Reposting an article;https://kernel.meizu.com/2023/12/13/Full-stack-resolution-of-the-Linux-time-subsystem/The time management in ARMv8 is primarily based on the same time base + different offsets = specific time. Let’s take a look at the main data structures.
Let’s take a look at the main data structures.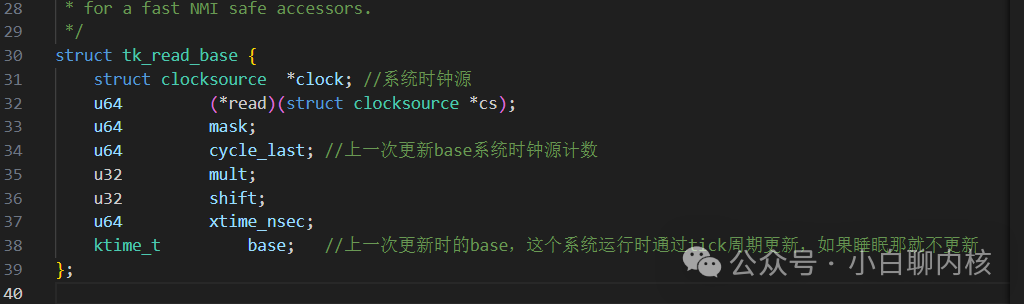 Used to calculate the time value under a certain offset; assuming we read the real time starting from 1970.
Used to calculate the time value under a certain offset; assuming we read the real time starting from 1970.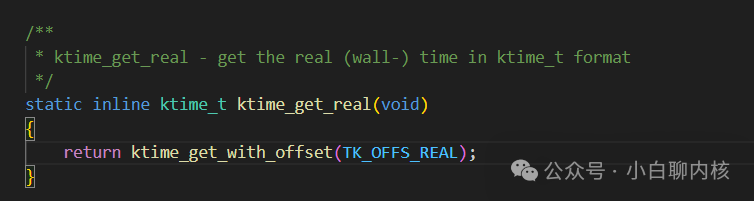
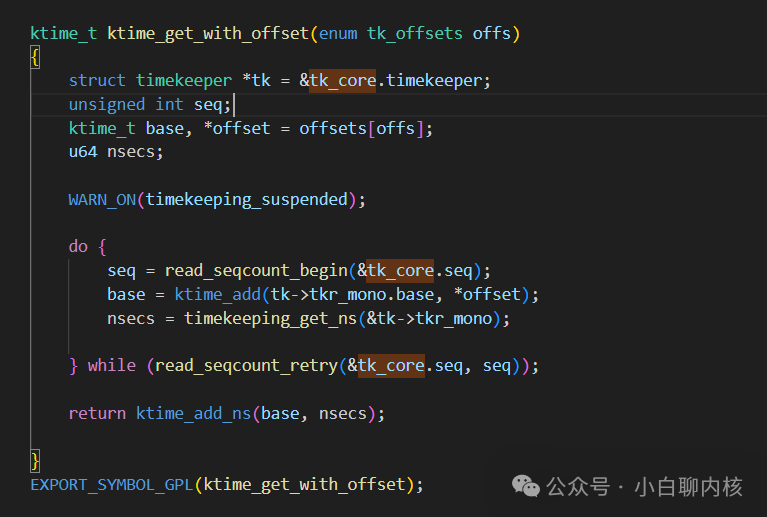
 Here, the current base + offset 【【TK_OFFS_REAL】 is equal to the world time corresponding to the last time I recorded the modified base;Then, starting from the last recorded base, I might have gone to sleep, so I need to compensate for this sleep time difference. How do we do that? We rely on the system time counter (which continues counting during this sleep) to calculate the time difference, and then add it to the previous calculation;
Here, the current base + offset 【【TK_OFFS_REAL】 is equal to the world time corresponding to the last time I recorded the modified base;Then, starting from the last recorded base, I might have gone to sleep, so I need to compensate for this sleep time difference. How do we do that? We rely on the system time counter (which continues counting during this sleep) to calculate the time difference, and then add it to the previous calculation;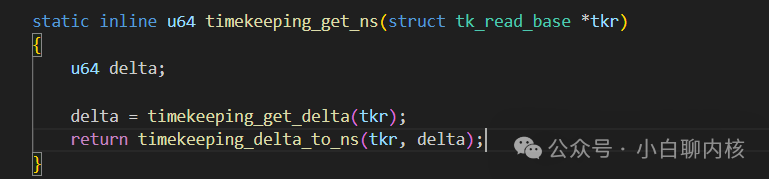
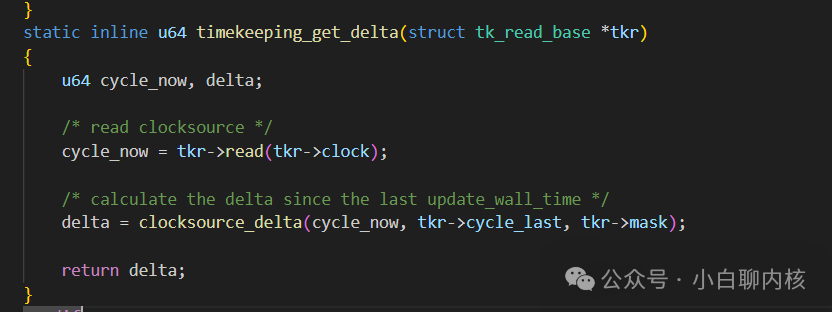 This is to calculate the count difference from the system clock source since the last base update. The system clock source has counted how many counts have passed, converted to ns based on the clock frequency, and then added; to calculate the difference, we must have the count corresponding to the last modification of the base,u64 cycle_last; this value is;
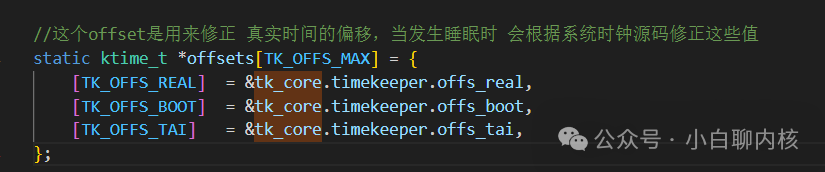
This is to calculate the count difference from the system clock source since the last base update. The system clock source has counted how many counts have passed, converted to ns based on the clock frequency, and then added; to calculate the difference, we must have the count corresponding to the last modification of the base,u64 cycle_last; this value is;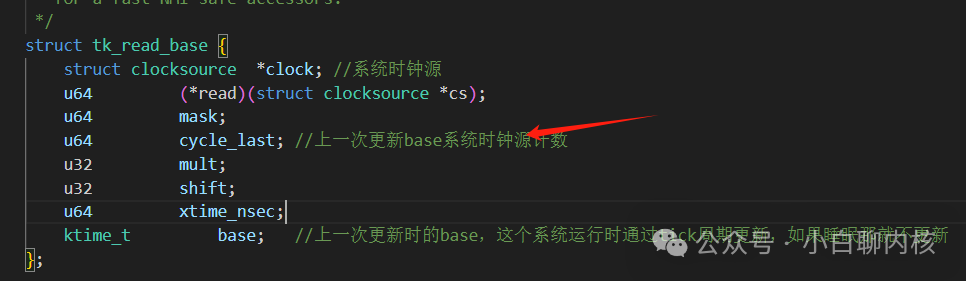 Real world time can be obtained through the base;When is this offset updated? For example, when the device is just powered on, there is no world time, so real_offset = 0; but after a period of time, when the world time is obtained through the network, real_offset can be set to the real time, and then it can be directly used as base + offset + the time difference from the last recorded base = real world time;
Real world time can be obtained through the base;When is this offset updated? For example, when the device is just powered on, there is no world time, so real_offset = 0; but after a period of time, when the world time is obtained through the network, real_offset can be set to the real time, and then it can be directly used as base + offset + the time difference from the last recorded base = real world time;