CO₂ welding, it has a beautiful weld appearance, less spatter, easy for double-sided forming welding and all-position welding, and suitable for high-speed welding.
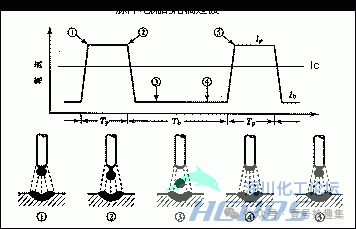
Pulsed MIG (GMAW) Welding: Mostly used for welding aluminum, using pulse control. It can achieve minimal spatter through spray transfer, has a beautiful weld appearance, can obtain a flat weld reinforcement shape. In thin plate welding, it can improve wire feeding performance and reduce wire cost, and has advantages in the automation and robotics of aluminum and alloy welding. The principle is to periodically repeat the welding current in the form of pulse current Ip and base current Ib to achieve droplet transfer.
3. Tungsten Inert Gas Welding (TIG or Gas Tungsten Arc Welding, GTAW)
Principle: In an inert gas environment such as argon, an arc is generated between the tungsten electrode and the base metal to melt and weld the base metal and the filler metal.
Classification and Characteristics
DC TIG Welding: Using a DC arc welding power supply as the welding power source, with the electrode negative and the base metal positive, it is widely used for welding stainless steel, titanium, copper, and copper alloys.
AC TIG Welding: Using an AC arc welding power supply as the welding power source, the polarity of the electrode and the base metal changes alternately. When the electrode is positive (EP polarity), it can remove the oxide layer on the surface of the base metal (cleaning effect), and is used for welding aluminum, magnesium, etc.
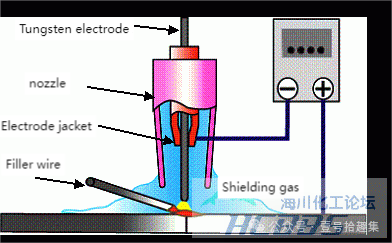
Overall Characteristics: It can weld almost all industrial metals and alloys, with good welding quality, high reliability, good welding formation, no need to remove slag, no spatter, less smoke and dust, and suitable for thin to thick plates.
4. Resistance Welding
Principle: By concentrating a large current and applying pressure, the base metal at the joint of the welded materials is melted and joined by the resistance heat, including resistance spot welding, projection welding, seam welding, and roll welding.
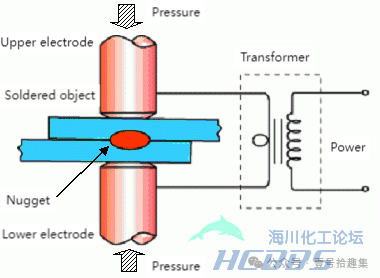
Characteristics: High efficiency and speed for two-piece lap spot welding, suitable for mass production, easy for beginners to operate, small welding deformation, no need for welding wire, flux, and no consumables, low production cost.
5. Plasma Cutting
Principle: An arc discharge is carried out between the base metal (including the nozzle in the cutting torch) and the electrode in the cutting torch, and the compressed gas is heated by the discharge heat energy to generate a high-temperature and high-speed plasma arc to melt and cut the base metal. The small hole in the nozzle makes the plasma flow finer and denser.
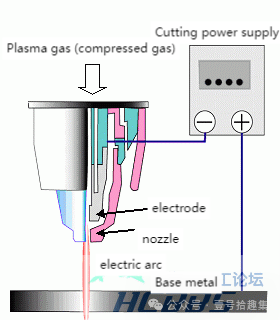
Characteristics: It can cut all metals, with fast cutting speed, small cutting deformation, no need for fixing clamps, unrestricted cutting shape, small heat-affected zone, both contact and non-contact cutting are possible, simple operation, and relatively inexpensive equipment.