
Introduction:
With the arrival of the intelligent era, robots are increasingly participating in our lives and work. The popular movies “Big Hero 6” and “Avengers 2” featuring AI robots have sparked interest and reflection on artificial intelligence among many movie fans and even professionals.
When were intelligent robots invented? What are the key periods in their development? With these questions in mind, let’s take a look at the history of artificial intelligence spanning half a century.

■ What is Artificial Intelligence?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is essentially a simulation of human consciousness and cognitive processes. AI robots are robots that possess self-awareness similar to humans. It is a field of technology science that researches and develops theories and applications used to simulate, extend, and enhance human intelligence. Research in this field includes robotics, language recognition, image recognition, natural language processing, and expert systems.
AI robots are robots that possess self-awareness similar to humans (Image source: pinterest)
Artificial intelligence is an important branch of computer science and a highly challenging scientific field. It consists of different domains, such as machine learning, computer vision, etc. Today, we will focus on one of its important branches: AI robots.
■ The Birth of Artificial Intelligence Discipline in the Mid-20th Century
◆ In 1942, American science fiction writer Isaac Asimov proposed the “Three Laws of Robotics”.
When talking about AI robots, one cannot ignore Asimov, who proposed the “Three Laws of Robotics” that later became the de facto development principles in academia. Law 1: A robot must obey the orders given it by human beings except where such orders would conflict with the First Law. Law 2: A robot must not harm a human being or, through inaction, allow a human being to come to harm. Law 3: A robot must protect its own existence as long as such protection does not conflict with the First or Second Law.

In 1942, American science fiction writer Isaac Asimov proposed the “Three Laws of Robotics”, which later became the de facto development principles in academia.
◆ In 1956, the Dartmouth Conference: The Birth of AI
In the summer of 1956, a two-month academic conference was held at Dartmouth College in the USA by assistant professor John McCarthy, Marvin Minsky from Harvard University, and others. They discussed the basis of human learning and other functional characteristics from different disciplinary perspectives and explored how to accurately describe these characteristics and simulate human intelligence with machines, thus coining the term “artificial intelligence”. The Dartmouth Conference established the name and tasks of AI and saw the emergence of initial achievements and the first batch of researchers, making this event widely recognized as the mark of AI’s birth.

At the Dartmouth Conference, the name and tasks of AI were established, and the first achievements and researchers appeared.
This event is widely recognized as the mark of AI’s birth, as shown in the image of Claude Shannon.
In 1956, at the Dartmouth Conference, Marvin Minsky presented his views on intelligent machines: intelligent machines “can create abstract models of their surrounding environment and can find solutions from these models when encountering problems.” This definition influenced the research direction of intelligent robots for the next 30 years.
◆ In the early 1950s, people began to notice the connection between human intelligence and machines.
The discipline of artificial intelligence was born in the mid-20th century, as the emergence and development of computers initiated genuine research into artificial intelligence.
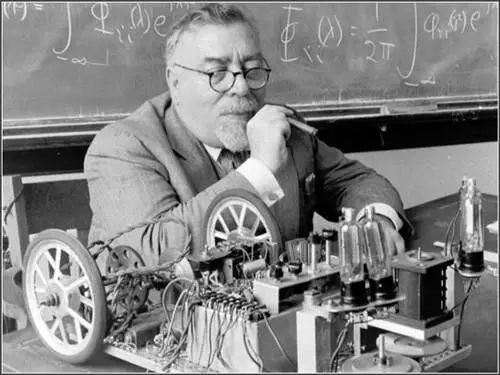
In the early 1950s, people began to notice the connection between human intelligence and machines.
Norbert Wiener was one of the first Americans to study feedback theory.
Although computers provided the necessary technical foundation for AI, it was not until the early 1950s that people began to recognize the connection between human intelligence and machines. Norbert Wiener was one of the earliest researchers of feedback theory, and the most familiar example of feedback control is the automatic thermostat, which compares the room temperature it collects with the desired temperature and responds by adjusting the heater to maintain the environment’s temperature. This discovery greatly influenced the early development of AI.
■ First Generation Robots: Teaching-Reproducing Robots
This type of robot is controlled by a computer to operate a multi-degree-of-freedom mechanism. By teaching and storing programs and information, the robot can read the information and issue commands during work, allowing it to reproduce actions based on the results demonstrated by the human at that time. The characteristic of this type of robot is that it does not sense the external environment.
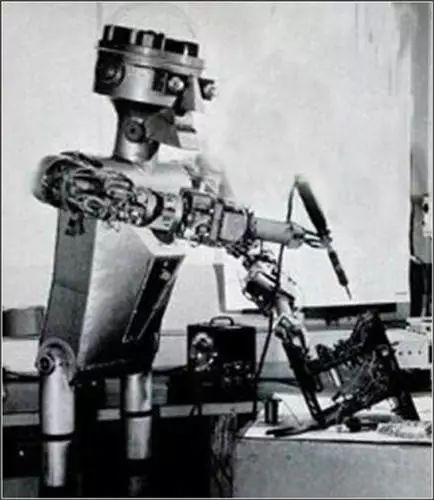
In 1959, Devol and American inventor Joseph Engelberger jointly created the first industrial robot.
In 1959, Devol and American inventor Joseph Engelberger jointly created the first industrial robot. Subsequently, they established the world’s first robot manufacturing company, Unimation. Engelberger is known as the “father of industrial robots” due to his research and promotion of industrial robots.
◆ In 1962, a global wave of robot research was ignited.
In 1962, the American company AMF produced “VERSTRAN” (meaning universal handler), which, along with Unimation’s “Unimate”, became the first commercially available industrial robots and were exported worldwide, igniting a global wave of robot research.
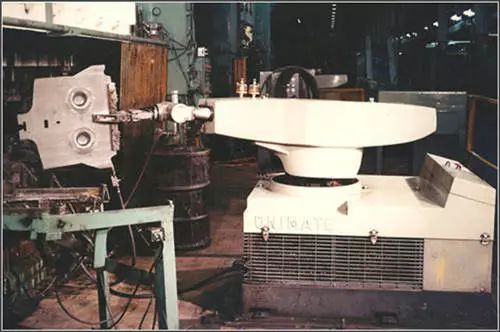
In 1962, the American company AMF produced “VERSTRAN” (universal handler).
◆ In 1965, research on second-generation robots with sensors and “sensing” capabilities began, progressing towards artificial intelligence.
In 1965, the Applied Physics Laboratory at Johns Hopkins University developed the Beast robot. The Beast could correct its position based on the environment using sonar systems and photoelectric tubes.

In 1965, the Applied Physics Laboratory at Johns Hopkins University developed the Beast robot.
In the mid-1960s, the USA saw a rise in research on second-generation robots with sensors and “sensing” capabilities, progressing towards artificial intelligence.
In the mid-1960s, robot laboratories were established at MIT, Stanford University, and the University of Edinburgh, among others, marking a rise in research on second-generation robots with sensors and “sensing” capabilities, progressing towards artificial intelligence.
■ Second Generation Robots: Sensing Robots
These sensing robots are similar to humans in certain sensory functions, such as force perception, touch, and hearing, to assess the magnitude of forces and sliding conditions.
◆ In 1968, the world’s first intelligent robot was born.
In 1968, the Stanford Research Institute announced the successful development of the Shakey robot. It was equipped with visual sensors and could discover and grasp blocks based on human commands, although the computer controlling it was as large as a room, making it the world’s first intelligent robot.
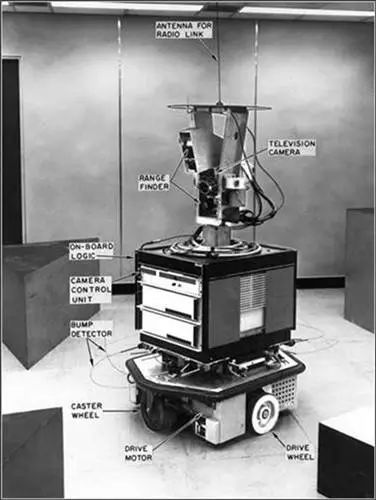
In 1968, the world’s first intelligent robot was born, equipped with visual sensors to discover and grasp blocks based on human commands.
In 1978, the American company Unimation launched the universal industrial robot PUMA, marking the complete maturity of industrial robot technology. PUMA is still operational in factories today.

In 1978, the American company Unimation launched the universal industrial robot PUMA, marking the complete maturity of industrial robot technology.
In 1999, Sony Corporation in Japan launched the dog-like robot AIBO, which sold out immediately, marking one of the pathways for entertainment robots to enter ordinary households.
◆ In 2002, American company iRobot launched the vacuum cleaning robot Roomba.
In 2002, American company iRobot launched the vacuum cleaning robot Roomba, which can avoid obstacles, autonomously design its travel route, and return to its charging dock when low on battery. Roomba is currently the world’s best-selling household robot.
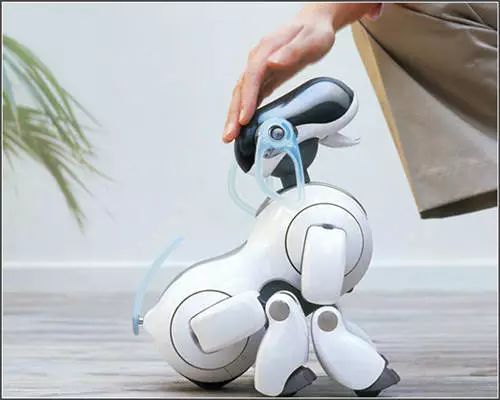

In 2002, American company iRobot launched the vacuum cleaning robot Roomba.
In June 2006, Microsoft launched Microsoft Robotics Studio, marking a trend towards modularity and platform unification in robotics. Bill Gates predicted that household robots would soon sweep the globe.
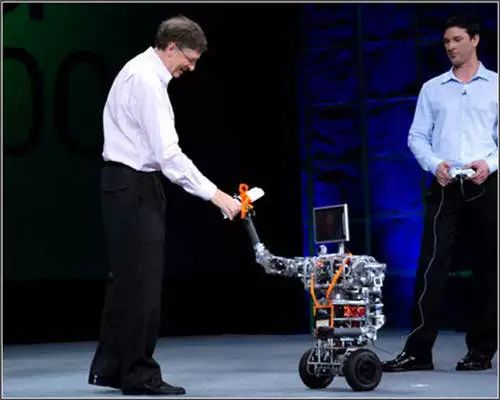

In June 2006, Microsoft launched Microsoft Robotics Studio.
◆ In 2012, a robotic astronaut was sent into space.
The final space mission of the Discovery Space Shuttle was to send the first humanoid robot to the International Space Station. This robotic astronaut was named “R2”, capable of performing tasks too dangerous for human astronauts. NASA stated, “As we move beyond low Earth orbit, these robots are crucial for NASA’s future.”
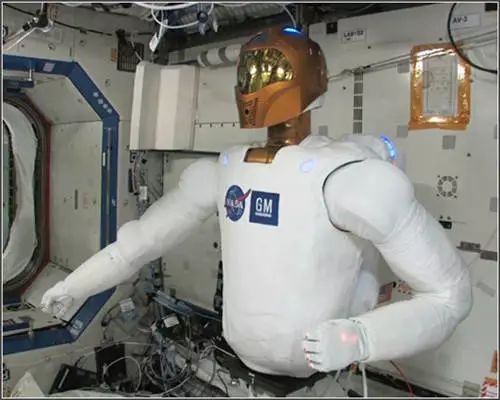

The robotic astronaut was named “R2”, capable of performing tasks too dangerous for human astronauts.
In 2014, at the 116th China Import and Export Fair, the robot “Benebot” (旺宝) from Ecovacs could enthusiastically greet visitors. This shopping robot can engage in video or audio conversations with humans, allowing consumers to quickly understand product information.

“Benebot” can engage in video or audio conversations with humans, allowing consumers to quickly understand product information.
Artificial intelligence is humanity’s simulation of “intelligence”, aiming to achieve tasks that humans can complete. However, it is limited by our understanding of intelligence. Even with neural network models and genetic algorithm training, the program itself will not evolve new capabilities; it can only accept training and cannot create new things. Currently, artificial intelligence can be seen as just a tool.
■ Third Generation Robots: Intelligent Robots
The ideal stage pursued is intelligent robots that can complete tasks just by being told what to do. Current development remains relatively limited to specific concepts and meanings. From a realistic perspective, since its inception, artificial intelligence has matured in theory and technology, with its application fields continuously expanding. It is conceivable that the emergence of AI robots as depicted in movies is not mere fantasy.
◆ Idea One: Intelligent robots can think and act like humans, even surpassing humans in many aspects.
In many movies, humans attempt to understand the essence of human intelligence and produce a new type of intelligent robot that reacts similarly to human intelligence. For instance, the robot Chappie from the recently released “Chappie” and Ultron from “Avengers 2” both represent AI robots capable of thinking and acting like humans, with the potential to surpass humans in many aspects.

Intelligent robots can think and act like humans, even surpassing humans in many aspects (Image source: comicvine)
◆ Idea Two: Self-learning and growth are believed to be realizable in the future.
In the movie “Chappie”, the reformed robot Chappie awakens like a human infant, possessing self-awareness and continuously growing while observing and understanding the world around him. Chappie has emotions towards humans, fears death, has a talent for art, and a desire to learn. Aside from being a machine, he appears no different from humans. The scene depicted in the movie of intelligent robots self-learning and growing is believed to be realizable in the future.

In the future, intelligent robots will possess self-awareness and continuously grow while observing and understanding the world around them (Image source: blog.naver)
◆ Idea Three: Breaking the Three Laws could make them humanity’s most formidable enemies.
The famous “Three Laws of Robotics” created by science fiction writer Isaac Asimov in 1942 are considered crucial for the peaceful coexistence of humans and robots. However, Ultron not only completely violates these laws but also creates a brutal robot army like himself, becoming humanity’s most formidable enemy.

Breaking the “Three Laws of Robotics” and creating a brutal robot army like himself.
Artificial intelligence holds immense potential, and it is crucial to explore how to utilize it while mitigating potential risks. AI systems should fulfill the responsibilities we wish them to execute. Therefore, some firmly believe that artificial intelligence and intelligent robots will have significant utility in the future.
■ In Conclusion:
As a new generation of production and service tools, intelligent robots are increasingly participating in our lives to serve us. However, some workers at the forefront of technology are not optimistic, stating that if artificial intelligence develops autonomously and redesigns itself at an accelerated pace, humanity, limited by slow biological evolution, may not compete and could ultimately be replaced. Regardless, the original intention of robots is to serve humanity. If humans cannot control the potential risks of artificial intelligence within acceptable limits, the consequences may be beyond our capacity to bear.
Source: Zhongguancun Online
