The Internet of Things has truly become the “star” of tech companies in recent years, but in the world of IoT, everything lacks a mouth; how can they communicate and connect with each other? That’s right, various communication protocols are needed at this point. There are many wireless communication technologies for IoT, which can be mainly divided into two categories: one is short-range communication technologies such as Zigbee, WiFi, Bluetooth, and Z-wave; the other is LPWAN (Low-Power Wide-Area Network) technologies, which are wide-area communication technologies. LPWA can be further divided into two categories: one operates in unlicensed spectrum, such as LoRa and SigFox; the other operates in licensed spectrum, supported by 3GPP cellular communication technologies like EC-GSM, LTE Cat-M, and NB-IoT.
Actually, short-range communication technologies, such as WiFi, Bluetooth, 3G/4G, and Zigbee, were the most common at the beginning. However, IoT applications need to consider many factors, such as node cost, network cost, battery life, data transmission rate (throughput), latency, mobility, network coverage, and deployment type. It can be said that no single technology can meet all the needs of IoT. For example, WiFi has high power consumption, while Bluetooth is limited to communication between two objects. We know that the IoT world can be a super big family; it’s not just a couple talking sweetly to each other. At this point, technologies like NB-IoT and LoRa emerged.
The Past and Present of NB-IoT
NB-IoT boldly claims its power, showing no humility at all. Well, actually, NB-IoT does not stand for Niubility Internet of Things; its real name is Narrow Band Internet of Things.

Huawei has been at the forefront of the development of IoT standards. In May 2014, Huawei proposed the narrowband technology NB M2M; in May 2015, it merged with NB OFDMA to form NB-CIOT. Previously, compared to Ericsson, Nokia, and Intel’s promotion of NB-LTE, Huawei focused more on building the ecosystem of NB-CIOT, which includes mainstream operators, chip manufacturers, and equipment system industry chains such as Qualcomm, Vodafone, Deutsche Telekom, China Mobile, China Unicom, and Bell. NB-CIoT proposed a brand new air interface technology, which made significant changes to the existing LTE network. However, NB-CIoT is the only cellular IoT technology that meets the five major goals proposed in the TSG GERAN #67 meeting (enhancing indoor coverage performance, supporting large-scale device connections, reducing device complexity, reducing power consumption, and latency). Notably, the communication module cost of NB-CIoT is lower than that of GSM and NB-LTE modules. NB-LTE is more inclined to be compatible with existing LTE, with its main advantage being ease of deployment.
Ultimately, after intense negotiations at the RAN #69 meeting in September 2015, NB-IoT can be seen as a fusion of NB-CIoT and NB-LTE. Thus, a unified NB-IoT was established.
Speaking of NB-IoT, We Must Mention LoRa
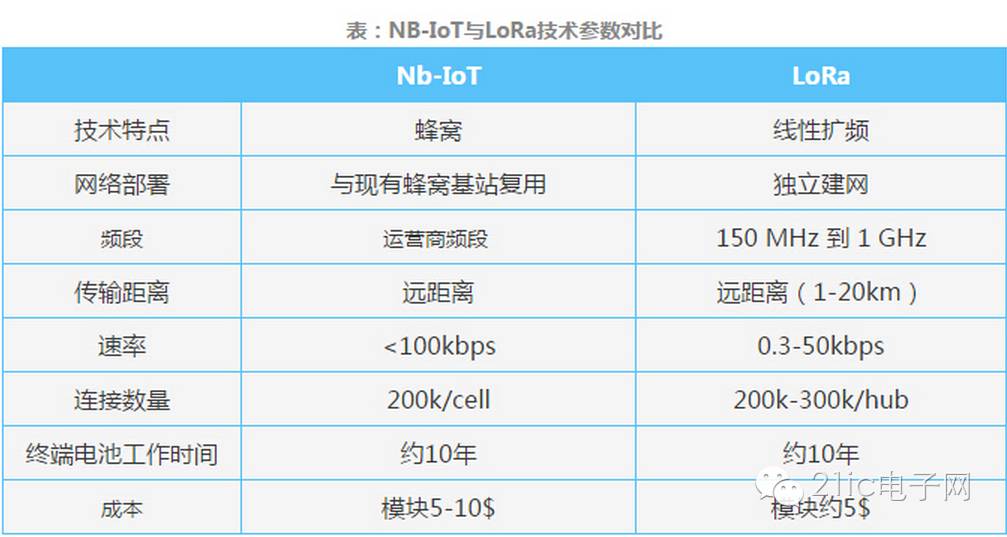
Now, when we talk about NB-IoT, we cannot overlook its biggest “competitor”—LoRa. LoRa, which stands for Long Range, is an LPWAN technology released by Semtech. Some believe that the emergence of the NB-IoT standard will lead to the demise of competing technologies like Sigfox and LoRa, which rely on unlicensed spectrum to provide services. However, it seems that neither technology can eliminate the other. NB-IoT and LoRa have different technical and commercial characteristics, leading to different application scenarios.
Let’s first talk about what makes NB-IoT impressive. NB-IoT supports efficient connections for devices that require long standby times and high network connectivity. It is said that the battery life of NB-IoT devices can be extended to at least 10 years while providing comprehensive indoor cellular data connection coverage. NB-IoT technology features wide coverage, multiple connections, low rates, low costs, low power consumption, and superior architecture. After the protocol is frozen, the cost of new communication modules is expected to decrease by over 50% compared to previous models, significantly reducing product costs and communication fees, which will be very beneficial for companies promoting IoT in the market.
Initially, LoRa was just a private wireless technology without a solid foundation for large-scale promotion. However, in an era where connections matter, it quickly became a star in the IoT world with the backing of the “LoRa Alliance.”

The LoRa Alliance is an open, non-profit organization initiated by leading industry players, aimed at promoting Low-Power Wide-Area Networks (LPWAN) globally to enable IoT, M2M, and smart city applications. Alliance members work together to successfully establish the LoRa protocol as a global standard.
From its inception, the LoRa Alliance has focused on building an ecosystem, collaborating reasonably with companies across the industry chain to promote the commercial use of this technology. Currently, the alliance includes multinational telecom operators, equipment manufacturers, system integrators, sensor manufacturers, chip manufacturers, and innovative startups from regions including Europe, North America, Asia, and Africa. Members of the LoRa Alliance are categorized into founding members, contributing members, and application members.

The main characteristics of LoRa wireless technology are: long range: 1-20 km; number of nodes: tens of thousands, even millions; battery life: 3-10 years; data rate: 0.3-50 kbps. As a wireless technology, LoRa operates in the Sub-GHz frequency band, making it easier to communicate over long distances with low power consumption, powered by batteries or other energy harvesting methods. The lower data rates also extend battery life and increase network capacity. LoRa signals also have strong penetration through buildings. These technical features of LoRa are more suitable for low-cost, large-scale IoT deployments.
Application Scenarios of NB-IoT
Compared to LoRa, which achieved commercial use in 2013, NB-IoT is still a newcomer, having only started commercial deployment in 2016. Currently, looking at the application of LoRa, it mainly involves data transmission and the LoRaWAN protocol. At present, most applications still use LoRa for data transmission, and due to the high technical threshold for gateway technology and development, applications using the LoRaWAN protocol are relatively few.

The most widespread application scenario for NB-IoT is the extremely impressive—”smart water meter reading”! Who can remain calm after hearing this?
With the implementation of the tiered pricing policy for gas in domestic households, gas companies are motivated to upgrade to smart meters to capture the benefits of tiered pricing. The labor and additional costs associated with manual meter reading have prompted gas companies to pursue smart upgrades to increase profit margins. From a technical solution perspective, compared to four technical solutions for gas meters, namely mechanical meters, IC card meters, small wireless meters, and GPRS meters, the NB-IoT meter has lower comprehensive costs, lower network construction costs, lower failure rates and maintenance costs, and a reading success rate greater than 98%. With public telecom-level services and high one-time reading rates, it effectively meets the needs of gas companies for smart gas meters.
NB-IoT can also be applied in smart waste bins. During the “2016 Barcelona Communication Exhibition,” Huawei showcased a smart waste bin solution based on NB-IoT, which intelligently retrofits waste bins in service areas by installing ultrasonic sensors embedded with NB-IoT wireless chips to detect whether the bins are full and report status information back to the management server. The server then plans the optimal route for garbage trucks based on the reported information, which is expected to double the efficiency of garbage truck scheduling and save cities millions of dollars each year in vehicle and labor costs.
Moreover, in the realm of smart environmental protection, NB-IoT technology has also made contributions. Environmental protection has been one of the most concerning topics in recent years, but pollution arises from various aspects of production and life. Manual inspections require a significant investment of human and material resources, while smart sensors based on NB-IoT technology can provide functions such as hazardous gas detection, water quality monitoring, soil monitoring, forest fire monitoring, and hazardous materials management, helping to solve deployment challenges.
So, do you think NB-IoT technology is really impressive now?
Recommended
The mutual disdain between “Analog Electronics” and “Digital Electronics” led to a meeting, and the result was…

Understanding VCC, VDD, VEE, VSS Voltage

Expand Your Knowledge! Experts Guide You to Understand Embedded C Language Reliability Design
