
“China Manufacturing 2025” and “Internet Plus” are inseparable. To advance Chinese manufacturing towards intelligence, it must rely on the Internet, cloud computing, and big data. This is how over 200 industrial products produced in China, which rank first in the world, can leap to a new level,” said Premier Li during a meeting with entrepreneurs at the 2016 Summer Davos Forum.

Industrial Internet
By interconnecting industrial resources, enabling data communication, and ensuring system interoperability, we can achieve flexible configuration of manufacturing materials, on-demand execution of manufacturing processes, reasonable optimization of manufacturing techniques, and rapid adaptation to manufacturing environments, thus achieving efficient resource utilization and building a new service-driven industrial ecosystem.
Based on the interconnection of machines, raw materials, control systems, information systems, products, and people, we can realize intelligent control, operational optimization, and transformation of production organization methods through comprehensive and in-depth perception of industrial data, real-time transmission and exchange, rapid computing and processing, and advanced modeling and analysis.
The earliest concept of the Industrial Internet originated in the United States, first proposed by GE. We know that in traditional manufacturing, most production equipment, product manufacturing, maintenance, and traceability are operated manually, heavily relying on the experience and judgment of veteran workers, with a long inheritance cycle.
In the era of the Industrial Internet, the method of interconnecting all things allows production equipment, products, and services to be analyzed through cloud computing and big data, ultimately achieving optimal solutions, significantly increasing the efficiency of the manufacturing industry, marking it as the fourth industrial revolution. Therefore, the Industrial Internet has much in common with Industry 4.0. However, the concept of Industry 4.0 in Germany lacks the integration of cloud computing and big data, focusing more on the intelligence of the manufacturing industry.
The Industrial Internet is a new strategy, new technology layout, and a new vision for the future, arising from decades of strong technological accumulation in industrialized countries combined with the Internet. If we interpret these visions and strategies solely from the perspective of the Internet, it is far from sufficient. In fact, the Industrial Internet has strong technological support.

Reference Architecture for Industrial Internet Platforms
So where is the Industrial Internet currently? Unfortunately, while the Industrial Internet represents the highest stage of industry, it has only reached the stage of the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT). This means there is still a long way to go. Perception is the precursor technology of the Internet of Things, and ensuring the stable operation of the IoT relies on numerous sensing technologies, with sensors being one of the most critical technologies.
Sensors are the foundation and core of the Industrial Internet, and are key components of automated intelligent devices. The vigorous development of the Industrial Internet will bring enormous opportunities to sensor companies.
Industrial Internet Brings Huge Market Opportunities for Sensor Companies
Referring to the stages of Industry 2.0, 3.0, 4.0, and AI 1.0, 2.0, the Industrial Internet can be divided into three stages: Industrial Internet 1.0, which establishes a network connection system based on IP technology to connect the factory IT network with the OT network, and connect external enterprises with upstream and downstream, smart products, and users; Industrial Internet 2.0, which uploads and aggregates detailed data on products, equipment, raw materials, and industrial chains through industrial data collection technology, laying the foundation for industrial Internet platforms and industrial apps; Industrial Internet 3.0, which achieves seamless intelligent connection between the physical world and the digital world through artificial intelligence and edge computing technologies.
Most industrial enterprises in our country are still in the process of transitioning to Industrial Internet 1.0, while a few leading enterprises are exploring and practicing Industrial Internet 2.0, and some enterprises have begun to layout research on Industrial Internet 3.0. The different stages of Industrial Internet development impose varying requirements on sensors, and sensor and sensing system companies also need to accurately position themselves, not only to see the blue ocean brought by the development of the Industrial Internet for the sensor industry, but also to explore effective markets to achieve final output value and profit.
On one hand, the Industrial Internet brings opportunities to sensor companies; on the other hand, it also imposes new requirements on sensors, mainly reflected in higher demands for sensitivity, stability, and robustness. Meanwhile, the popularization of the Industrial Internet makes sensors ubiquitous, and the extensive use of sensors requires lightweight, low-power, and low-cost designs, as well as increased demands for networking, integration, and intelligence.
In addition, the applications of sensors in the Industrial Internet cover a broader scope, leading to greater demand for the quantity and industrialization of sensors. Currently, the domestic sensor industry still faces issues such as small enterprise scale and insufficient innovation capabilities, and there is still a significant gap to fully meet the demands of the Industrial Internet. The recent outbreak of trade frictions between China and the United States and the embargo on core chips have also sounded the alarm for our sensor and application industries. Sensors, like integrated circuit chips, are key components with high technological content. If domestic companies do not increase their efforts in independent innovation, they will face similar situations in the future.
Wireless Sensor Networks
With the development and integration of sensor, computer, wireless communication, and micro-electromechanical technologies, Wireless Sensor Networks (WSN) have emerged. Wireless sensor network technology uses the same standard as today’s mainstream wireless network technology—802.15.14. It is a new type of information acquisition and processing technology that will significantly impact human society’s production and lifestyle, following the Internet. Wireless sensor networks integrate embedded computing technology, sensor technology, distributed information processing technology, and communication technology, enabling collaborative real-time monitoring, perception, and information collection of various monitored objects within the network distribution area.
Wireless Sensor Network Systems (WSNS) typically consist of sensor nodes, aggregation nodes, and management nodes.
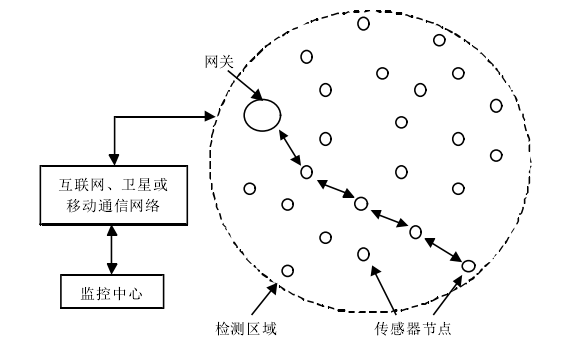
Wireless Sensor Network Communication Architecture Diagram
The emergence of wireless sensor networks has attracted widespread attention globally and is regarded as one of the most influential technologies of the 21st century; one of the top 10 new technologies changing the world; and one of the four high-tech industries of the future globally. Wireless sensor network technology will soon enter the fields of the Industrial Internet and industrial measurement and control. With the future integration of wireless transmission capabilities into most industrial instruments and automation products, the transition from wired to wireless will be completed.
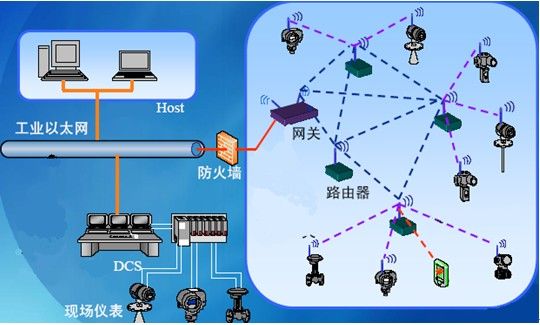
Typical Industrial Wireless Sensor Network
The industrial wireless sensor network schematic diagram shows that the core components are low-power sensor nodes (which can be powered long-term by batteries, solar cells, or generated from wind energy and mechanical vibrations), network routers (with mesh network routing capabilities), and wireless gateways (which transmit information to the industrial Ethernet and control center or connect through the Internet).
In the field of industrial automation, established leaders such as GE and Honeywell have launched various industrial wireless sensor network products and systems, and many research institutions and large companies in China are also conducting related research.
Applications of Sensor Networks in the Industrial Internet
The Industrial Internet is now generally understood as the automation of industrial environments using sensor networks and machine-to-machine (M2M) communication.
Market analysis company Nano Markets published a report titled “Sensor Market for the Industrial Internet” in November 2014, categorizing factory automation, building automation, smart grids, and public transportation as applications of the Industrial Internet, predicting that the consumption of sensors in this field will exceed $20 billion annually by 2019. In the future, technicians and maintenance personnel will increasingly use powerful tablets to collect and process information from sensors integrated into industrial machinery.
1. Industrial Environment Monitoring The monitoring scope of industrial environments has involved all aspects of the ecological environment, including routine environmental monitoring such as air, water, electromagnetic radiation, and radioactive monitoring; there are also special area environmental monitoring, such as deserts, high mountains, and areas with radiation sources. These environments impose high requirements on the flexibility, reliability, and safety of sensor products. Wireless sensor network products can break through traditional monitoring methods, reducing costs for industrial environmental monitoring while meeting flexibility, reliability, and safety requirements, significantly simplifying traditional monitoring processes and facilitating the acquisition of random research data. As public attention to industrial environments increases, the demand for environmental data collection will also expand, leading to a gradual increase in demand for wireless sensor network products.
2. Smart Grids Currently, global issues such as energy, environment, and climate change are becoming increasingly prominent, prompting countries worldwide to prioritize the development and utilization of clean energy. Smart grids have now become one of the important applications of IoT technology and an inevitable trend in grid development. Smart grids ensure the safety, reliability, and economy of power supply through advanced sensing measurement technology, communication technology, advanced control methods, and decision support system technologies.
To ensure the continuous operation of smart grids, equipment safety assurance has become a key issue. Since grid equipment operates under high voltage and high current for extended periods and faces threats from extreme natural environments such as thunderstorms, implementing intelligent monitoring of the equipment is particularly important. Wireless sensor network products can monitor grid equipment remotely, understand the operational status of the equipment, and transmit data to the control center for unified management, while real-time monitoring also improves maintenance efficiency. With the advancement of smart grid plans, the demand for intelligent monitoring of grid equipment has created a huge market for wireless sensor network products.
3. Digital Oilfields The rapid increase in the number of oil wells due to economic development and social demand has accelerated the overall expansion of oilfield development. Therefore, the intelligentization of oilfield production, management, and operation has become a development trend, leading to the emergence of digital oilfields. In the digitalization process of oilfields, wireless sensor network products can achieve real-time monitoring of oil well environments and wellhead equipment, transmitting important information such as equipment status and environmental parameters to the control center, issuing alarms and arranging scheduling when necessary. As wireless sensor network products are promoted and demonstrated in oilfields, the number of digital oilfields will gradually increase, and the market demand for wireless sensor network products will show rapid growth.
4. Smart Industry China’s manufacturing industry is facing a new round of industrial revolution opportunities, with a pressing demand for manufacturing enterprises to upgrade using IoT technology. Information technology companies are also actively leveraging IoT technology to penetrate the industrial sector. The proposal of Industry 4.0, centered on intelligence, aligns with the trend of integrating IoT technology into the industrial field, indicating immense market development potential. One of the cores of smart manufacturing is the intelligent monitoring of industrial processes.
Applying wireless sensor network technology to intelligent monitoring will help optimize industrial production processes, while also enhancing the capabilities and levels of process detection, real-time parameter collection, production equipment monitoring, and material consumption monitoring, thereby continuously improving the levels of intelligent monitoring, control, diagnosis, decision-making, and maintenance in production processes. With the rapid development of IoT and the further advancement of Industry 4.0, industrial process control centered on intelligence will develop rapidly, thereby driving the market demand for industrial process monitoring system solutions based on wireless sensor network technology.
The rapid growth of industrial wireless sensor network products is primarily due to the maturation of the entire IoT ecosystem, with the industrial IoT slowly developing from government-led initiatives. The number of industrial sensing terminals in China has been rapidly increasing, with around 700 million industrial sensing terminals in 2014. It is expected that with the implementation of China Manufacturing 2025, the number of industrial sensing terminals in China will exceed 2 billion by 2020.
At the same time, developments in wireless communication, power consumption, extreme miniaturization (one of the driving forces is MEMS sensors), and embedded computing have also contributed to the rise of wireless sensor networks designed for harsh industrial environments. Industrial wireless sensor network products will continue to grow rapidly until 2019, driven by the transformation of production lines and IT equipment upgrades prompted by the proposal of “China Manufacturing 2025,” and will maintain an upward trend.
In the future, sensors in the field of the Industrial Internet will not only be hardware but also creators of data and services.

