
Wireless networks are widely used and have given rise to various short-range wireless technologies such as infrared, Bluetooth, ZigBee, ANT, NFC, UWB, LiFi, and TransferJet. With the increasing attention on the Internet of Things (IoT), the cost-effective and widely applicable Bluetooth technology has gained significant attention. Bluetooth is a wireless personal area network originally created by Ericsson, initially referred to in Chinese as 【蓝芽】 and later correctly named 【蓝牙】.
The term Bluetooth comes from King Harald Bluetooth of Denmark and Norway in the 10th century, where the nickname Blåtand was directly translated into Chinese as 蓝牙.
Bluetooth versions have evolved from the earliest version 0.7 in 1988 to the current version 5.0 released in June 2016.
What are the differences between the various versions? What features does the latest Bluetooth 5.0 offer? How does Bluetooth 5.0 differ from WiFi?
1. Bluetooth Versions Bluetooth is standardized by the Bluetooth Special Interest Group (SIG) and communicates in the 2.4 to 2.485 GHz ISM band, primarily targeting personal area networks (PAN). Bluetooth has had 14 versions since the first version 0.7 in 1988, with the latest being Bluetooth 5.0 announced in June 2016. The specifications have evolved since V2.0 with +EDR and +HS. What do +EDR and +HS mean? EDR (Enhanced Data Rate) relates to data transmission acceleration; without it, the speed is only 1Mbps, but with +EDR, the speed increases to 3Mbps. HS (High Speed) represents high-speed transmission; versions from V3.0 onwards include +HS (High Speed), which uses Wi-Fi’s Generic Alternate MAC/PHY (AMP) and 802.11 protocol adaptation layer (PAL), allowing Bluetooth to achieve speeds close to Wi-Fi, reaching up to 24Mbps, which is eight times faster than +EDR, but requires a distance of 10 meters or less. The “+” symbol indicates that it is optional and not a standard specification.
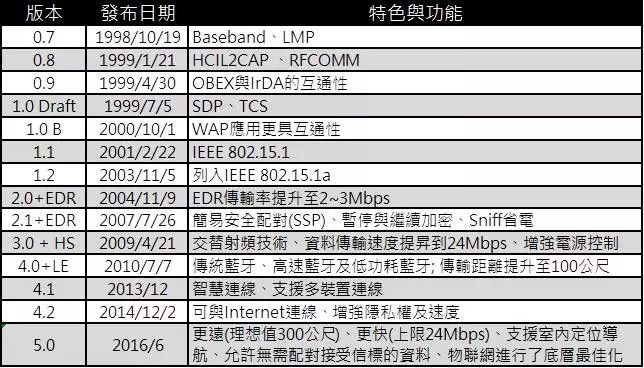
Bluetooth specifications from V4.0 introduced traditional Bluetooth, high-speed Bluetooth, and low-energy Bluetooth. What do they mean? Traditional Bluetooth standards primarily aim for message transmission and device connectivity, with a transmission speed of 1 to 3Mbps and a distance of 10 to 100 meters; High-Speed Bluetooth (Bluetooth HS) focuses on data exchange and transmission, with speeds up to 24Mbps, which is eight times faster than traditional Bluetooth; Low-Energy Bluetooth (BLE, Bluetooth Low Energy, also known as Bluetooth Smart) targets the low energy needs of wearable devices (such as watches, fitness/health products) or industrial automation, announced as a branch standard in 2010, with a distance of up to 30 meters and a transmission speed of 1Mbps. Additionally, Bluetooth 4.0 is divided into Single mode and Dual mode. Single mode can only transmit with BT4.0 and is not backward compatible (cannot communicate with 3.0/2.1/2.0); Dual mode can transmit with BT4.0 and is backward compatible with 3.0/2.1/2.0.
2. Features of Bluetooth 5.0 Bluetooth 5.0 was officially announced in June 2016, offering 2 times the transmission speed compared to Bluetooth 4.2 in low-energy technology (BLE), a 4 times increase in coverage, and an 8 times increase in broadcast data capacity. The main features include: A. Faster Speed: Bluetooth transmission speed is 2Mbps, which is double that of the previous 4.2 LE (Low Energy) version. B. Longer Effective Range: The effective range of Bluetooth 5.0 is 4 times that of the previous 4.2 LE version, theoretically allowing an effective working distance of up to 300 meters between Bluetooth transmitting and receiving devices. C. More Transmission Functions: Bluetooth 5.0 can increase more data transmission functions, achieving an 8 times increase in data transmission capacity. Additionally, hardware manufacturers can create more complex connection systems with Bluetooth 5.0, such as Beacons or location services. D. Indoor Navigation Function: Bluetooth 5.0 enhances navigation capabilities, allowing the technology to be used as an indoor navigation beacon or similar positioning device, achieving indoor positioning with an accuracy of less than 1 meter when combined with Wi-Fi. F. Lower Power Consumption Optimized for IoT Standards: Bluetooth 5.0 has undergone many optimizations for IoT at the lower levels and targets important standards for smart homes, audio, and IoT, striving for lower power consumption and higher performance for smart home applications. G. Better Security and Interference Resistance: The security level of Bluetooth 5.0 meets U.S. federal safety standards, ensuring that all Bluetooth devices can meet and exceed stringent government security standards. Furthermore, Bluetooth 5.0 has stronger resistance to interference, especially against Wi-Fi and LTE signals, mitigating “signal congestion” in confined spaces to some extent. H. Requires New Hardware: Unlike previous Bluetooth versions that only required software updates, Bluetooth 5.0 requires new processor chip hardware, such as the Qualcomm S835 processor, to support Bluetooth 5.0 features. Bluetooth 5.0 still maintains backward compatibility with earlier Bluetooth versions. 3. Differences Between Bluetooth 5.0 and WiFi Bluetooth 5.0’s technical specifications primarily target IoT and smart home standards. Compared to WiFi transmission, the advantages of Bluetooth transmission are low power consumption, high security, high compatibility, longer effective range, and lower cost, but the downside is slower network speed.
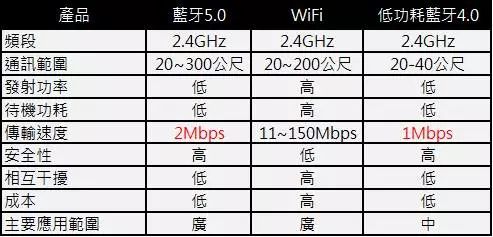
A. Power Saving: The transmission power and standby power consumption of Bluetooth 5.0 are lower than that of WiFi. In standby mode, sharing with one device, Wi-Fi consumes an average of 10% power in one hour, while Bluetooth consumes one-third of Wi-Fi’s power. B. Higher Security: Bluetooth also provides two layers of password protection, while WiFi’s security risks are similar to other networks; once someone gains partial access, they can enter the entire network. In terms of security, Bluetooth 5.0 is superior to WiFi. C. Longer Communication Distance: The effective distance of traditional Bluetooth is about 10 meters, while Bluetooth 5.0 can reach up to 150 meters; WiFi’s effective distance generally ranges from 50 to 100 meters. WiFi has a longer effective distance than traditional Bluetooth but is outperformed by Bluetooth 5.0. D. Lower Cost: Bluetooth 5.0 is smaller and cheaper than WiFi modules. E. Lower Mutual Interference: Bluetooth 5.0 has stronger resistance to interference, especially against Wi-Fi and LTE signals, and can mitigate “signal congestion” in confined spaces. However, both Bluetooth and WiFi operate in the 2.4GHz band, which is quite crowded. To reduce signal interference, many users choose 5GHz Wi-Fi instead of 2.4GHz. F. Slow Transmission Speed: Due to its low-power design, Bluetooth 5.0’s maximum transmission speed is about 1 to 3Mbps, which is significantly slower than Wi-Fi (fourth generation 802.11n) that can operate at 2.4GHz or 5GHz with bandwidths of 20 and 40MHz, achieving speeds of up to 72 and 150Mbps. Therefore, Bluetooth 5.0’s transmission speed is not suitable for video or large file transfers.
Overall, Bluetooth 5.0 is a technical standard set for the Internet of Things, smart appliances, and wearable devices, leading over WiFi in these areas. However, WiFi still holds an irreplaceable position in wireless transmission speed, especially in large data transfers and mobile network sharing. While short-range wireless technologies are emerging rapidly, apart from NFC, which has firmly established itself in mobile payments, Bluetooth and WiFi, with their advantages of widespread adoption in mobile devices, remain the two most promising short-range wireless technologies.
——This article is adapted from IoT Home——
Previous Popular Articles (Click on the title to read directly):
-
Here is the complete IoT industry chain
-
What is the difference between the Internet and the Internet of Things?
-
Do you understand NB-IoT and LoRa??
-
Someone secretly drew a picture for you
-
12 pictures to help you understand the current status and future of IoT
-
In 2017, what else can’t be shared?

WeChat ID: iotmag

Long press the fingerprint recognition QR code to follow