

Digital measuring instruments have become mainstream because they are highly sensitive, accurate, clearly displayed, have strong overload capacity, are portable, and easier to use.

▲ Figure 1
Below, we will take this model of digital multimeter as an example to briefly introduce its usage and precautions.





1. Insert the black probe into the COM port and the red probe into the VΩ port.
2. Turn the function rotary switch to V~ (AC), V- (DC), and select the appropriate range.
3. Touch the red probe to the positive terminal of the circuit being tested and the black probe to the ground or negative terminal, effectively connecting it in parallel with the circuit being tested.
4. Read the digital value displayed on the LCD screen.
1. Turn off the power to the circuit.
2. Select the resistance range (Ω).
3. Insert the black probe into the COM input socket and the red probe into the Ω input socket.
4. Connect the probe tips across the two ends of the component or the part of the circuit whose resistance you want to measure.
5. Check the reading and confirm the measurement unit – ohms (Ω), kilohms (kΩ), or megohms (MΩ).
① Judging the Condition of the Diode
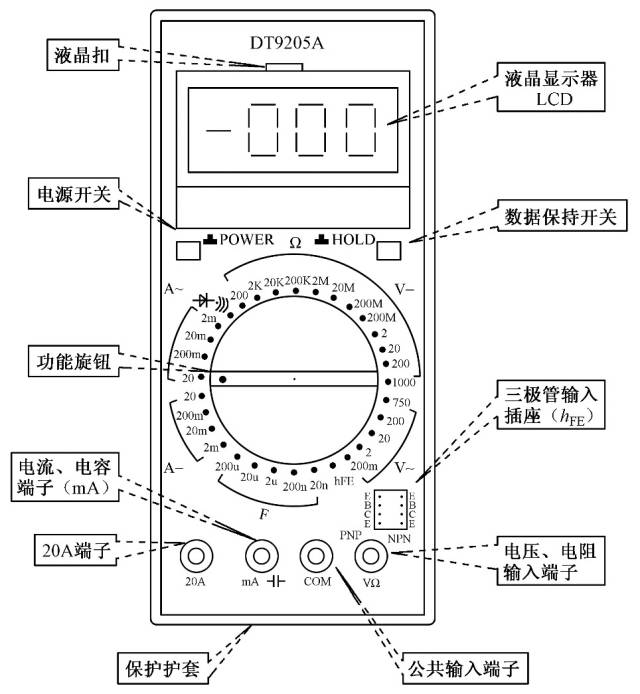
Set the dial to the ( 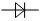 ) range, insert the red probe into the rightmost hole and the black probe into the second hole from the right. Connect the probe tips to the two terminals of the diode as shown in the image below, then reverse the probes and measure again.
) range, insert the red probe into the rightmost hole and the black probe into the second hole from the right. Connect the probe tips to the two terminals of the diode as shown in the image below, then reverse the probes and measure again.
Measurement Results: If the results from the two measurements are: one shows “1” and the other shows a small number, then this diode is a normal diode. If both measurements show the same result, then the diode is damaged, and the number displayed on the LCD is the forward voltage drop of the diode: about 0.6V for silicon and about 0.2V for germanium. Based on the characteristics of the diode, it can be determined that the red probe is connected to the positive terminal and the black probe is connected to the negative terminal.
The most important characteristic of a diode is:
▲ Unidirectional Conductivity
② Short Circuit Check (Judging Circuit Continuity):
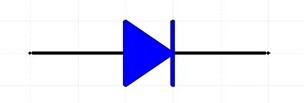
Set the dial to the short circuit (  ) range, with the probes positioned as above. Connect the other ends of the probes to the two points being tested; if these two points are indeed shorted, the multimeter’s buzzer will sound.
) range, with the probes positioned as above. Connect the other ends of the probes to the two points being tested; if these two points are indeed shorted, the multimeter’s buzzer will sound.
1. Disconnect the circuit;
2. Insert the black probe into the COM port and the red probe into the mA or 20A port;
3. Turn the function rotary switch to A~ (AC), A- (DC), and select the appropriate range;
4. Disconnect the circuit being tested and connect the digital multimeter in series with the circuit; the current in the circuit flows into the red probe from one end, out through the black probe, and back into the circuit;
5. Reconnect the circuit;
6. Read the digital value displayed on the LCD screen.
1. Short the two terminals of the capacitor to discharge it, ensuring the safety of the digital multimeter.
2. Turn the function rotary switch to the capacitance (C) measurement range and select the appropriate range.
3. Insert the capacitor into the C-X socket of the multimeter.
4. Read the digital value displayed on the LCD screen.
Quick Knowledge:Unit of Capacitance:
1F=1000mF=1000uF=1000nF=1000pF
1. If the voltage or current to be measured cannot be estimated in advance, first set it to the highest range to measure once, then gradually reduce the range to an appropriate position based on the situation. After measurement, set the range switch to the highest voltage range and turn off the power.
2. When at full scale, the instrument will only display the digit “1” in the highest position, with other positions disappearing; at this time, a higher range should be selected.
3. When measuring voltage, the digital multimeter should be connected in parallel with the circuit being tested. When measuring current, it should be connected in series with the circuit being tested, and when measuring DC, polarity does not need to be considered.
4. When mistakenly using the AC voltage range to measure DC voltage, or mistakenly using the DC voltage range to measure AC voltage, the display will show “000” or the digits will fluctuate in the lower position.
5. It is prohibited to change the range while measuring high voltage (above 220V) or large current (above 0.5A) to prevent arcing and burning out the switch contacts.
Disclaimer: This article is reproduced from the internet, and the copyright belongs to the original author. If there are copyright issues regarding the work, please contact us in a timely manner for deletion. Thank you!
Complete Question Bank for Beginner Electricians (with Answers) 2021
3 Essential Tools for Electricians, Easily Accessible via WeChat!
[Collection] The “Path” for a Veteran Electrician, Secrets to Earning Over Ten Thousand a Month!
The Top Five Electrical Drawing Software (CAD, Eplan, CADe_simu…), Which One Will You Pick?
The Latest Electrical CAD Drawing Software, with a Detailed Installation Guide!
The Latest Electrical Drawing Software EPLAN, with a Detailed Installation Guide!
Common Issues for Beginners Using S7-200 SMART Programming Software (with Download Links)
Comprehensive Electrical Calculation EXCEL Sheets, Automatically Generated! No Need to Ask for Electrical Calculations!
Bluetooth Headphones, Books for Electricians/PLC, Free to Claim Your Electrical Gifts!
Basic Skills of PLC Programming: Ladder Diagrams and Control Circuits (with 1164 Practical Cases for Mitsubishi PLC)
Still Can’t Understand Electrical Diagrams? Grab the Basics of Electrical Diagram Reading and Simulation Software, Quickly Get Started with Theory and Practice!
12 Free Electrician Video Courses, 10GB Software/E-books, 30 Days of Free Live Electrician Courses!
