1. SELinux and Firewall Optimization
1. SELinux
SELinux, or Security-Enhanced Linux, is a Linux kernel module and a security subsystem for Linux, primarily developed by the National Security Agency (NSA). Its main purpose is to minimize the resources accessible to service processes in the system (principle of least privilege). Due to this principle, many operations may not execute correctly, so for beginners, it is advisable to disable this subsystem before using SELinux.
SELinux Operating Modes
SELinux has three operating modes:
1.Enforcing: In this mode, actions that violate SELinux rules are blocked and logged.
2.Permissive: In this mode, violations of SELinux rules are only logged. This mode is generally used for debugging.
3.Disabled: SELinux is turned off.
The SELinux operating mode can be set in /etc/selinux/config.
If you want to switch from disabled to enforcing or permissive, a system reboot is required. The same applies in reverse.
Enforcing and permissive modes can be quickly switched using the setenforce 1|0 command.
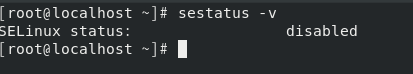
Note that if the system has been running with SELinux disabled for a while, the first reboot after enabling SELinux may be slower. This is because the system must create security contexts for the files on the disk. Now, let’s see how to disable SELinux. First, log in to the system as root, open a terminal, and enter the command gedit /etc/selinux/config. After pressing Enter, a file will open. Change the marked part from enforcing to disabled, save, and then reboot the Linux system.

After rebooting, you can use the sestatus -v command to check if it was successful. If the status is not disabled, you need to repeat the operation.
2. Firewall
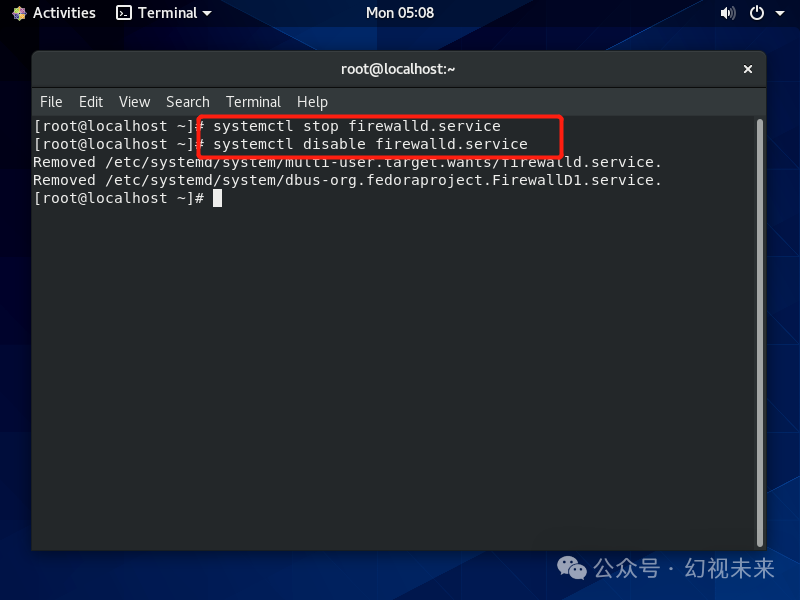
Firewall technology combines various software and hardware devices for security management and filtering, helping to create a relatively isolated protective barrier between internal and external networks to protect user data and information security. In CentOS 8, firewalld is used as the firewall, while the iptables-based firewall is not started by default but can still be used. CentOS 8 supports multiple firewalls: firewalld, iptables, ebtables, etc. Firewalld is the default firewall, managed through the firewall-cmd tool, although the underlying commands still call iptables. While the firewall is security software, some of its default settings can confuse beginners, so we should first disable firewalld. Stop the firewall using systemctl stop firewalld.service and disable it from starting at boot with systemctl disable firewalld.service. Next, let’s see how to set up Chinese input.
2. Chinese Language Settings Optimization
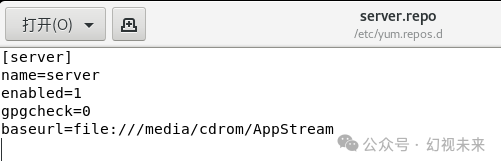
We selected Chinese during system installation, but there is no Chinese input method in the system. To input Chinese, we need to add a Chinese input method. After logging in as the root user, we use gedit /etc/yum.repos.d/server.repo, enter the following content, save, and exit, ensuring that the virtual machine’s CD drive is loaded with the CentOS 8 ISO and is connected.
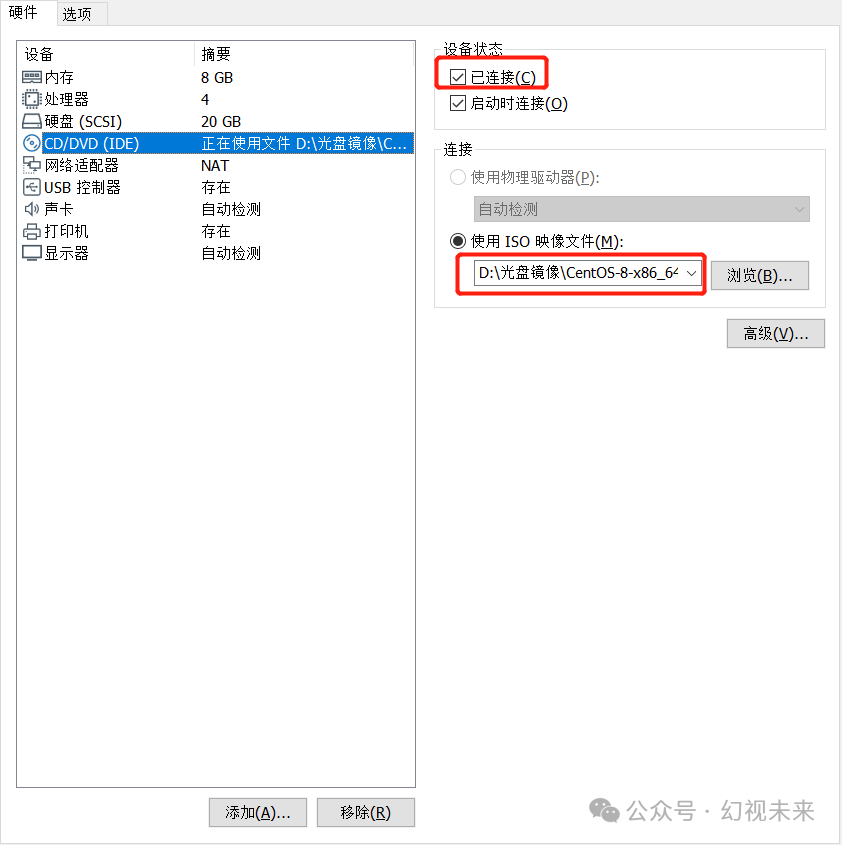
After the setup is complete, execute the mkdir command to create a directory, then mount the CD.
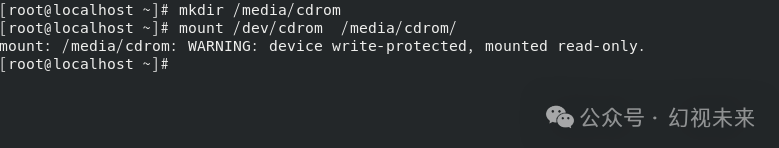
After the CD is mounted, execute yum install ibus* -y, wait for the software package to install, then reboot the system and log in again.

After installation, click the button in the upper right corner and then click Settings.
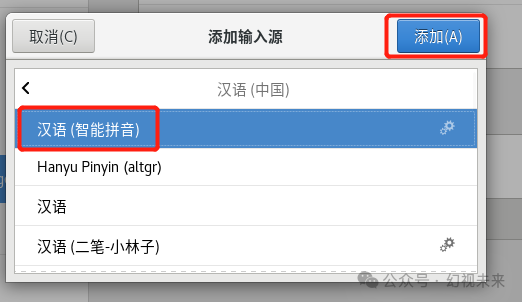
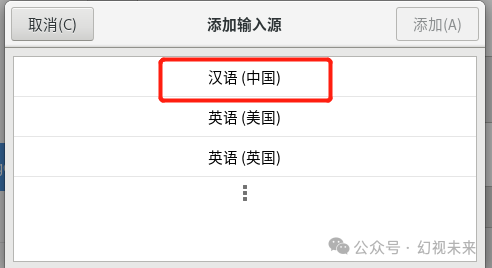
In the new window, find Language, select Add, choose Chinese, then select a suitable Chinese input method and click Add to start using the Chinese input method.

After setting up the input method, let’s look at the time-related settings.
3. Network Time Server Optimization
If the system time is inaccurate, manually setting it can be cumbersome. Let’s see how to optimize it.
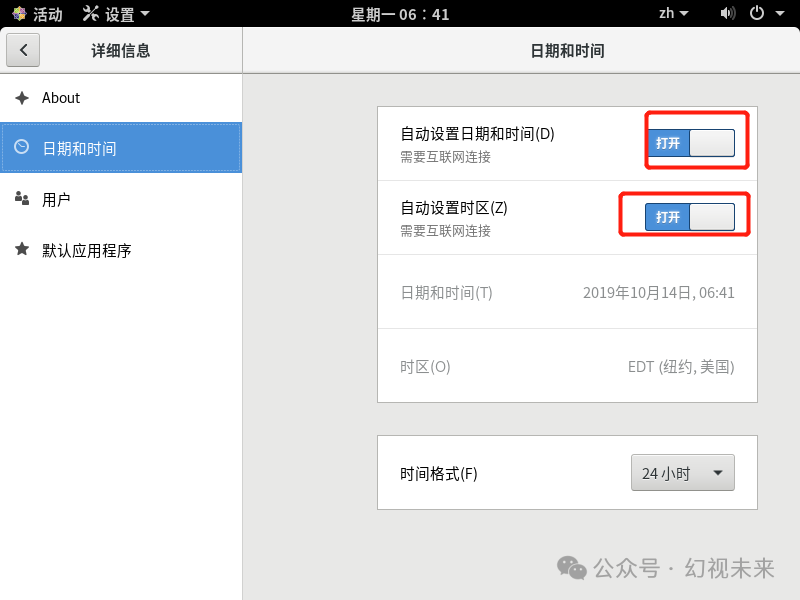
Again, find Settings, locate Detailed Information, expand it, and you will see the date and time settings. Enable both automatic settings options. If your virtual machine can connect to the internet, you will see the time corrected shortly.
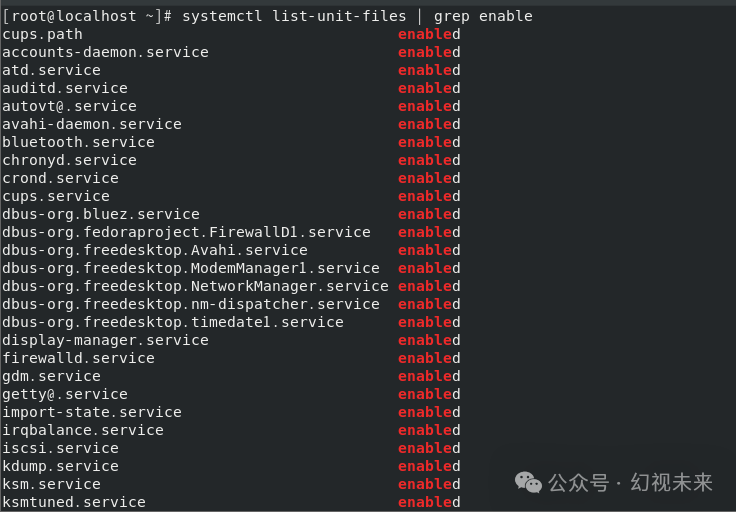
4. Autostart Service Optimization
The method for optimizing autostart services is similar to what we previously mentioned for stopping firewalld. First, we need to confirm which services are set to start at boot, and then use the previously used commands systemctl stop servername and systemctl disable servername to stop the corresponding services, such as Bluetooth and firewall services. However, please note that you should not stop services you do not understand, as this may lead to system functionality failure or even crashes.