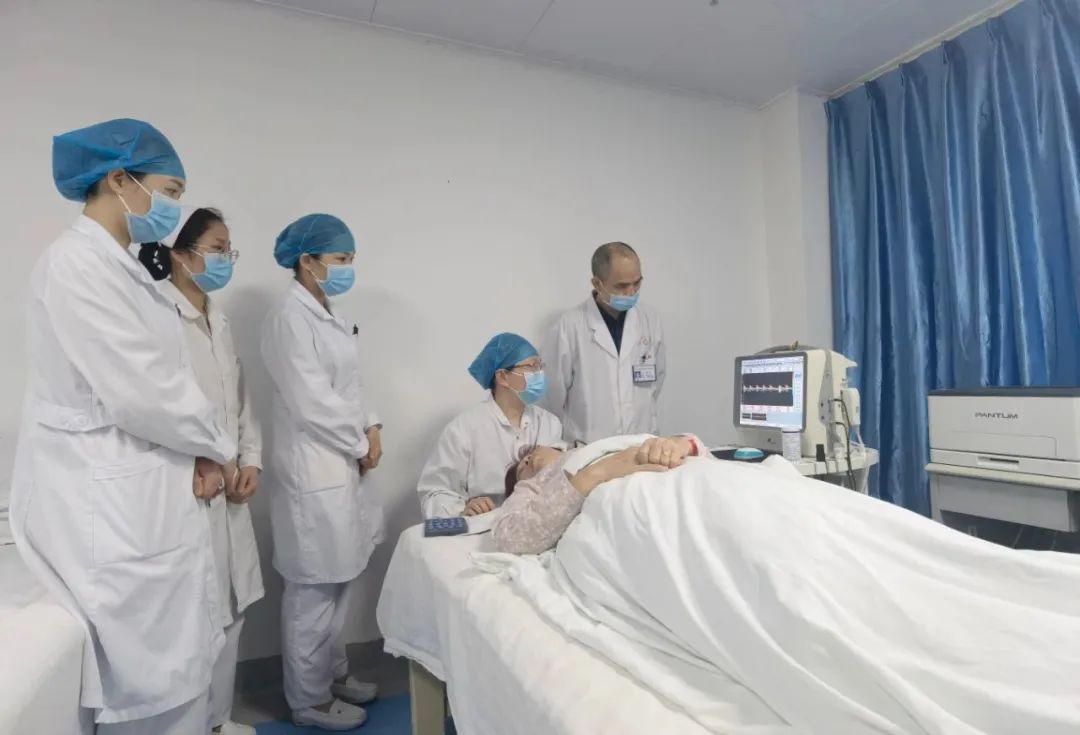

Recently, our hospital has introduced a multifunctional vascular ultrasound device for the neurology department, which is now in regular use. This device can quickly diagnose intracranial arterial vascular lesions and provide a more comprehensive assessment of the intracranial arterial blood vessels, allowing for more accurate diagnoses.
Transcranial Doppler (TCD) is a new technology that utilizes the Doppler effect of ultrasound to study the hemodynamics of large blood vessels inside and outside the skull. Because TCD can non-invasively penetrate the skull, it is easy to operate and has good reproducibility, allowing for continuous and long-term dynamic observation of patients. It mainly examines whether there are deformities in the middle cerebral artery, anterior cerebral artery, and posterior cerebral artery, whether the vessels are narrowed, and whether there are changes in blood flow velocity. Therefore, it has significant importance in evaluating cerebrovascular diseases and differential diagnosis.
Department Phone: 0770-3299126
1
Who Are the Suitable Candidates for Transcranial Doppler Examination?
1. Headache, dizziness, lightheadedness, vertigo, syncope;
2. Limb weakness, numbness, slurred speech;
3. Visual abnormalities such as blurriness, decreased vision, and dark spots;
4. Screening and postoperative review of carotid artery surgery;
5. Preoperative examination and risk assessment for high-risk surgical patients;
6. Routine health checkups, especially for high-risk cerebrovascular patients: hypertension, hyperlipidemia, diabetes, coronary heart disease, history of TIA, carotid artery bruits, and those with a family history of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases. This includes obese individuals, smokers, and drinkers.
2
Indications
1. Cerebral arteriosclerosis, to clearly determine the location and severity of cerebral arteriosclerosis.
2. Cerebral insufficiency, to determine the location (vessels) and degree of cerebral insufficiency.
3. Cerebral artery stenosis, to assess the location (vessels, segments) and degree of stenosis.
4. Cerebral vascular spasm, to evaluate the location (vessels) and degree of spasm.
5. Diseases of the vertebral artery and basilar artery system, to determine the location (vessels), nature (ischemia, occlusion, spasm), and degree of lesions.
6. Vertebral artery type cervical spondylosis, where transcranial Doppler testing is an important basis for diagnosis in addition to clinical symptoms and cervical spine X-ray films.
7. Subclavian steal syndrome.
8. Stenosis of the common carotid artery, external carotid artery, and internal carotid artery.



