Microcontrollers, as a common type of embedded device, are an essential part of many electronic devices and systems. In the design and application of microcontrollers, the supply voltage is a very important parameter, and among them, VCC and VDD are the two most critical supply pins in microcontrollers. This article will introduce the differences between VCC and VDD and their applications in microcontrollers.
Differences Between VCC and VDD
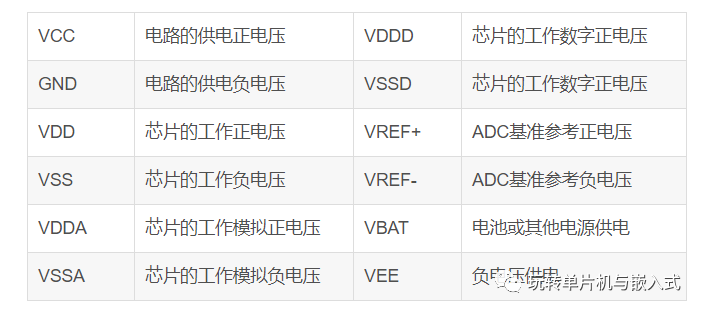
In microcontrollers, VCC is the most common power pin, typically used to provide the positive voltage needed in digital circuits. The voltage of VCC is usually 3.3V or 5V, but there are also microcontrollers with other voltage levels.
On the other hand, VDD is a special type of supply voltage, referring to the power voltage used in CMOS circuits. In CMOS circuits, the transistors used are MOSFETs, which require two types of voltages to operate: positive voltage and negative voltage. VDD refers to the positive voltage required for MOSFET operation, which is typically lower than VCC, usually between 1.8V and 3.3V.
The differences in usage between VCC and VDD mainly reflect in the type of circuit and voltage levels. VCC is suitable for general digital circuits, while VDD is mainly used for CMOS circuits. This is because MOSFET transistors in CMOS circuits need two voltages: positive and negative voltages. In digital circuits, usually only one positive voltage is needed, so VCC is typically used to provide the positive voltage.
Applications of VCC and VDD in Microcontrollers
In microcontrollers, the applications of VCC and VDD are basically the same as in other digital circuits. VCC and VDD are used to provide the supply voltage required for the operation of the microcontroller, ensuring that the microcontroller can function properly. Additionally, other pins of the microcontroller also need to be connected to VCC and VDD to ensure they can operate normally.
In the design of microcontrollers, to avoid circuit instability, it is usually necessary to connect ceramic capacitors to VCC and VDD. These capacitors help filter out high-frequency noise from the power supply, thus improving the stability and reliability of the circuit. It is important to select appropriate capacitance values and capacities for these capacitors to ensure they can filter out the necessary noise.
It should be noted that in some microcontrollers, VCC and VDD may be used for different functions. For example, some microcontrollers may require VCC to provide internal logic voltage, while VDD may be used to provide voltage for analog circuits. Therefore, when using microcontrollers, it is necessary to refer to the corresponding datasheet to determine the specific purposes and voltage requirements of VCC and VDD.
Conclusion
VCC and VDD are two important power pins in microcontrollers, playing a critical role in the design and application of microcontrollers.
VCC is typically used to provide the positive voltage needed in digital circuits, while VDD is used to provide the positive voltage needed in CMOS circuits.
In the design and application of microcontrollers, it is essential to pay attention to the voltage range, stability, and noise filtering of VCC and VDD to ensure the stability and reliability of the microcontroller’s operation.
END


