Satellite communication typically occurs in one of ten frequency bands. The specific frequencies available within each band depend on applicable licensing regulations. While certain portions of the bands are allocated globally for satellite use, others may be exempt from licensing and can be used in specific circumstances. The International Telecommunication Union (ITU) is responsible for allocating radio frequencies, including those for satellites. Satellite operators register with their respective local regulatory authorities, such as the Federal Communications Commission in the USA and the European Commission in Europe.
Here is a compilation of the frequency ranges used by satellites:
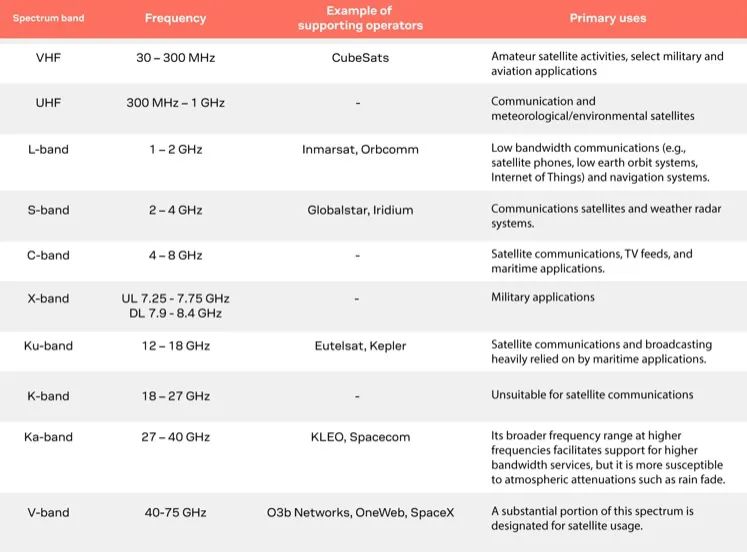
The growing demand for higher data rates is driving the transition to higher frequency bands. However, higher frequencies mean greater attenuation and lower Signal-to-Noise Ratios (SNR). Therefore, the Ka band is more suitable for broadband services rather than Internet of Things (IoT) applications. Overcoming the challenges of high frequencies requires higher power transmission, more expensive steerable and high-gain antennas, and directional beams. High Throughput Satellite (HTS) systems employ beamforming technology.
Frequency Bands for Satellite IoT Applications
The most common frequency bands in IoT applications, listed in descending order, are L band, S band, C band, and X band. The higher frequency bands, which offer increased bandwidth capabilities, are often unnecessary for IoT and involve relatively higher power requirements.
1. L Band (1-2 GHz)
Propagation Characteristics: L band signals perform well in penetrating buildings and vegetation, which is crucial for IoT devices operating in urban environments or forested areas.
Coverage: L band satellites can provide a wide coverage area, suitable for applications requiring extensive coverage, such as logistics tracking and environmental monitoring.
Cost-Effectiveness: L band equipment is relatively inexpensive, making it suitable for cost-sensitive IoT projects.
2. S Band (2-4 GHz)
Flexibility: S band offers better flexibility and can support multiple communication protocols and data rates, suitable for IoT applications requiring flexible configurations.
Interference Resistance: S band signals are relatively resistant to interference, making them suitable for use in areas with complex electromagnetic environments.
System Capacity: S band can provide higher system capacity, suitable for IoT networks that need to handle large volumes of data.
3. C Band (4-8 GHz)
Mature Technology: C band technology is mature, with widely available equipment and infrastructure, reducing deployment and operational costs.
High Power Transmission: C band allows for high power transmission, which helps improve the signal’s SNR, suitable for IoT applications requiring long-distance communication.
Global Coverage: C band satellites are typically used for global communication, suitable for cross-border IoT solutions.
4. X Band (8-12 GHz)
High Data Rates: X band can provide higher data transmission rates, suitable for IoT applications that require fast data exchange.
Narrow Beams: X band satellites typically use narrow beams, providing more precise positioning and higher frequency reuse efficiency.
Security: X band signals are harder to intercept and interfere with due to their higher frequency, suitable for applications with high-security requirements.
The selection of these frequency bands reflects the varying needs of IoT applications regarding coverage, data rates, cost, and security. As technology advances, satellite IoT may explore more frequency bands to meet the growing market demand.
Source: Satellite IoT Observer
This article aims to share industry trends. Please contact for removal if there is any infringement.