Ansible is an agentless automation tool based on SSH and HTTPS, which allows for batch server configuration management and application deployment through simple YAML scripts. It is widely used in enterprise IT environments for batch operations and DevOps process optimization. This article provides a detailed introduction to the installation, configuration, and compatibility handling of Ansible using CentOS 7 as an example.

1. Environment Preparation
1. Create a regular user (for example, ralap)
useradd ralap
passwd ralap
usermod -aG wheel ralap2. Configure SSH key authentication
ssh-keygen -t ed25519
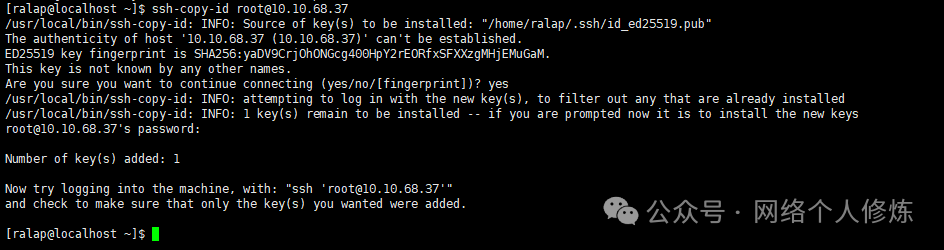
ssh-copy-id root@target_server_IP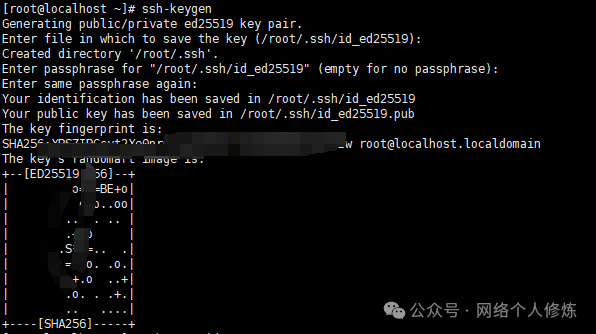
2. Installing Ansible (choose installation method based on needs)
Method 1: Install via pip (recommended, supports new versions)
Applicable scenario: Target server Python version ≥ 3.7, or if you need to use the latest features of Ansible.
1. Install the latest version of Ansible (the control machine must have Python 3 installed in advance):
python3 -m pip install --user ansible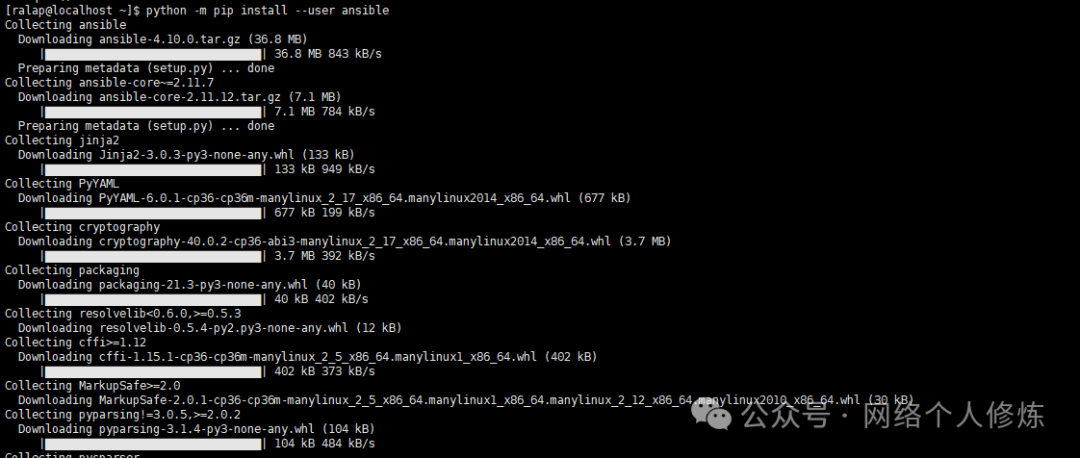
2. Add execution path (temporary effect):
export PATH="$HOME/.local/bin:$PATH"3. Permanently add execution path (write to environment variables):
echo 'export PATH="$HOME/.local/bin:$PATH"' >> ~/.bashrc
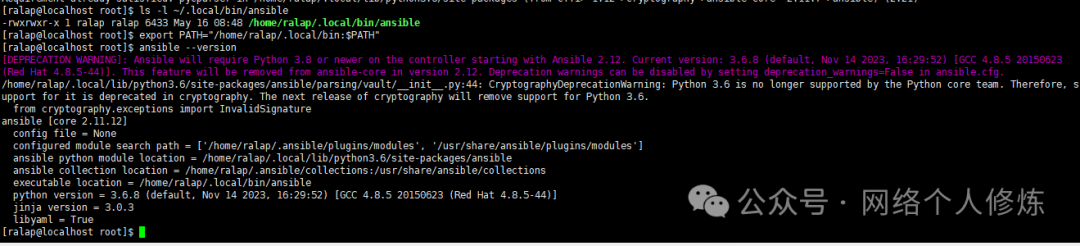
source ~/.bashrc # Take effect immediately4. Verify installation version:
ansible --version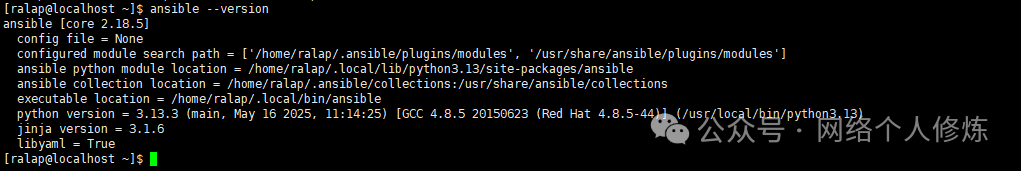
Method 2: Install via yum (old compatibility solution, no longer maintained)
Note: The version of Ansible installed this way is 2.9.27 (released in 2020), which is no longer officially maintained and has security vulnerabilities. It is only recommended for transitional scenarios on old systems that cannot be upgraded.
Install the EPEL repository (provides old versions of Ansible)
yum install -y epel-release Install the old version of Ansible (compatible with Python 2.7.5)
yum install -y ansibleVerify installation version:
ansible --version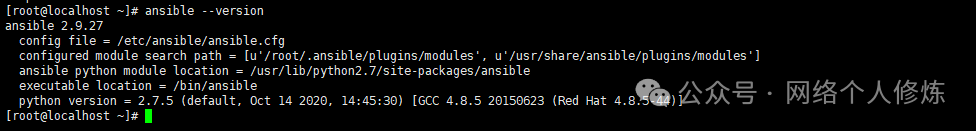
3. Connection Testing
1. Create a host inventory file host.ini, with the following example content:
[servers]
10.10.69.92
[all:vars]
ansible_user=root
ansible_ssh_private_key_file=~/.ssh/id_ed25519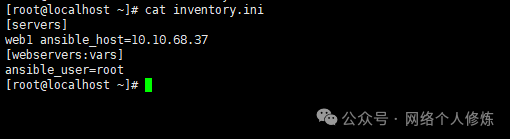
2. Test the connection:
ansible all -i host.ini -m ping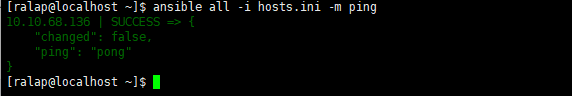
4. Compatibility Configuration and Host Inventory Example
Scenario 1: Target server Python version ≥ 3.7
If the target server’s Python path is non-default, specify the Python 3 interpreter path in host.ini:
[servers]
Target_server_IP ansible_python_interpreter=/usr/bin/python3
[all:vars]
ansible_user=root
ansible_ssh_private_key_file=~/.ssh/id_ed25519Scenario 2: Target server Python version is 2.7.5
Force the use of the Python 2 interpreter:
[servers]
Target_server_IP ansible_python_interpreter=/usr/bin/python
[all:vars]
ansible_user=root
ansible_ssh_private_key_file=~/.ssh/id_ed255195. Version and Compatibility Notes
| Installation Method | Ansible Version | Control Machine Python | Target Machine Python | Maintenance Status | Applicable Scenarios |
| pip | 2.18.x+ | 3.8+ | 3.7+ | Active Maintenance | New systems, production environments |
| yum | 2.9.27 | 2.7+/3.5+ | 2.6+ | Stopped Maintenance | Old systems like CentOS 7 |
Reference Links
[1]https://docs.ansible.com/ansible/latest/installation_guide/intro_installation.html#installation-guide
[2]https://documentation.wazuh.com/current/deployment-options/deploying-with-ansible/guide/install-ansible.html#remote-connection)
[3]https://docs.ansible.com/ansible/latest/network/getting_started/index.html)
-End-
If you find my sharing useful
[Like +Share+Follow
+Share+Follow ]
]