
PLC control cabinets can adapt to various scales of industrial automation control scenarios. The PLC control cabinet has a compact structure, stable operation, and complete functions. It can be combined according to the actual control scale, achieving both single-cabinet automatic control and multiple cabinets forming a distributed control system (DCS) through industrial Ethernet or fieldbus networks.
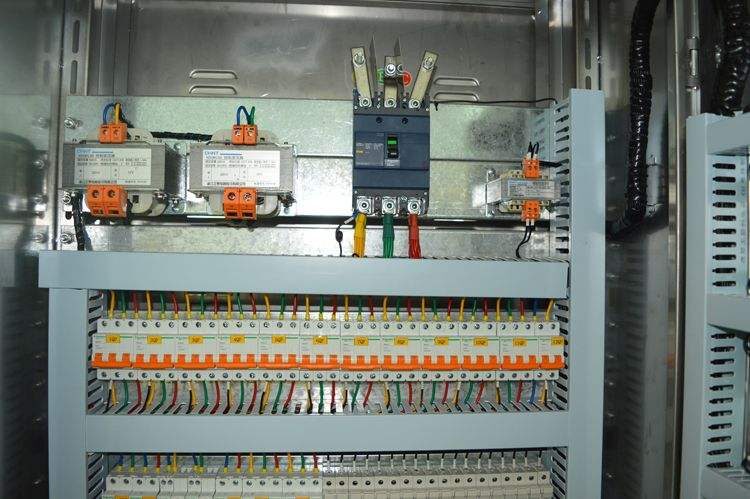
PLC control cabinets consist of air switches, power supplies, PLCs, relays, terminals, wiring ducts, signal isolators, distribution devices, safety barriers, and other equipment. The specific introduction is as follows: Switches, circuit breakers, contactors, and motor protection devices are designed and selected with redundancy in capacity and specifications to meet the reliable operation requirements of the electrical system. The control cabinet is equipped with a main power circuit breaker, and each load and control power supply has a separate circuit breaker, with terminals for power input and output. The cabinet should use national standard wires for connecting cables, neatly bundled and laid in cable trays. The wiring of primary devices should use phase color differentiation and numbered heads. The cabinet color follows the “Paint Film Color Standard Color Card” GSB05-1426-2001 specified by the National Coatings and Color Standardization Technical Committee, specifically 82 Y13 light yellow-gray, and requires consistency inside and out; the control cabinet sealing must meet the IP65 protection level.
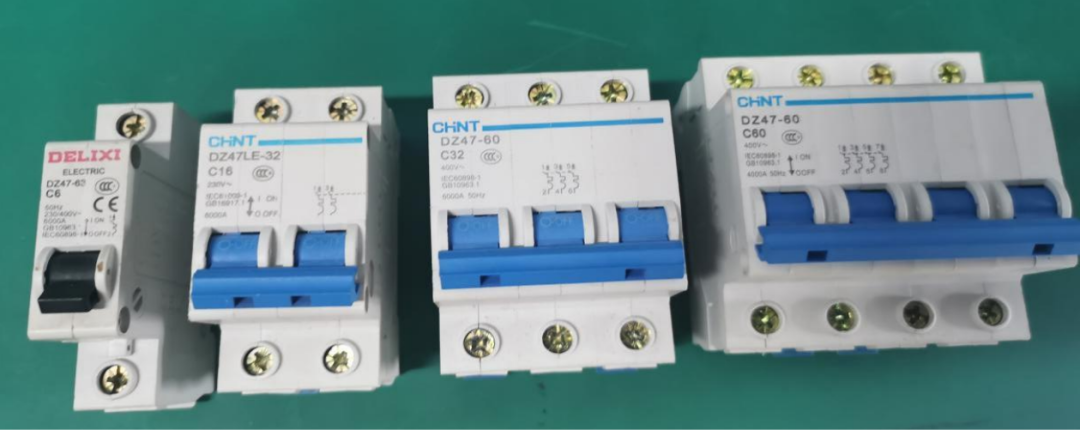
A、 Air Switch: This is the power control for the entire cabinet.

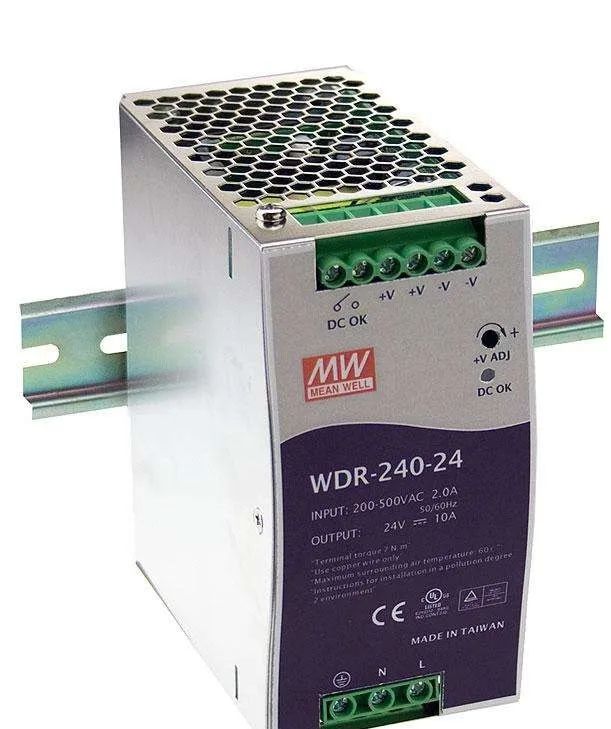
B、 24VDC Switching Power Supply: Most PLCs come with a 24VDC power supply, and whether to use a switching power supply depends on the needs.



C、 Programmable Logic Controller (PLC): Usually selected based on engineering needs, the basic elements for choosing a PLC include stable performance, reliable operation, high cost-effectiveness, simplicity, practicality, ease of expansion, and strong compatibility. For larger or more critical projects, PLC redundancy (i.e., two sets in alternating use) should also be considered. This should be selected according to engineering needs. For smaller projects, a single integrated PLC may suffice, while larger projects may require modular or card-based systems, and may also need redundancy (i.e., two sets in alternating use).

D、 Terminals and Wiring Ducts: The number of terminals is determined by the number of input and output circuits. This is an essential component for every cabinet, which can be configured according to the number of signals. If powering certain field instruments or small control boxes, you may need to increase the number of air switches. Or if you need to connect the PLC to a host computer, you may need to add switches etc. Wiring ducts are used for wiring within the PLC cabinet, and their specifications are determined by the number of cables inside the cabinet.

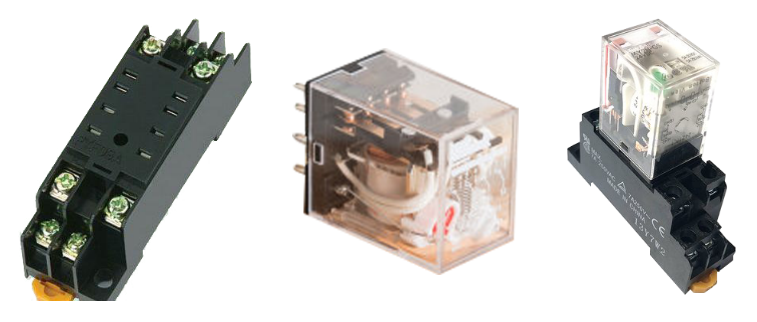
E、 Relays: Generally, the PLC can directly send commands to the control circuit, but it may also go through a relay. If the output of your PLC is 24VDC, but the control circuit requires a node that needs 220VAC, then you must add a relay at the PLC output. When the command is sent, the relay operates, and the control circuit’s node connects to the relay’s normally open or normally closed point. The use of relays is also based on the situation. The programmable controller’s DO output should not directly enter the external control circuit; it should be passed through a high-performance intermediate relay (coil voltage DC24V), which is beneficial for extending the service life and safety of the PLC DO output module. The number of intermediate relay contacts should be selected based on needs, either two normally open/two normally closed types or four normally open/four normally closed types..
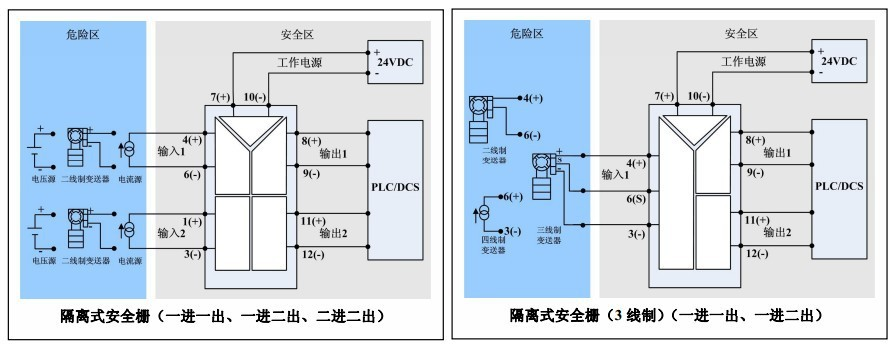
F、 Signal Isolators and Distributors: Using signal isolators and distributors can enhance the entire system’s anti-interference capability and stability. Field two-wire transmitter signals are converted into 4-20mA signals sent to the programmable controller’s AI input; various external signals such as 4-20mA, 0-5V, 0-20mA, etc., are converted into 4-20mA signals and sent to the programmable controller’s AI input through signal isolators.

G、 Safety Barriers: If the programmable controller’s AO output or DI output needs to be sent to a hazardous area, the corresponding safety barriers should be selected according to requirements.
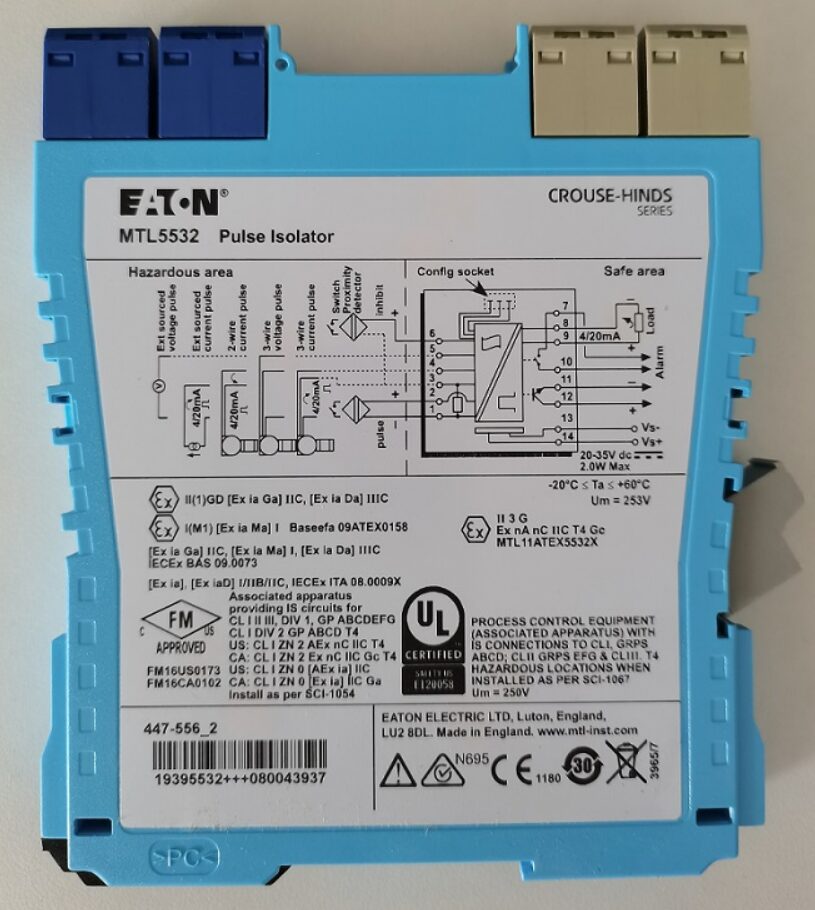
H、 Other Equipment:: The PLC cabinet usually also includes buttons, signal lights, contactors, inverters, switches, human-machine interface touch screens, and other devices.

Note: The above is organized by Teacher Luo Bing from Industrial Control Help, and if there are any copyright issues regarding the videos, images, or texts used in this article, please notify us immediately. We will confirm copyright based on the materials you provide and pay remuneration according to national standards or delete the content immediately! The content of this article reflects the original author’s views and does not represent the views of this public account or its authenticity.
—THE END—
Click to give the editor a thumbs up