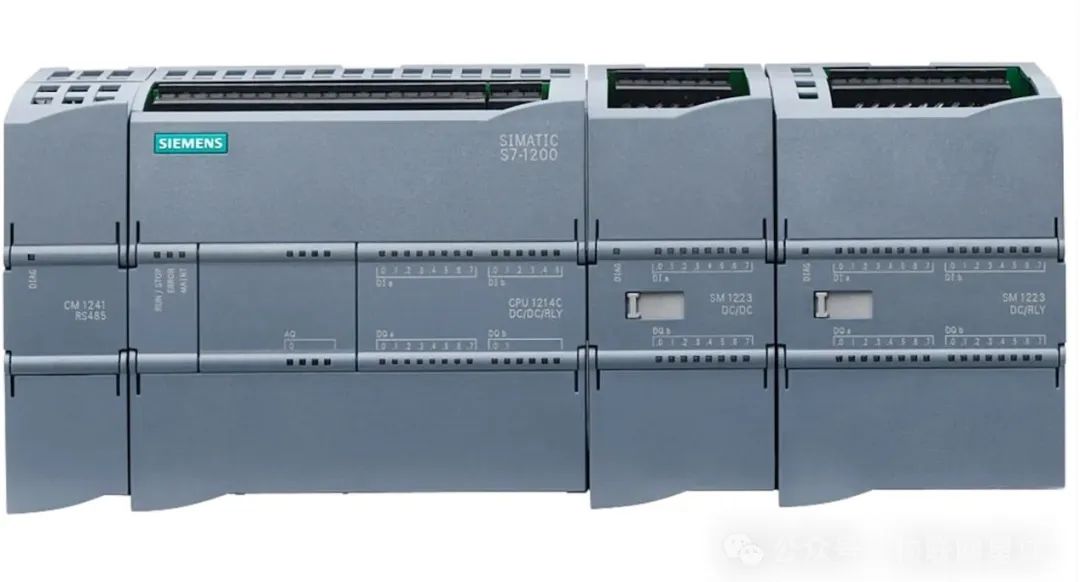
In the field of industrial automation, Programmable Logic Controllers (PLC) play a core role, and their communication capabilities directly affect the efficiency and reliability of the entire system. This article will delve into the commonly used communication protocols for PLCs and analyze their applications in different scenarios.


Common Protocols
Overview of PLC Communication Protocols
PLC communication protocols are the core technology for interconnecting devices in industrial automation. They allow PLCs to efficiently exchange data with various devices such as sensors, actuators, Human-Machine Interfaces (HMI), and databases. These protocols can be based on traditional bus technologies or utilize modern Ethernet technologies to adapt to different industrial environments and needs. Bus-based protocols like Modbus RTU are widely used in simple master-slave control systems due to their simplicity and strong compatibility. Ethernet-based protocols like Ethernet/IP and EtherCAT, with their high-speed communication capabilities and real-time performance, are particularly suitable for complex automation systems and scenarios that require high data transmission speeds. Choosing the right communication protocol is crucial for enhancing the performance and reliability of the entire automation system.
Common PLC Communication Methods
1. Modbus RTU
Definition: Modbus RTU is a widely used serial communication protocol that typically operates on the RS-485 physical layer.
Features:
-
Simple and easy to use
-
Strong compatibility
-
Relatively slow speed
-
Limited distance
Usage Scenarios:
-
Modbus RTU is suitable for basic master-slave control scenarios, such as temperature regulation and data acquisition systems, meeting basic industrial communication needs with its simplicity and wide compatibility.
2. Profibus

Definition: Profibus is an industrial fieldbus standard developed by Siemens, mainly consisting of two types: Profibus-DP and Profibus-PA.
Features:
-
High-speed communication
-
High reliability
-
High implementation cost
-
High complexity
Usage Scenarios:
-
Profibus is suitable for high-demand automation environments, particularly in factory automation and process control fields, meeting the needs of complex systems with its high-speed communication and reliability.
3. Ethernet/IP

Definition: Ethernet/IP is an industrial network protocol based on standard Ethernet, developed by ODVA.
Features:
-
High-speed communication
-
Suitable for large data volume transmission
-
Compatible with standard Ethernet devices and infrastructure
-
Supports real-time data transmission
Usage Scenarios:
-
The Ethernet/IP protocol is suitable for highly complex industrial automation systems, including factory automation, process control, and robotic control, meeting the demands for large data volumes and complex control with its high-speed data transmission and real-time performance.
4. EtherCAT

Definition: EtherCAT is a real-time industrial Ethernet protocol developed by Beckhoff.
Features:
-
Extremely high real-time performance and synchronization
-
Low latency and jitter
-
Efficient data processing capabilities
Usage Scenarios:
-
The EtherCAT protocol is designed for applications requiring extremely high real-time performance and precise synchronization, widely used in motion control, robotics, and high-performance testing and measurement equipment, ensuring precision and efficiency in operations.
-
Reviewing the Top Ten Industrial Ethernet Protocols, Which is Stronger? As an IoT Practitioner, How Many Have You Used? -
What Open Source Projects Are Used in Domestic IoT Platform Visualization Screens? -
List of Common IoT Protocols (Collector’s Edition, Please Save) -
Recommendations for Excellent Domestic Edge AIoT Platform Products, Edge-Cloud Collaboration, Disconnection Resumption, NodeRED..

Focusing on AIoT Field Research


Join the Community
Technical Exchange
Please note when joining: Name – Industry


Join the IoT Community
