Tip: This article shares the basic commands of the Linux system, providing a detailed explanation of the top command, including its functions, format, common options, interactive commands, and examples of the top command.
1. Overview of the top Command
1. Function
❝
The top command: displays active processes in real-time, showing the resource usage of each process and enabling real-time monitoring of the system’s CPU and memory status, similar to the Windows Task Manager.
2. Command Format
❝
top 【options】[ parameters ]
3. Common Options
| Option | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| -b | Display output in batch mode | top -b |
| -c | Show the full command path of processes | top -c |
| -d | Specify the refresh interval for output (in seconds) | top -d 5 |
| -i | Do not display idle processes | top -i |
| -n | Specify the number of updates for output (exit after completion) | top -n 5 |
| -s | Run the command in secure mode | top -s |
| -u | Specify user filtering for output | top -u root |
4. Interactive Commands
❝
Interactive commands: These are commands used during the execution of the top command.
| Interactive Command | Description |
|---|---|
| h or ? | Display help information, output descriptions of interactive commands |
| c | Show the full command path of processes |
| f | Add or remove items from the current display list |
| i | Do not display idle processes |
| k | Terminate a process by entering its PID |
| l | Toggle display of average load and startup time information |
| m | Toggle display of memory information |
| o | Change the order of displayed items in the output (input lowercase to move right; uppercase to move left; press enter to confirm) |
| q | Exit the top command display |
| r | Change the priority of a process by entering its PID (input positive value to lower, negative to raise; default is 10) |
| s | Specify the refresh interval for output (in seconds) |
| t | Toggle display of process and CPU status information |
| M | Sort output by memory usage |
| P | Sort output by CPU usage |
| S | Switch to cumulative mode |
| T | Sort output by time or cumulative time |
| W | Write current settings to ~/.toprc file |
2. Examples of the top Command
1. Examples of Common Options
1.1 top -b
top -b ## Display output in batch mode
1.2 top -c
top -c ## Show the full command path of processes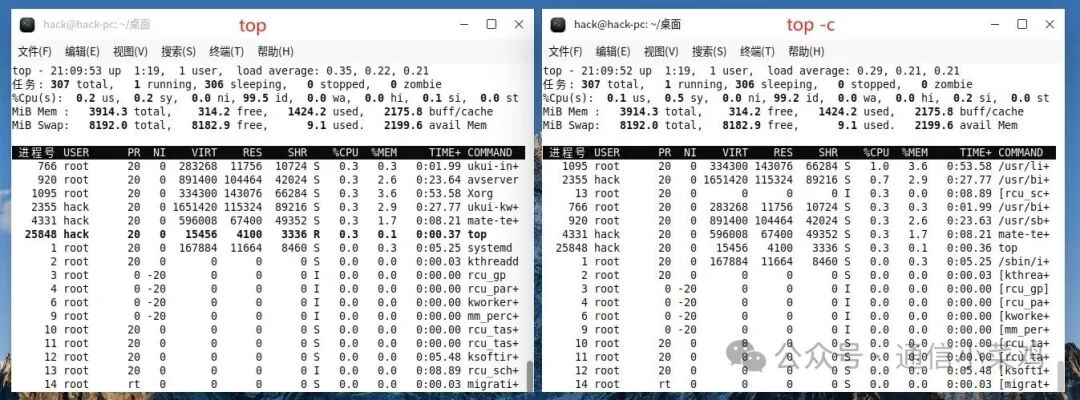
1.3 top -d 5
top -d 5 ## Specify refresh output every 5 seconds (default is 3 seconds)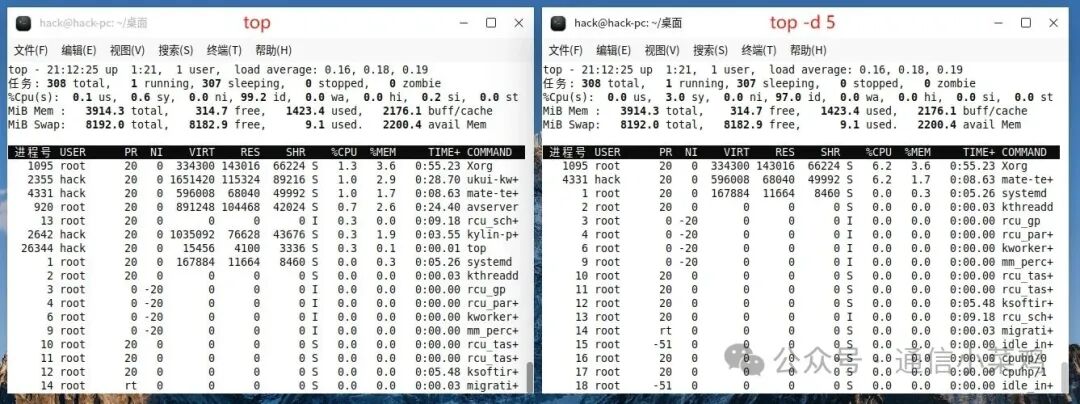
1.4 top -i
top -i ## Do not display idle processes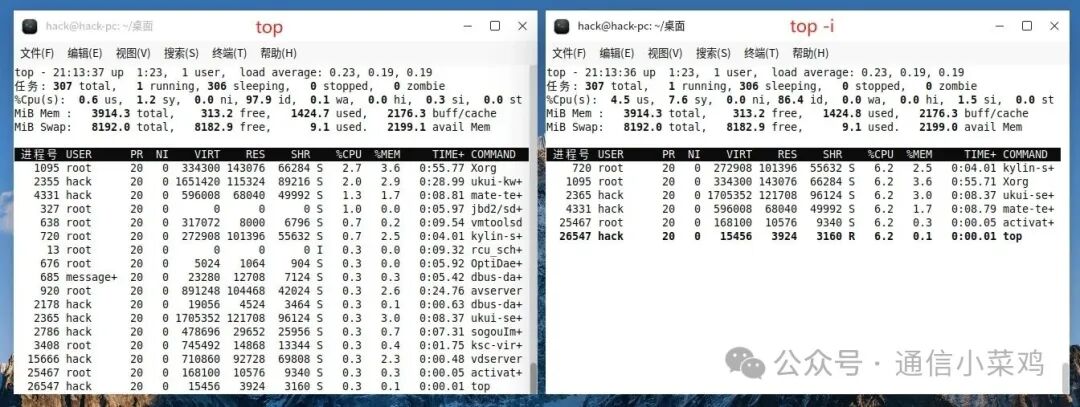
1.5 top -n 5
top -n 5 ## Specify to exit after updating output 5 times (default does not exit)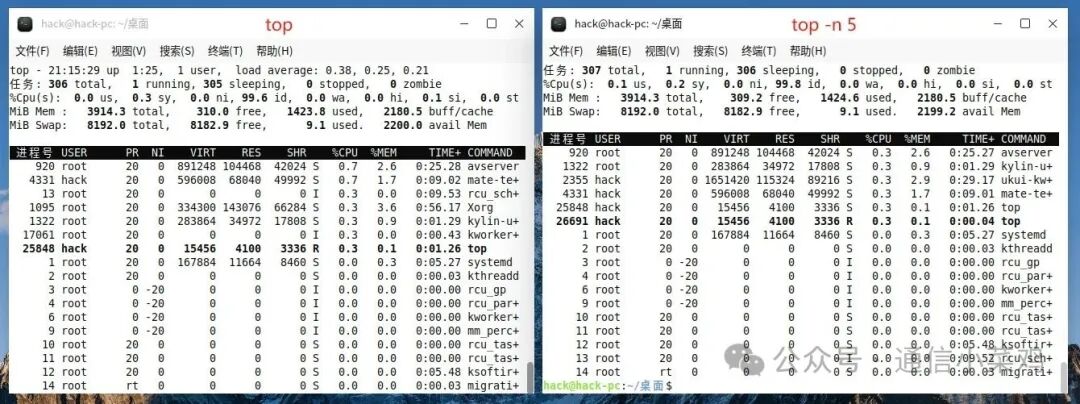
1.6 top -u root
top -u root ## Specify to filter output as the root user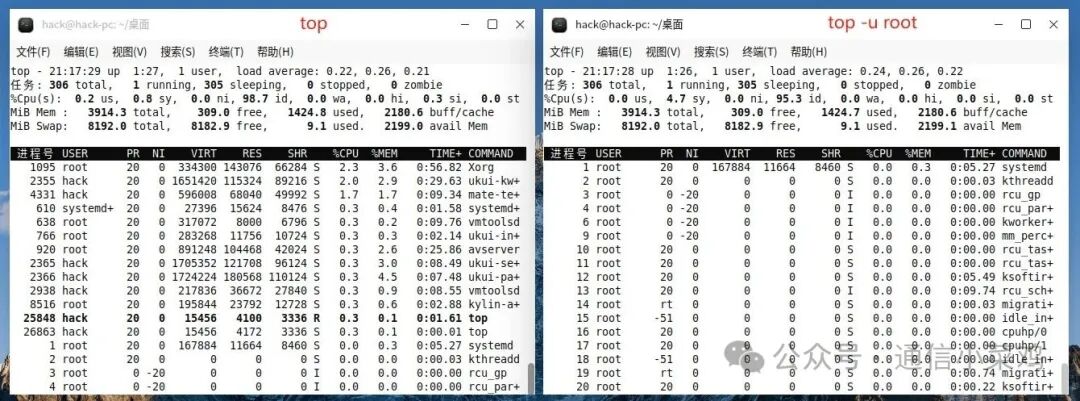
2. Examples of Interactive Commands
2.1 h
❝
Display help information

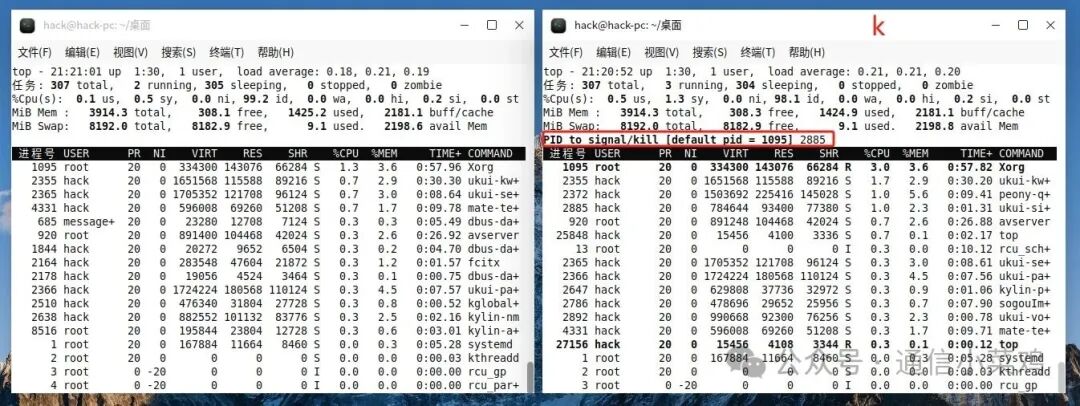
2.2 k
❝
Terminate a process by entering its PID
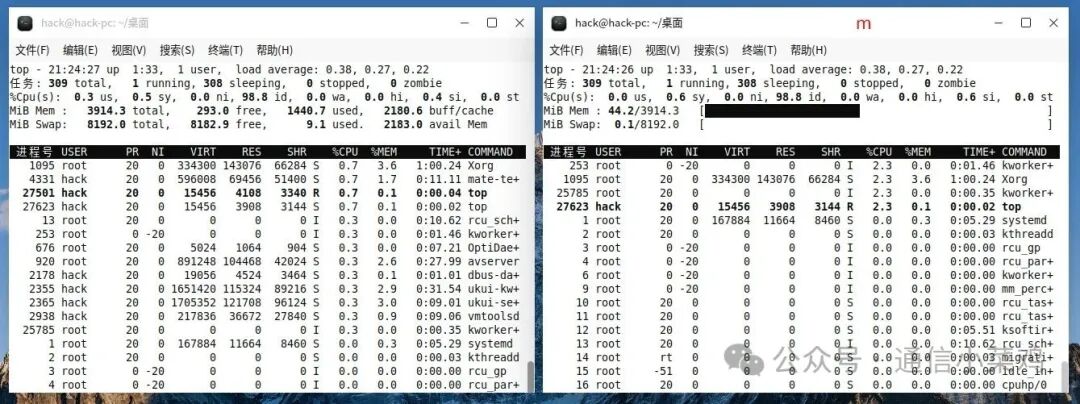
2.3 m
❝
Toggle display of memory information
2.4 t
❝
Toggle display of process and CPU status information
2.5 M
❝
Sort output by memory usage

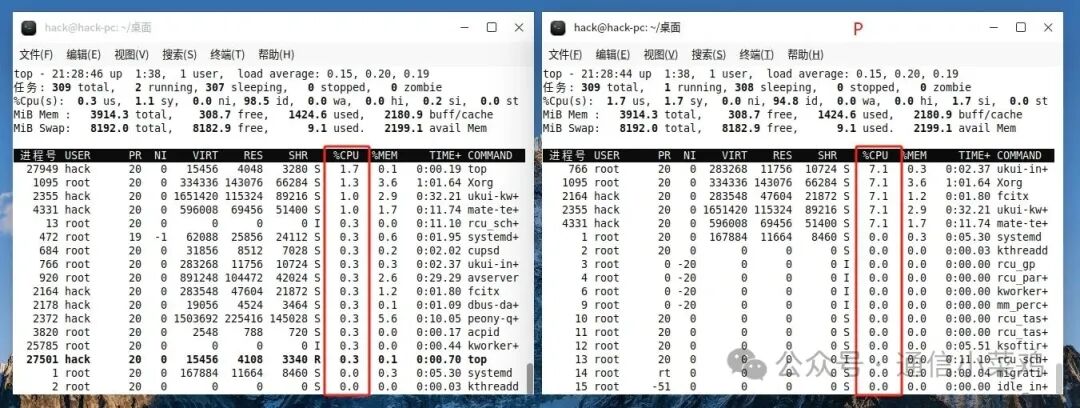
2.6 P
❝
Sort output by CPU usage