The traditional embedded course teaching model faces issues such as low student interest and initiative, rapid knowledge updates and iterations, a lack of practical cases, and a single evaluation format, which cannot meet the requirements for personalized learning. To address these issues, this case study utilizes generative AIs like ChatGPT, Douyin, Wenxin Yiyan, and Xinghuo during the teaching process, promoting a shift from “teacher-student interaction” to a deep interaction involving “teacher/student/machine”; updating teaching resources and content through AI, constructing a knowledge graph for embedded courses, and transforming the teaching content from static subject knowledge to dynamic comprehensive tasks; shifting the teaching mode from teacher-centered to student-centered, combining project-based learning and human-machine collaborative learning, providing more intelligent and personalized teaching services and learning support, and offering students a better learning experience and practice; transitioning the educational philosophy from knowledge-centered to a stronger emphasis on “capability first, values first”; changing evaluation methods from “result evaluation” to “diversified evaluation”; and enhancing students’ innovation capabilities through AI-enabled course competitions.
Keywords: AI empowerment; teaching reform; course-competition integration; innovation capability
Authors: Zhao Zhihuan, Jiang Mingming, Liao Xijie Shandong Agricultural Engineering College, School of Mechanical and Electronic Engineering
The report of the 20th National Congress of the Communist Party of China first proposed the need to “promote digital education and build a learning society and learning nation for all.” In 2023, General Secretary Xi Jinping emphasized during the fifth collective study session of the Political Bureau of the CPC Central Committee that “digital education is an important breakthrough for our country to open up new tracks for educational development and create new advantages in educational development.” The 2024 World Digital Education Conference proposed implementing AI empowerment actions to promote the deep integration of intelligent technology with education and teaching, using intelligence to assist teaching and learning, and developing intelligent learning companions and intelligent teaching assistants. With the rapid development and increasing popularity of artificial intelligence technology, the deep integration of AI and education is imperative.
Generative artificial intelligence represented by ChatGPT has a significant impact on education. ChatGPT empowers teaching, shifting the teaching model from a “teacher-student” binary structure to a “teacher-machine-student” ternary structure, facilitating the transition of teaching content from manual production to intelligent production, and catalyzing the evaluation model of “knowledge + competence”; ChatGPT empowers learning, promoting the ubiquity of learning spaces, meeting the personalized needs of the entire learning process, and forming a human-machine collaborative learning model; ChatGPT empowers education, shifting the educational philosophy towards cultivating higher-order abilities and comprehensive quality, and innovating the educational model of interdisciplinary integration.
The traditional embedded teaching model has several issues, such as low student interest and initiative, rapid knowledge updates and iterations, few practical cases, and a single evaluation format, which cannot meet the personalized learning requirements. To solve these problems, this project utilizes generative AI technologies like ChatGPT, Douyin, Wenxin Yiyan, and Xinghuo during the teaching process, promoting a shift from “teacher-student interaction” to a deep interaction involving “teacher/student/machine”; updating teaching resources and content through AI, transforming the teaching content from static subject knowledge to dynamic comprehensive tasks; shifting the teaching mode from teacher-centered to student-centered, combining project-based learning and human-machine collaborative learning, providing more intelligent and personalized teaching services and learning support to offer students better learning experiences and practices; transitioning the educational philosophy from knowledge-centered to a stronger emphasis on “capability first, values first”; and changing evaluation methods from “result evaluation” to “diversified evaluation”.
1. Constructing a “Dual Teacher Classroom” Project-Based Teaching Model Based on Artificial Intelligence
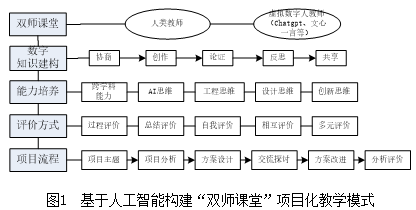
2. Teacher-Student Collaboration, Updating Teaching Resources and Content Based on AI, and Constructing an Embedded Knowledge Graph
Leveraging generative AIs like ChatGPT, Douyin, Wenxin Yiyan, and Xinghuo, combined with embedded course resources, teachers and students collaboratively update teaching resources (digitally constructed basic materials, digital syllabi, digital lesson plans, student-participated digital online courses, knowledge graphs, virtual teacher materials, digital ideological and political materials, etc.). Utilizing digital platforms, teaching content and resources are updated in real-time to ensure synchronization with the latest technological advancements. AI course teaching emphasizes active student participation in knowledge construction, actively exploring and posing questions, and through cooperation and communication with others, continuously constructing, reconstructing, and optimizing their knowledge systems, thus helping students better understand the essence and core of knowledge and cultivate their higher-order thinking abilities. In AI course teaching, learning tasks need to be contextualized, allowing students to create project works through autonomous inquiry learning and group collaborative learning, ultimately completing innovative works. Therefore, knowledge construction theory can help students gain a deeper understanding of AI knowledge and promote the application of knowledge and the formation of innovative thinking in practice.
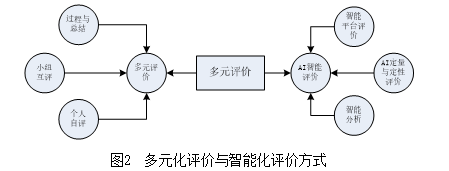
3. Constructing Diversified Evaluation and Intelligent Evaluation Methods
In design-thinking-based AI course teaching, diversified and intelligent evaluation is emphasized throughout the teaching activities. Adopting diversified evaluation allows for multidimensional consideration, focusing on the cultivation of various student abilities. Students’ innovative designs are not formed in one go but require continuous improvement through collaboration and communication with peers. Diversified evaluation increases interaction and communication between teachers and students, as well as among students, helping teachers and students view the project design process from multiple perspectives, thereby assisting students in forming outcomes. Intelligent evaluation can achieve high-efficiency collaborative evaluation across multiple scenarios. The diversified learning effect evaluation methods are shown in Figure 2.
4. AI Empowered Curriculum Ideology Reform
To address the uncertainties brought by digitalization and the increasingly severe ethical and security challenges, it is essential to adhere to safety bottom lines and ensure the secure operation of digital educational technologies. Key points for curriculum ideology include data network security, personal privacy protection, intellectual property protection, anti-algorithm discrimination, and embedded ideological and political case studies, strengthening digital ethics and security education training for teachers and students, and enhancing the legal, safety, and risk prevention awareness of digital education participants, thereby constructing a safer, fairer, and more responsible global digital education environment.
5. Promoting the Digitalization Process of Education
In the context of educational digitalization, the “Embedded” course will fully utilize information technology to promote the digitalization process of education and teaching. By constructing online courses, knowledge graphs, and other teaching resources, it will provide students with convenient learning experiences. At the same time, the course will utilize AI and other technological means to achieve personalized teaching, intelligent recommendations, and other functions to enhance teaching effectiveness and learning efficiency.
6. AI Empowered Course-Competition Integration to Enhance Student Innovation Levels
Focusing on the concept of “promoting teaching through competition and integrating courses with competitions”, relying on AI to allow teaching to extend beyond the classroom, both in-class and out-of-class teachers can obtain real-time student learning situations, and through intelligent platforms, conduct digital evaluations, establishing personalized evaluation models for each student to assist them in conducting personalized project design and innovation. Students rely on innovative projects to participate in various subject competitions, continuously enhancing their innovation levels.
1. Establishing a Quality-Capability-Knowledge System Structure
The AI-empowered embedded course quality-capability-knowledge system structure refers to enhancing and optimizing individuals’ or organizations’ systems in quality, capability, and knowledge through artificial intelligence technology, as follows:
(1) Quality: Enhancing students’ digital literacy, AI literacy, professional ethics, safety awareness, environmental awareness, and social responsibility; cultivating students’ innovative thinking, critical thinking, and lifelong learning abilities; training innovative talents with good professional ethics, teamwork spirit, innovative consciousness, and global vision.
(2) Capability: Training students’ AI application abilities; improving students’ ability to use AI tools to solve practical problems in embedded systems; enhancing students’ teamwork abilities to complete design project implementations.
(3) Knowledge: Rapidly and conveniently acquiring a large amount of embedded knowledge using AI, learning knowledge integration and updating.
2. Teaching Chapter Design – Constructing a “Dual Teacher Classroom” Project-Based Teaching
The project-based teaching process of constructing a “Dual Teacher Classroom” based on artificial intelligence is shown in Figure 3, where the teaching process is divided into three steps: pre-class, in-class, and post-class. Human teachers take the lead role, guiding project planning; students are the main body, undertaking project exploration and research roles; and virtual digital teachers are the main lecturers, responsible for course teaching and consulting services.
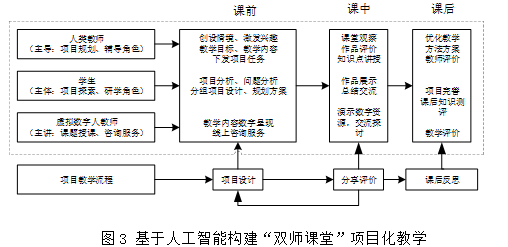
Virtual digital teachers (ChatGPT, Doubao, Wenxin Yiyan, etc.): The virtual digital person technology is a fusion of various technologies such as speech recognition, speech synthesis, natural language understanding, and animation generation. Creating a virtual digital person involves importing the text of the teaching content into a production platform, generating teaching videos driven by AI. Before class, students watch the teaching videos of the virtual digital teacher for preview; during class, the virtual digital teacher teaches the content, and students can replay the virtual digital teacher’s explanation video until they learn all the content; after class, if they need to reinforce what they have learned, students can review at any time. At the same time, students can communicate with ChatGPT and others to complete information collection and organization.
Human teachers: Responsible for project planning and classroom activity guidance, human teachers can focus their main energy on solving students’ temporary difficulties during the project planning and design process, guiding students in designing solutions, helping them find effective ways to realize their ideas, and paying attention to individual student needs, providing immediate guidance.
Students work in groups, relying on human teachers and AI to complete three tasks: pre-class project research, in-class project reporting, and post-class summarization and evaluation.
3. Teaching Resource Construction Achievements
(1) Constructing virtual digital teachers: Uploading all embedded courseware, lesson plans, PBL questions, and related materials from recent years to the AI system to build virtual digital teachers.
(2) Constructing a digital teaching resource library: Including online courses (building project-based online courses in new energy technology with student participation), chapter-based project cases (constructed by students + human teachers + AI), smart graphs (constructed by students + human teachers + AI), digital syllabi, digital lesson plans, digital ideological and political materials, video analyses, etc. Utilizing digital platforms, timely updates of teaching content and resources ensure synchronization with the latest technological advancements.

Figure 4 Knowledge Graph + Online Resources + Textbook Diagram
(3) Constructing diversified evaluation and intelligent evaluation methods, including student self-evaluation, group peer evaluation, teacher evaluation, and AI intelligent evaluation.
(4) Forming a project-based teaching model based on artificial intelligence with a “Dual Teacher Classroom” and conducting practice.
(5) AI empowerment in curriculum ideology reform, forming a case library focused on AI ethics, data network security, personal privacy protection, intellectual property protection, anti-algorithm discrimination, and traditional new energy ideology.
(6) Course-competition integration has led students to achieve over 300 subject competition awards, continuously enhancing students’ innovation capabilities.


Figure 5 Participation in Subject Competitions and Some Award Certificates
4. Conclusion
This case study utilizes generative AIs like ChatGPT, Douyin, Wenxin Yiyan, and Xinghuo during the teaching process, promoting a shift from “teacher-student interaction” to a deep interaction involving “teacher/student/machine”, enhancing students’ interest in learning and meeting personalized learning needs; through AI, updating teaching resources and content, constructing an embedded course knowledge graph, transitioning teaching content from static subject knowledge to dynamic comprehensive tasks, enriching teaching resources; shifting the teaching model from teacher-centered to student-centered, combining project-based learning and human-machine collaborative learning, providing more intelligent and personalized teaching services and learning support to offer students better learning experiences and practical opportunities; transitioning the educational philosophy from knowledge-centered to a stronger emphasis on “capability first, values first”; changing evaluation methods from “result evaluation” to “diversified evaluation”, transforming the single evaluation model; and enhancing students’ innovation capabilities through AI-enabled course-competition integration.
Statement
This article is sourced from the Shandong Provincial Education Technology Center.The above images and text are valuable for sharing, and copyright belongs to the original author and source. The content reflects the author’s views and does not represent the position of this public account. If there are any copyright issues, please contact us in a timely manner.