●Di Dehai, Liu Zhihui, Lin Zhihua●
(Xiamen Moore Universe Communication Technology Co., Ltd., Xiamen, Fujian 361011)
Abstract: IoT products mainly connect through wireless communication technologies, which include long-distance communication technologies such as 2G, 3G, 4G, and 5G, as well as short-distance communication technologies like WiFi and Bluetooth. In order to ensure the quality, performance, and safety of wireless communication products or terminals, the government mandates that products sold domestically must undergo mandatory certification before being marketed. This includes China Compulsory Certification (CCC certification), Radio Transmission Equipment Model Approval Certification (SRRC certification), and Network Access License Certification (CTA certification), obtaining the corresponding certificates. This article elaborates on the overview, certification processes, testing standards, and testing items of IoT product certifications such as CCC, SRRC, and CTA, which helps IoT product developers and certification personnel better understand the requirements of domestic mandatory certifications, thereby improving product quality and shortening certification cycles.
Keywords: IoT; Mandatory Certification; China Compulsory Certification; Radio Transmission Equipment Model Approval Certification; Network Access License Certification; Certification Process; Testing Standards; Testing Items
Introduction
The Internet of Things (IoT) connects various items through information sensing devices, smart terminals, and communication technologies to achieve data exchange, sharing, and management [1]. Sensing technology and wireless communication technology are the technical foundations of IoT development, and their continuous evolution and upgrade provide strong technical support for the widespread application of IoT in various scenarios [2].
Most IoT products use wireless communication technology for connection, so they generally belong to the category of wireless communication products. Wireless communication products sold in China must undergo mandatory regulatory certifications and obtain the corresponding certificates before being sold in the domestic market. These include SRRC certification, CTA certification, and CCC certification [3].
1 IoT Wireless Communication Technology
IoT primarily transmits data through wireless communication technology. Wireless communication technology is categorized based on the distance of data transmission into long-distance wireless transmission technology (2G, 3G, 4G, 5G, etc.) and short-distance wireless transmission technology (WiFi, BT, Zigbee, etc.). Short-distance wireless communication technology is generally used in local area network communication scenarios, while long-distance wireless communication technology is mainly applied in industrial IoT and mobile communications [4].
1.1 Cellular IoT
Cellular IoT is a type of IoT connection technology that refers to IoT devices connecting to the internet using the same network infrastructure as mobile phones, primarily through 2G, 3G, 4G, and 5G mobile communication network technologies.
1.2 Cat M1 and NB-IoT
Cat M1 and NB-IoT are currently the two most popular IoT connection options. LTE Cat M1 is a new cellular technology designed to meet the application needs for IoT or machine-to-machine (M2M) communication. NB-IoT is a narrowband IoT, an important branch of the Internet of Everything network, supporting devices in wide area network cellular data connections, and can be directly deployed on GSM, UMTS, or LTE networks.
1.3 Short-Distance Communication Technology
WiFi is a wireless local area network technology based on the IEEE 802.11 standard, operating on 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequency bands. The 2.4 GHz band supports 802.11b/g/n/ax standards, while the 5 GHz band supports 802.11a/n/ac/ax standards. Bluetooth technology is a globally recognized standard for wireless data and voice communication, operating on the 2.4 GHz band, based on low-cost short-range wireless connectivity technology. ZigBee technology has been widely applied in specific fields in China, currently focusing primarily on areas with high energy management requirements, with common applications in access control and lighting control [5].
2 CCC Certification Analysis
2.1 Overview of CCC Certification
Household appliances, automobiles, safety glass, wires and cables, toys, and other products are included in the “Product Catalog for Implementing Mandatory Product Certification”. The China Quality Certification Center (CQC) is responsible for the mandatory product certification business covering 15 categories and 95 products (including 17 products that adopt self-declaration). The certification scope categories on the CQC official website include 01 wires and cables, 02 circuit switches and protective or connecting electrical devices, 07 household and similar use devices, 08 electronic products and safety accessories (originally categories 08, 09, 16), 10 lighting equipment, 11 vehicles and safety accessories (originally categories 11, 12), 21 building materials (originally categories 13, 21), 22 children’s products, 23 explosion-proof electrical devices, and 24 household gas appliances. IoT products are certified under category 08.
The supervisory management agencies for mandatory certification include the National Certification and Accreditation Administration (CNCA), the State Administration for Market Regulation, local quality technical supervision agencies, and local entry-exit inspection and quarantine agencies. Certification agencies include CQC, Telecommunication Certification, Wika, Saibo, and Shenzhen Measurement Quality Testing Research Institute (SMQ), among others. Testing agencies include Zhongren Yingtai, National Radio Monitoring Center Testing Center, Telecommunication Labs, SMQ, Wika, Saibo, etc.
2.2 CCC Certification Process
For the 08 category CCC certification of IoT products, the CQCC0901-2023 “Implementation Rules for Mandatory Product Certification of Electronic Products and Safety Accessories” is followed. The CCC certification process mainly includes application and acceptance, document review, sampling inspection, factory audit, evaluation and approval of certification results, and post-certification supervision, as shown in the detailed flowchart [6].
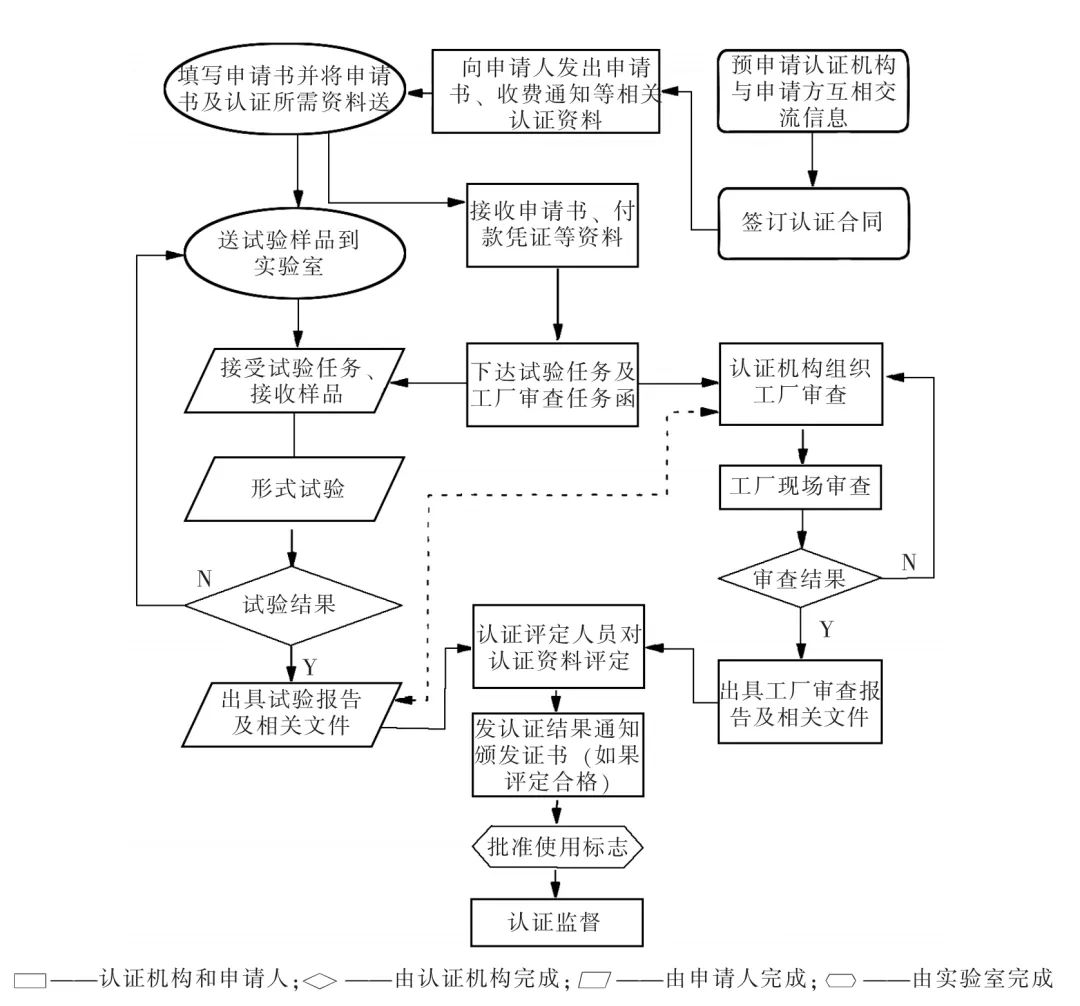
Figure 1 CCC Certification Process Flowchart
The list of materials required for CCC certification includes:
a) Certification application form;
b) Registration proof for the certification client, producer, and manufacturing enterprise (business license, organization code, etc.);
c) Self-assessment report or declaration of the manufacturing enterprise’s quality assurance capability;
d) Factory inspection survey form;
e) Relevant agreements or contracts signed between the certification client, producer, and manufacturing enterprise;
f) Product description information (technical specifications, circuit diagrams, schematics, etc.);
g) Chinese user manual.
The validity period of the product CCC certification certificate is 5 years, and within this period, the validity of the certificate relies on post-certification supervision.
2.3 Standards and Testing Items for CCC Certification
The testing standards for CCC certification of category 08 products are shown in Table 1. The safety standard is based on GB 4943.1-2022 “Audio, Video, Information Technology, and Communication Technology Equipment Part 1: Safety Requirements”, which specifies the basic requirements for devices regarding electrical, mechanical, radiation, and safety aspects to ensure that the devices do not pose a risk to personal safety during use. Specifically, the GB 4943.1-2022 standard mainly includes the following aspects.
Table 1 Standards for CCC Certification of Category 08 Products

a) Electrical safety requirements
This standard specifies the electrical safety requirements for devices in terms of power supply, signal interfaces, etc., including insulation, withstand voltage, and grounding indicators.
b) Mechanical safety requirements
This standard specifies the safety requirements for devices in terms of mechanical aspects, including the shell, structure, drop resistance, and shock resistance indicators.
c) Radiation safety requirements
This standard specifies the safety requirements for devices regarding electromagnetic radiation, including the intensity, frequency, and waveform of electromagnetic radiation.
d) Safety control requirements
This standard specifies the requirements for devices regarding safety control, including safety control measures for software, hardware, and operations.
Electromagnetic compatibility testing is based on GB/T 9254.1-2021 “Information Technology Equipment, Multimedia Equipment, and Receiver Electromagnetic Compatibility Part 1: Emission Requirements”. The GB/T 9254.1-2021 testing items include: a) Conducted emissions at AC power ports; b) Conducted emissions in asymmetric mode; c) Radiated emissions (below 1 GHz); d) Radiated emissions (above 1 GHz); e) FM receiver local oscillator and its harmonic emissions; f) Conducted differential mode voltage emissions; g) Emissions from outdoor units of household satellite reception systems.
3 SRRC Model Approval Certification Analysis
3.1 Overview of SRRC
All radio transmission equipment produced or sold domestically must undergo SRRC model approval certification [7]. The categories of products subject to model approval certification include mobile communication, specialized communication, wireless access, broadcast transmission, radar, navigation, satellite communication, and other devices, totaling 8 categories and 126 subcategories [8]. The types of communication standards involved include 2G (GSM), 3G (CDMA, CDMA 2000, WCDMA, TDSCDMA), 4G (TD-LTE, LTE FDD, NB-IoT), 5G, RFID, WiFi, and Bluetooth wireless communication technologies.
3.2 SRRC Certification Process
The basic process and time requirements for model approval certification are shown in Figure 2.
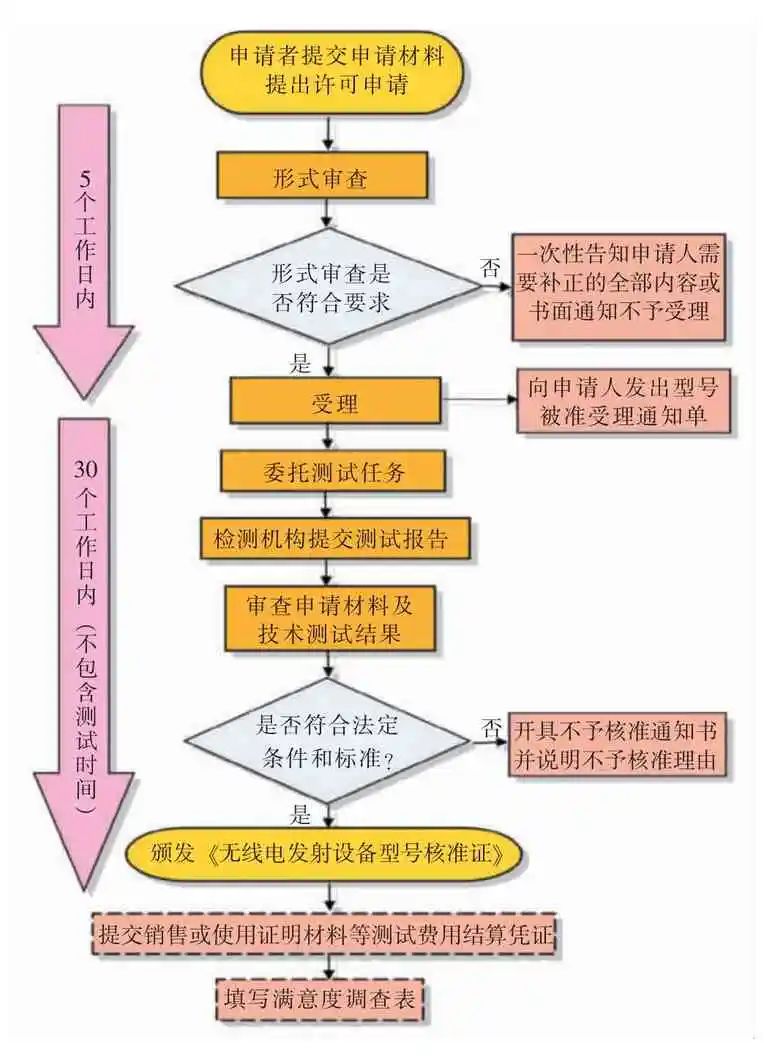
Figure 2 Model Approval Process Flowchart
Starting from December 1, 2023, the new “Model Approval Certificate Style for Radio Transmission Equipment” and “Model Approval Code Encoding Rules” will be implemented. The new model approval certificate style is shown in Figure 3. This adjustment adopts a format that combines the certificate main page with an appendix, where the main page reflects major information such as the certified unit and equipment name, while the appendix reflects specific information such as technical parameters [9]. The format of the model approval code is adjusted to CMIITID: AABCCDDDEEEE, where the CMIITID remains unchanged, and the model approval code consists of 12 digits, with AA representing the year code, B representing the equipment code, CC representing the area code, DDD representing the enterprise code, and EEEE representing the autonomous code.

Figure 3 New Model Approval Certificate Style
3.3 Standards and Testing Items for SRRC Certification
Products with WiFi or Bluetooth functionality undergo SRRC mandatory certification based on the standard GB/T 12572-2008 “General Requirements and Measurement Methods for Radio Transmission Equipment Parameters” [10]. For 5G terminal devices, the RF project requirements for SRRC certification reference standards are SA mode: 3GPPTS 38.521-1, NSA mode: 3GPP TS38.521-3 [11]. The standards for 2.4G wireless local area network testing include the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (2021) No. 129 document, GB 15629.11-2003, GB 15629.1102-2003, IEEE P802.11ax/D6.0-2019, YD/T 3168-2016. The testing methods reference standards include YD/T 3168-2016, GB/T 32420-2015, GB/T 12572-2008, ETSI EN 300328. Testing items include equivalent isotropic radiated power, equivalent isotropic radiated power spectral density, out-of-band emissions, frequency range, occupied bandwidth, carrier frequency tolerance, and spurious emissions (radiated) power.
4 CTA Certification Analysis
4.1 Overview of CTA Certification
The state implements the CTA system for telecommunications equipment such as mobile phone terminals, wireless data terminals, switches, and routers that connect to public telecommunications networks like 2G, 3G, 4G, and 5G. Wireless communication devices within the scope of the CTA system must obtain a CTA certificate (including a network access trial approval). Devices without a CTA certificate are prohibited from connecting to public telecommunications networks and being sold domestically.
4.2 CTA Certification Process
The CTA certification process flowchart is shown in Figure 4.
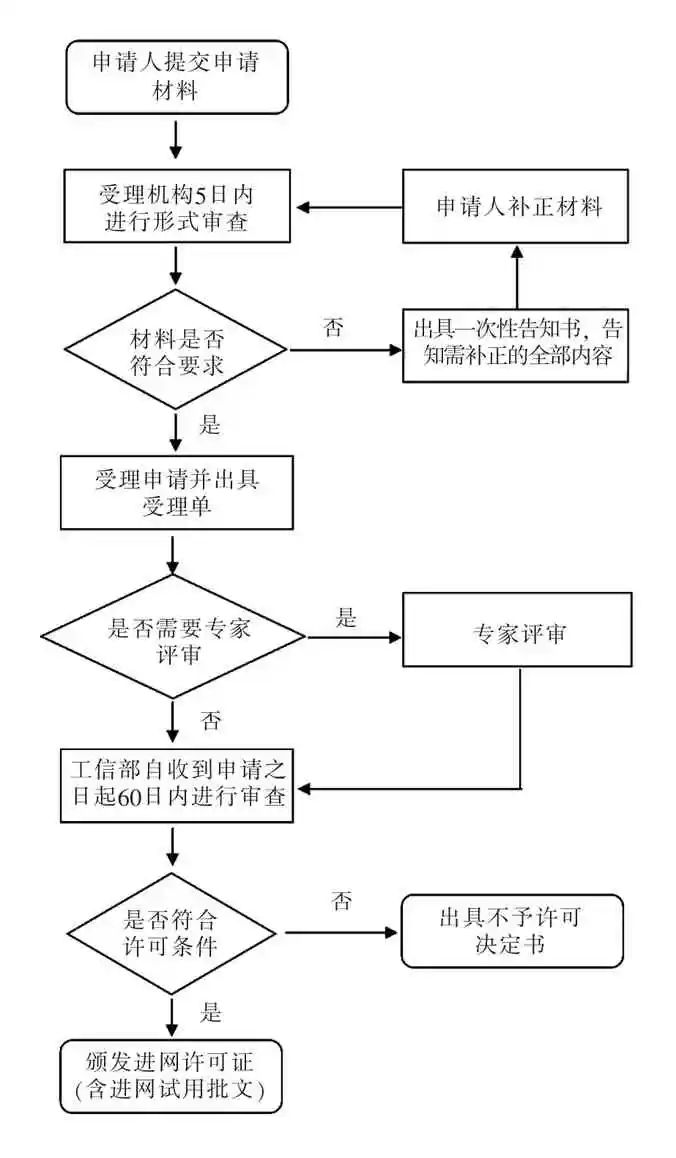
Figure 4 Telecommunications Equipment Network Access License Application Process Flowchart
The Ministry of Industry and Information Technology’s document [2023] No. 14 “Notice on Several Reform Measures for Telecommunications Equipment Network Access License System” proposes that 11 types of telecommunications equipment, including fixed telephone terminals, do not require CTA certification. Satellite internet devices and function virtualization devices are included in the CTA management [12], and unrelated testing items regarding telecommunications security and interoperability will be removed from subsequent CTA tests.
4.3 Standards and Testing Items for CTA Certification
Telecommunications equipment CTA certification is based on testing standards including YD/T 3627-2019, YD/T 2583.18-2019, YD/T 3230-2017, GB/T 9254-2008, 3GPP TS38.521-1, 3GPP TS38.523-1, YD/T 2576.1-2013, YD/T 2307-2011, YD/T 2582.1-2013, etc. The overall testing items total 138, covering IPv6, SAR, OTA, EMC, information security, basic performance, and functionality. Testing items specifically for 5G devices include electromagnetic compatibility testing, basic performance testing, SAR testing, and OTA testing. The standards for electromagnetic compatibility testing are based on “Electromagnetic Compatibility Testing Requirements for Mobile User Terminals”, totaling 6 items, including continuous radiation interference, continuous conducted interference, conducted disturbance immunity, radiated disturbance immunity, electrostatic discharge immunity, and surge immunity. The standards for basic performance testing are based on “Testing Requirements for Basic Performance of 5G Enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB) Type Mobile User Terminals”, totaling 57 items, including network information security (information security protocols), RF receiving performance (reference sensitivity level, maximum input level, etc.), interoperability and performance requirements, and basic services and functionalities. The standards for SAR testing are based on “Testing Requirements for Electromagnetic Radiation Performance of 5G Mobile User Terminals”, totaling 2 items, including electromagnetic radiation performance (head) and electromagnetic radiation performance (body). The standards for OTA testing are based on “Testing Requirements for Antenna Performance of 5G Enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB) Type Mobile User Terminals”, totaling 2 items, including Total Isotropic Radiated Power (TIRP) testing and Total Isotropic Radiated Sensitivity (TIRS) testing.
5 Conclusion
As an important component of the information society, the quality and safety of IoT products are of great significance for the development of society and information security. Wireless products sold in China must meet a series of certification requirements to ensure their quality and safety. CCC certification ensures that these products comply with safety and electromagnetic compatibility standards; SRRC certification ensures that wireless transmission equipment meets China’s radio management regulations and national safety standards; CTA certification ensures that products comply with China’s communication management regulations and national safety standards. This article introduces the basic overview, certification processes, and testing standards and items for these three domestic certifications, providing a reference for IoT products to obtain the corresponding certifications.
|
Author/Source | “Electronic Quality” Editor | Lu Sidi Proofreader | Wang Gang For submission, WeChat public account reprint cooperation, and related matters, please contact Customer Service |
|
