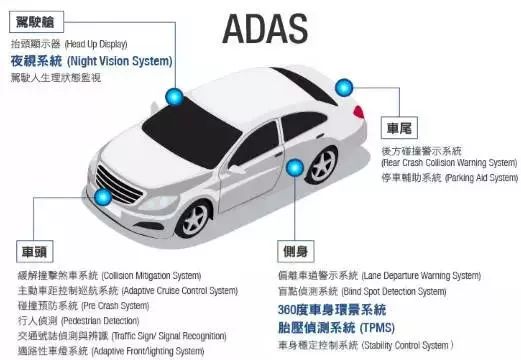
Based on functionality, ADAS can be classified into:
-
Active Control ADAS: ACC/AEB/LKS, etc.
-
Warning ADAS: FCW/LDW/PCW, etc.
-
Other Assistive ADAS: BSD/ADB/Parking Assistance, etc.
Let’s take a look at how each feature is implemented.
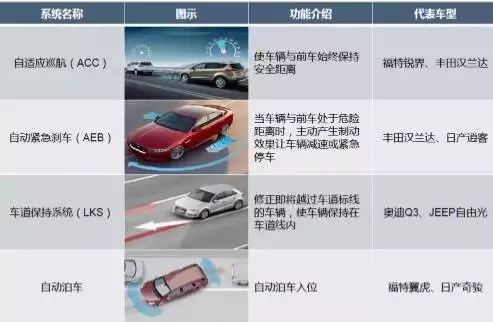
Adaptive Cruise Control System (ACC)
The Adaptive Cruise Control system is an intelligent automatic control system developed based on the existing cruise control technology. During vehicle operation, the distance sensor (radar) installed at the front of the vehicle continuously scans the road ahead, while the wheel speed sensor collects speed signals. When the distance to the vehicle in front is too small, the ACC control unit can coordinate with the Anti-lock Braking System and Engine Control System to appropriately brake the wheels and reduce engine output power, ensuring that the vehicle maintains a safe distance from the vehicle ahead.

Autonomous Emergency Braking (AEB)
AEB is an active safety technology in vehicles, mainly consisting of three modules. The core of the distance measurement module includes microwave radar, laser radar, and video systems, which can provide safe, accurate, and real-time images and road condition information ahead.
The AEB system uses radar to measure the distance to the vehicle or obstacle in front, then compares the measured distance with the warning distance and safe distance using a data analysis module. If the measured distance is less than the warning distance, an alert is triggered; if it is less than the safe distance, the AEB system will activate even if the driver has not had time to press the brake pedal, automatically braking the vehicle to ensure safety.
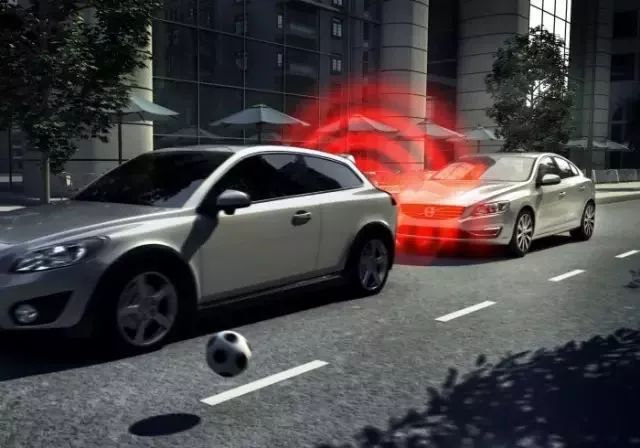

Adaptive Front Lights (AFL)
This is a technology that can be installed on vehicles to change the direction of headlights based on the shape of the road. Other intelligent headlight control systems can adjust the intensity of the headlights according to vehicle speed and road conditions.
Blind Spot Monitoring (BSM)
The blind spot detection system uses collision radar, Doppler radar, infrared radar, and other sensors arranged around the vehicle. Controlled by a computer, it provides necessary information about the vehicle’s surroundings to the driver through sound and light (a small light flashing on the side mirror) in hazardous situations such as overtaking, reversing, lane changing, fog, or rain, and can automatically take measures to effectively prevent accidents.
Driver Monitoring Systems (DMS)
This system uses sensors to monitor the driver’s attention. If the driver is looking straight ahead and a crisis situation is detected, the system will issue a warning with flashing lights and a loud sound. If the driver does not respond, the vehicle will automatically brake.

Forward Collision Warning (FCW)
FCW can monitor the distance, position, and relative speed between the vehicle and the vehicle in front using radar and cameras, warning the driver of potential collision risks.
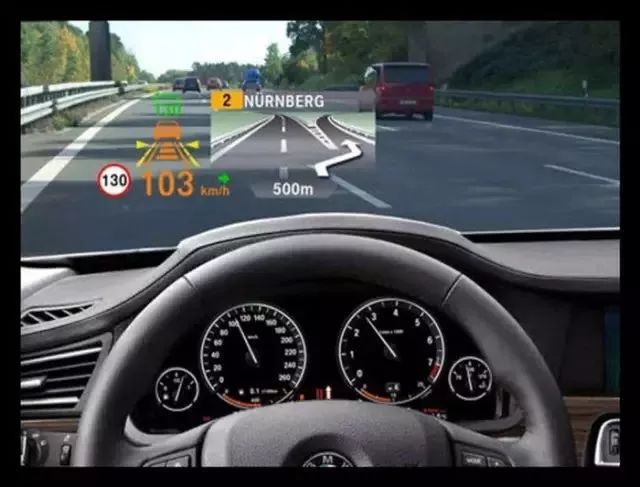
Heads-Up Display (HUD)
This technology projects important information (such as speed) onto the windshield during vehicle operation, helping inexperienced drivers control their speed and avoid violations due to speeding in many speed limit zones. More importantly, it allows drivers to read information instantly without shifting their gaze, maintaining optimal observation conditions.
Intelligent Speed Adaptation (ISA)
The Intelligent Speed Adaptation system can recognize traffic signs and control the throttle based on the maximum speed limit information read, ensuring that the driver operates within legal speed limits and effectively avoiding unintentional speeding.
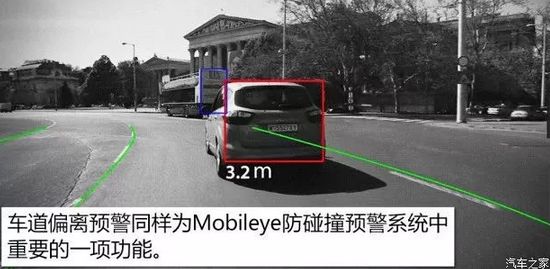
Lane Departure Warning (LDW)
The lane departure warning system mainly consists of a HUD, camera, controller, and sensors. When the lane departure system is activated, the camera (usually placed on the side of the vehicle or at the rearview mirror) continuously collects lane marking data, processing images to determine the vehicle’s position in the lane. If the vehicle drifts out of the lane, the sensors collect vehicle data and driver status, and the controller issues a warning signal, completing this process in about 0.5 seconds to provide the driver with more reaction time. If the driver signals a lane change, the system will not provide any alerts.
Night Vision System (NVS)
The night vision system uses infrared technology to illuminate darkness as if it were daylight, allowing the driver to see further and clearer at night. The system consists of two parts: an infrared camera and a light display system on the windshield.
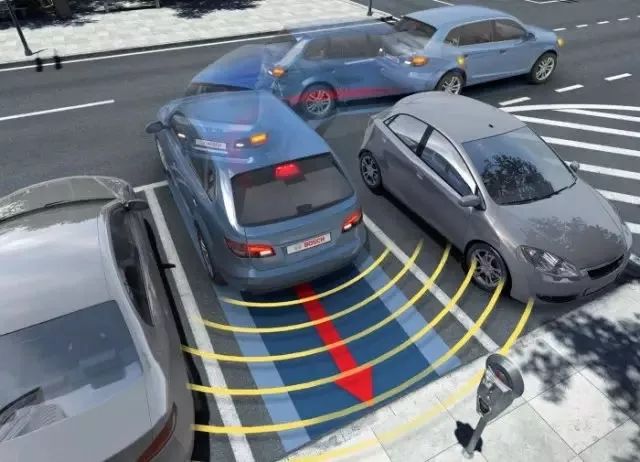

Parking Assistance (PA)
The parking assistance system detects parking spaces using cameras, ultrasonic sensors, and infrared sensors installed on the vehicle, creating a parking map and dynamically planning the parking path, guiding or directly controlling the steering wheel to park the vehicle.
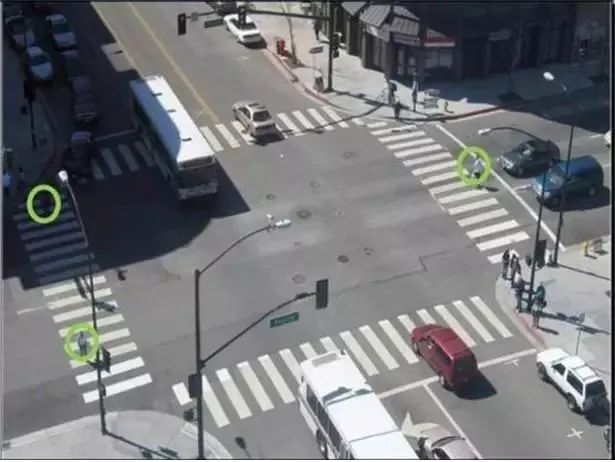

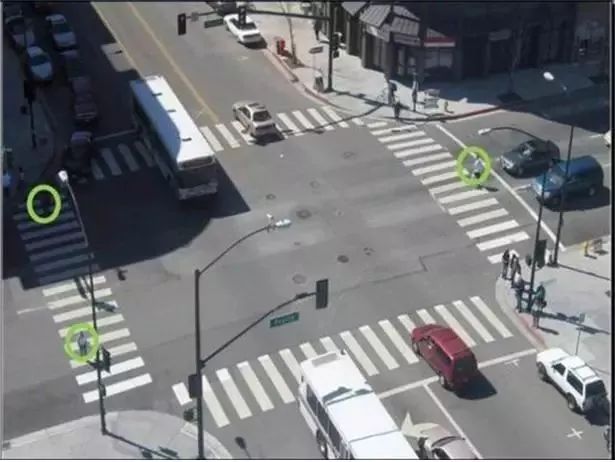
Pedestrian Detection System (PDS)
The system can detect pedestrians around the vehicle using camera radar and laser radar while controlling speed within a safe distance.

Road Sign Recognition (RSR)
This technology allows vehicles to automatically recognize traffic signals or signs, such as speed limits or stop signs.
Surround View Cameras (SVC)
The surround view camera system consists of four ultra-wide-angle fisheye cameras installed around the vehicle, collecting images of the surroundings. Through image processing, distortion correction, perspective transformation, image stitching, and enhancement, a seamless 360-degree overhead view around the vehicle is created. While displaying the panoramic image, the system can also show a single view from any side and accurately locate obstacles with reference lines.
Additionally, Mobileye has released a collision warning system that includes six ADAS features.
1. Distance Monitoring and Warning HMW
2. Forward Collision Warning FCW

3. Lane Departure Warning LDW
4. Intelligent High Beam Control IHC

5. Speed Limit Warning SLI

6. Pedestrian and Bicycle Warning PCW

Source: AI Automotive Manufacturing
—End—
Further Reading Click the Title
☞What is the Level of Domestic Car Brand Engines? Read to Be Completely Impressed
☞March 2018 Passenger Car Market Analysis Expected to Decline Month-on-Month in April
☞Major Mergers and Acquisitions in Automotive Parts Companies: Chinese Buyers Shine
☞National Independent Brand Car Production Base and Model Overview 2018 Collector’s Edition
☞Research Report | Analysis of Geely Automobile’s New Energy Business Planning and Layout
☞February 2018 Car Sales Ranking: Baojun 510 Breaks Haval H6 Sales Myth
☞NIO Automobile Business Planning and Industry Layout Analysis Report
☞Automobile Brand Reliability Ranking Released: Genesis Surpasses Audi to Rank First
☞Distribution of Vehicle Manufacturing Bases and Parts Company Directory Across Provinces
☞Exploring Geely Automobile’s Four Major R&D Centers, Revealing the Geely Car Kingdom
☞Overview of New Factories Established by Major Domestic and Foreign Automotive Parts Companies in China in 2017
☞Overview of Geely Automobile’s 14 Production Bases and Model Capacity Distribution
☞Exploring BAIC New Energy’s Vehicle Plant, Models, Capacity Layout, and Production Base
☞Comprehensive Distribution of Vehicle Manufacturing Bases Across Provinces (Updated Version)
☞Distribution Map of Joint Venture Brand Automakers’ Factories and Model Capacity Layout in China
▼ Click Here to See More Exciting Articles from Gaishi