
Currently, the communication for vehicle control in new energy vehicles is mainly based on the CAN bus. Almost all Electronic Control Units (ECUs) communicate via the CAN bus, including BMS, braking systems, motor control, etc. Since the vehicle CAN bus messages contain real-time data from key system components, parsing the vehicle CAN bus message data can provide the necessary signal support for vehicle benchmarking analysis, greatly improving the efficiency of this analysis.

Benchmark Analysis Based on CAN Signal Parsing
However, parsing vehicle CAN signals involves a series of issues such as ID filtering, protocol algorithms, and signal extraction. In recent years, vehicle manufacturers have utilized gateways to filter and encrypt CAN message data for vehicle information security, further increasing the difficulty of parsing vehicle CAN signals. The China Automotive Technology and Research Center (CATARC) has developed a mature CAN signal parsing process after years of research and application, ensuring high efficiency and accuracy in signal parsing.
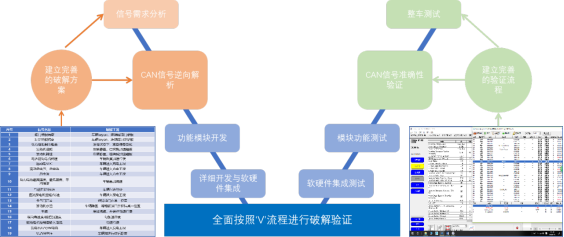
CAN Signal Parsing Process
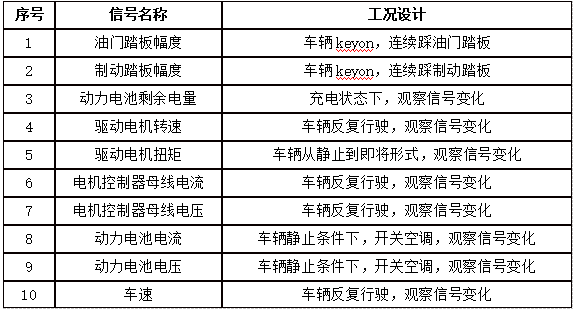
The foundation for conducting vehicle CAN signal parsing is to confirm the signal parsing list. Due to variations in structure and working principles among different vehicle models, such as EV, HEV, PHEV, and FCV, the types of signals also differ. Therefore, it is necessary to propose a corresponding signal parsing list based on the characteristics of the vehicle model while supplementing it according to benchmarking analysis needs.
Automobile CAN lines generally use twisted pairs of different colors (twisted pairs can improve anti-interference capability), one for high-level CAN_H, with a voltage between 2.5-3.5V, and the other for low-level CAN_L, with a voltage between 1.5-2.5V, and the sum of the two voltages is approximately 5V. The CAN line can be confirmed by measuring high and low levels, and resistance measurement can also be used.

Power CAN for a Certain Vehicle Model
Parsing vehicle CAN messages requires understanding the meanings of CAN message IDs and fields. Based on the characteristics of the signals being parsed, design the working conditions that trigger changes in signal parameters, minimizing interference from other signals during the process. For example, for throttle position signals, changes can be made to the throttle position while stationary to trigger parameter changes. This process helps lock the position, data type, coefficient, and offset of the signal message.
Signal Parsing Condition Design
To address the signal parsing challenges posed by gateway filtering and encryption, the CATARC team has developed a CAN signal parsing module. This module is based on the communication protocols of various control system signals and can communicate in real-time with internal vehicle controllers to obtain signals masked by the gateway and send them to the CAN line, ensuring signal integrity.
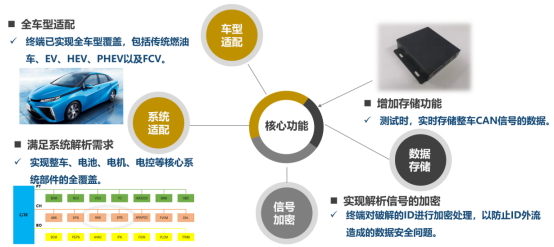
Vehicle CAN Signal Parsing Module
The validation of parsed signals is primarily done by comparing them with the displays of vehicle instruments, sensors, and onboard diagnostic devices to verify whether the values or states are consistent. If the values and states are consistent, it indicates that the signal parsing is correct. The validation work for parsed signals is mainly conducted based on the established working conditions, ensuring consistency between the validation conditions for each signal and the conditions set during the parsing process.
By relying on the construction of the above CAN signal parsing process system and developing CAN signal parsing software and hardware tools, CATARC has widely provided vehicle CAN signal parsing services in the industry. To date, over 50 vehicle models have been parsed, covering most mainstream competing vehicle models both domestically and internationally, with more than 15 enterprises served. Additionally, to meet personalized customer needs, CATARC can provide diverse service options such as “menu selection,” “customization,” and “CAN parsing assistant” products to support enterprises in conducting vehicle benchmarking analysis.
Business Contacts
Lei Nanlin
Zhao Ziqi