The “Interim Regulations on the Flight Management of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles” (State Order No. 761) issued by the State Council of the People’s Republic of China and the Central Military Commission of the People’s Republic of China will officially take effect on January 1, 2024.
Classification of Civil Unmanned Aerial VehiclesUnmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) refer to aircraft that do not have onboard pilots and are equipped with their own power systems. They are classified based on performance indicators such as empty weight, takeoff weight, and flight speed into: micro, light, small, medium, and large categories.(1) Micro Unmanned Aerial Vehicles, refer to UAVs with an empty weight of less than 0.25 kilograms, a maximum flight altitude not exceeding 50 meters, and a maximum horizontal flight speed not exceeding 40 kilometers per hour. They must comply with low-power short-range technical requirements for radio transmission equipment and can be manually controlled at any time during the flight.(2) Light Unmanned Aerial Vehicles, refer to UAVs with an empty weight not exceeding 4 kilograms and a maximum takeoff weight not exceeding 7 kilograms, a maximum horizontal flight speed not exceeding 100 kilometers per hour, and must have the capability to maintain airspace in accordance with airspace management requirements and reliable monitoring capabilities. They can be manually controlled at any time during the flight, excluding micro UAVs.(3) Small Unmanned Aerial Vehicles, refer to UAVs with an empty weight not exceeding 15 kilograms and a maximum takeoff weight not exceeding 25 kilograms, which must have the capability to maintain airspace in accordance with airspace management requirements and reliable monitoring capabilities. They can be manually controlled at any time during the flight, excluding micro and light UAVs.(4) Medium Unmanned Aerial Vehicles, refer to UAVs with a maximum takeoff weight not exceeding 150 kilograms, excluding micro, light, and small UAVs.(5) Large Unmanned Aerial Vehicles, refer to UAVs with a maximum takeoff weight exceeding 150 kilograms.Real-name RegistrationAccording to the regulations, owners of civil unmanned aerial vehicles must register their UAVs under their real names in accordance with the law, regardless of type and weight, and must complete real-name registration for their UAVs before flying.Violations of this regulation, where civil unmanned aerial vehicles are flown without real-name registration, will result in a correction order from the public security authorities, and a fine of up to 200 yuan may be imposed; in severe cases, fines ranging from 2,000 to 20,000 yuan may be imposed.The real-name registration process is as follows:(1) Access the Civil Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Comprehensive Management Platform (UOM) at: https://uas.caac.gov.cn
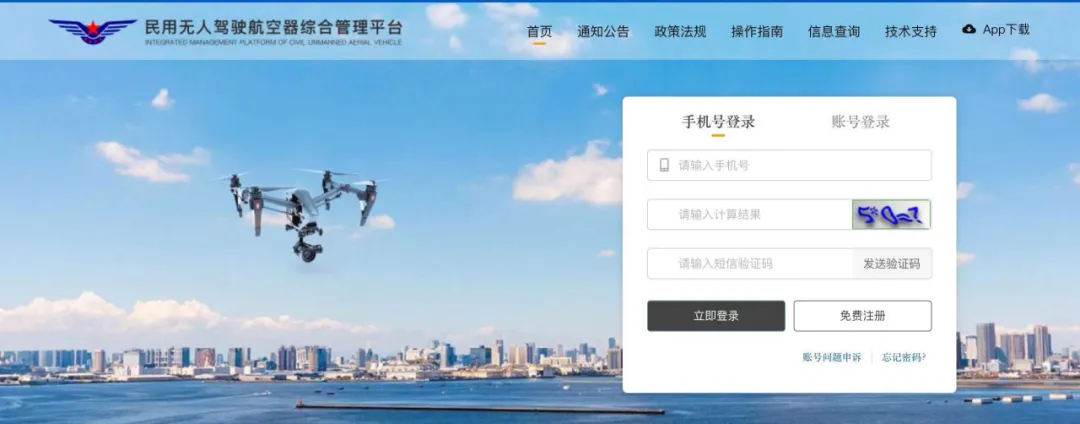
(2) Register the UAV. After logging in, go to the homepage—click on the registration management in the upper right corner—real-name registration—register the brand UAV—verify the owner’s information—scan the QR code for face verification—select the manufacturer’s name—select the model and other relevant information (the serial number must be entered manually)—upload photos as required—complete the registration.
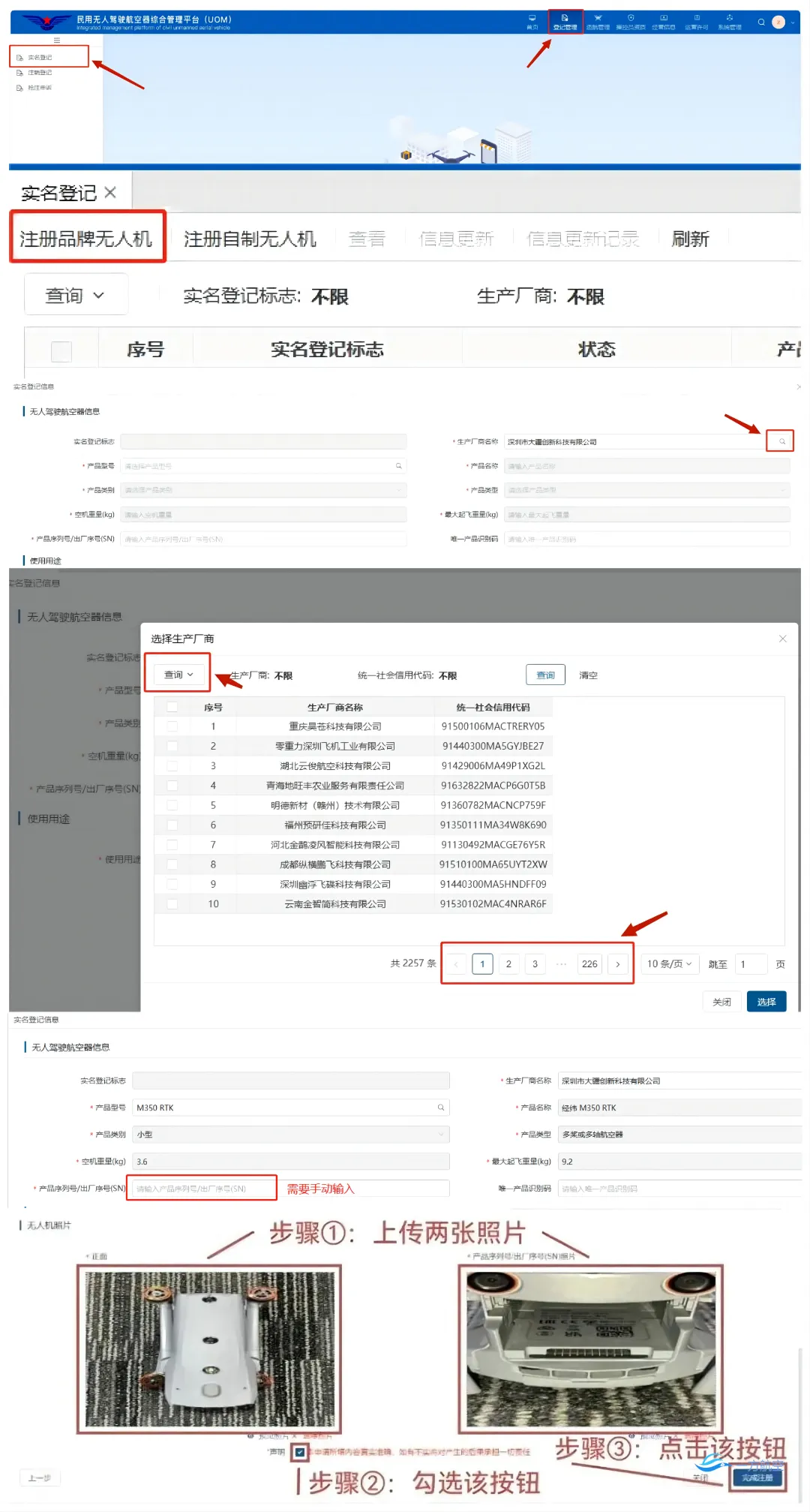
(3) After completing the registration, you can check the registered UAVs on the real-name registration page, click the “Send QR Code” button on the right, fill in your email, download the attachment and print it, and paste the QR code onto the UAV’s body.
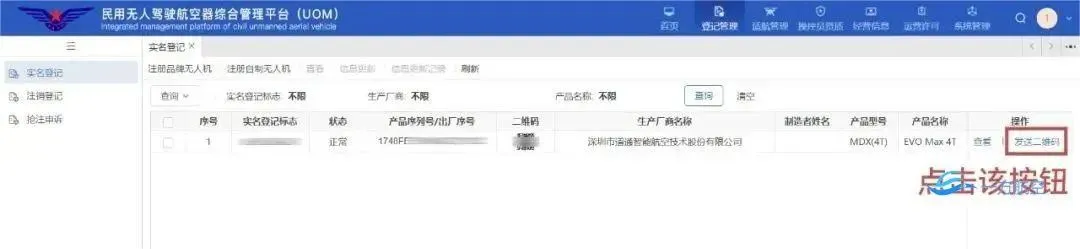
Flight DeclarationArticle 19 of the regulations states: Airspace above 120 meters, restricted airspace, military low-altitude flight airspace, airport and surrounding areas, military restricted areas, important revolutionary memorial sites, and other areas should be designated as controlled airspace.If you need to fly within controlled airspace, you must submit a flight application to the corresponding air traffic control authority in advance and obtain permission before flying.Controlled airspace includes:(1) Airports and surrounding areas;(2) Areas within a certain range on our side of the national border, actual control line, and boundary line;(3) Military restricted areas, military management areas, and surrounding areas of sensitive units;(4) Protection areas for important military industrial facilities, nuclear facility control areas, areas for the production and storage of flammable and explosive materials, and large storage areas for combustible important materials;(5) Public infrastructure such as power plants, substations, refueling stations, water supply plants, public transport hubs, aviation electronic hubs, major water conservancy facilities, ports, highways, electrified railway lines, and surrounding areas, as well as drinking water source protection areas;(6) Facilities requiring special electromagnetic environment protection such as radio astronomy observatories, satellite measurement and control (navigation) stations, aviation radio navigation stations, and radar stations, and surrounding areas;(7) Important revolutionary memorial sites, important immovable cultural relics, and surrounding areas;(8) Other areas specified by the national air traffic management authority.For micro, light, and small unmanned aerial vehicles, the regulations specifically designate permissible flight airspace: airspace below 120 meters (excluding controlled airspace) is permissible for free flight without the need to submit a flight activity application.It is important to note:Organizing flight activities for micro, light, and small unmanned aerial vehicles in permissible flight airspace, if there are five situations such as relay flights through communication base stations or the internet, carrying dangerous goods or dropping items (excluding conventional agricultural UAV operations), flying over crowds, controlling UAVs from moving vehicles, or implementing distributed operations or swarming, must also submit a flight activity application.Violations of the regulations, where micro, light, and small civil unmanned aerial vehicles are operated in controlled airspace without approval, or where model aircraft are operated outside the airspace designated by air traffic management authorities, will result in a correction order from the public security authorities, and a fine of up to 500 yuan may be imposed; in severe cases, the UAV used for illegal flight will be confiscated, and fines ranging from 1,000 to 10,000 yuan may be imposed.Flight Declaration Guidelines:The Civil Aviation Administration of China issued an announcement on December 31, 2023, regarding the supervision and service of civil unmanned aerial vehicles, stating that units or individuals organizing UAVs must submit a flight activity application through the Civil Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Comprehensive Management Platform (UOM) at least 12 hours before the planned flight.After logging in, go to the homepage—click on the operation management in the upper right corner—flight activity application—general flight activity.
Controlling Small, Medium, andLarge
Unmanned Aerial Vehicles
Requires Obtaining a License
According to Article 16 of the regulations, personnel operating small, medium, and large civil unmanned aerial vehicles must meet the following conditions and apply to the civil aviation authority of the State Council for the corresponding civil unmanned aerial vehicle operator license (hereinafter referred to as the operator license):(1) Must have full civil capacity;(2) Must have received safety operation training and passed the assessment by the civil aviation management department;(3) Must not have a medical history of diseases that may affect the operation of civil unmanned aerial vehicles, nor a record of drug abuse;(4) Must not have a criminal record for intentional crimes that endangered national security, public safety, or infringed on the personal rights of citizens, or disturbed public order within the last five years.Personnel engaged in conventional agricultural UAV operations do not need to obtain an operator license but must be trained and assessed by the UAV system manufacturer according to the regulations of the civil aviation and agricultural authorities of the State Council, and obtain an operation certificate upon passing.Violations of the regulations, where individuals operate civil unmanned aerial vehicles without obtaining an operator license, will be subject to penalties by the civil aviation management department.Minors Flying Must NoteIndividuals without civil capacity can only operate micro civil unmanned aerial vehicles, while individuals with limited civil capacity can only operate micro and light civil unmanned aerial vehicles.Individuals without civil capacity operating micro civil unmanned aerial vehicles or individuals with limited civil capacity operating light civil unmanned aerial vehicles must be guided on-site by individuals with full civil capacity (who must meet the conditions for obtaining an operator license).Violations of the regulations by individuals without civil capacity or individuals with limited civil capacity operating civil unmanned aerial vehicles will result in fines of 500 to 5,000 yuan imposed on their guardians by the public security authorities; in severe cases, the UAV used for illegal flight will be confiscated.(Note: Minors over eight years old are considered individuals with limited civil capacity; minors under eight years old, individuals who cannot recognize their actions, or minors over eight years old who cannot recognize their actions are considered individuals without civil capacity.)Foreign Drones and Personnel Must NoteViolations of the regulations, where foreign unmanned aerial vehicles or unmanned aerial vehicles operated by foreign personnel conduct surveying flights within China, will result in orders from the surveying and geographic information authorities of the county level or above to stop illegal activities, confiscation of illegal gains, surveying results, and the UAV used for illegal flights, and fines ranging from 100,000 to 500,000 yuan; in severe cases, fines ranging from 500,000 to 1,000,000 yuan, with the public security and national security authorities determining the deadline for exit or expulsion.
Source: Public Security Bureau, Comprehensive Huizhou Police
Editor: Rong Qianyi
Proofreader: Shan Yuqi
Reviewer: Cai Zhen
