1. Operating System Version
#include <windows.h> #include <iostream>
int main() { OSVERSIONINFOEX osvi; ZeroMemory(&osvi, sizeof(OSVERSIONINFOEX));
osvi.dwOSVersionInfoSize = sizeof(OSVERSIONINFOEX); if (GetVersionEx((OSVERSIONINFO*)&osvi)) { std::cout << "Operating System Version: " << osvi.dwMajorVersion << "." << osvi.dwMinorVersion << std::endl; }
return 0;}2. Retrieve CPU Information
#include <windows.h> #include <iostream>
int main() { SYSTEM_INFO sysInfo; GetSystemInfo(&sysInfo);
std::cout << "Processor Architecture: "; switch (sysInfo.wProcessorArchitecture) { case PROCESSOR_ARCHITECTURE_AMD64: std::cout << "AMD64" << std::endl; break; case PROCESSOR_ARCHITECTURE_IA64: std::cout << "IA64" << std::endl; break; case PROCESSOR_ARCHITECTURE_INTEL: std::cout << "x86" << std::endl; break; // Other architectures... default: std::cout << "Unknown" << std::endl; break; }
return 0;}3. Retrieve Memory Information
#include <windows.h> #include <iostream> int main() { MEMORYSTATUSEX statex; statex.dwLength = sizeof (statex); GlobalMemoryStatusEx (&statex); std::cout << "Total physical memory: " << statex.ullTotalPhys / (1024 * 1024) << " MB" << std::endl; std::cout << "Available physical memory: " << statex.ullAvailPhys / (1024 * 1024) << " MB" << std::endl; return 0; }4. Retrieve Disk Information
#include <windows.h> #include <iostream>
int main() { ULARGE_INTEGER freeBytesAvailable, totalNumberOfBytes, totalNumberOfFreeBytes; if (GetDiskFreeSpaceEx(L"C:\", &freeBytesAvailable, &totalNumberOfBytes, &totalNumberOfFreeBytes)) { std::cout << "Total number of bytes: " << totalNumberOfBytes.QuadPart / (1024 * 1024 * 1024) << " GB" << std::endl; std::cout << "Free bytes available: " << freeBytesAvailable.QuadPart / (1024 * 1024 * 1024) << " GB" << std::endl; } else { std::cerr << "Failed to get disk space information." << std::endl; }
return 0;}5. Retrieve Network Interface Information
#include <winsock2.h> #include <iphlpapi.h> #include <iostream>
#pragma comment(lib, "iphlpapi.lib") #pragma comment(lib, "ws2_32.lib")
int main() { PIP_ADAPTER_INFO pAdapterInfo; ULONG ulOutBufLen = sizeof(IP_ADAPTER_INFO); pAdapterInfo = (IP_ADAPTER_INFO*)malloc(sizeof(IP_ADAPTER_INFO));
if (pAdapterInfo == NULL) { std::cerr << "Error allocating memory needed to call GetAdaptersInfo" << std::endl; return 1; }
if (GetAdaptersInfo(pAdapterInfo, &ulOutBufLen) == ERROR_BUFFER_OVERFLOW) { free(pAdapterInfo); pAdapterInfo = (IP_ADAPTER_INFO*)malloc(ulOutBufLen); if (pAdapterInfo == NULL) { std::cerr << "Error allocating memory needed to call GetAdaptersInfo" << std::endl; return 1; } }
if (GetAdaptersInfo(pAdapterInfo, &ulOutBufLen) == NO_ERROR) { PIP_ADAPTER_INFO pAdapter = pAdapterInfo; while (pAdapter) { std::wcout << L"Adapter Name: " << pAdapter->AdapterName << std::endl; std::wcout << L"Description: " << pAdapter->Description << std::endl; std::cout << "IP Address: "; for (PIP_ADDR_STRING pIpAddressList = &pAdapter->IpAddressList; pIpAddressList; pIpAddressList = pIpAddressList->Next) { std::cout << pIpAddressList->IpAddress.String << " "; } std::cout << std::endl;
// Move to the next adapter pAdapter = pAdapter->Next; } } else { std::cerr << "GetAdaptersInfo failed with error: " << GetLastError() << std::endl; }
if (pAdapterInfo) { free(pAdapterInfo); }
return 0;}6. Retrieve Computer Name and Username
#include <windows.h>#include <stdio.h>void GetSysInfo() {
wchar_t szComputerName[MAXBYTE] = { 0 }; wchar_t szUserName[MAXBYTE] = { 0 }; unsigned long nSize = MAXBYTE; OSVERSIONINFO OsVer; OsVer.dwOSVersionInfoSize = sizeof(OSVERSIONINFO); GetVersionEx(&OsVer);
if (OsVer.dwPlatformId == VER_PLATFORM_WIN32_NT) { if (OsVer.dwMajorVersion == 5 && OsVer.dwMinorVersion == 1) { wprintf(L"window xp %s\r\n", OsVer.szCSDVersion); } else if (OsVer.dwMajorVersion == 5 && OsVer.dwMinorVersion == 0) { wprintf(L"windows 2k \r\n"); } else if (OsVer.dwMajorVersion == 6 && OsVer.dwMinorVersion >= 1) { printf("windows win7 \r\n"); } } else { wprintf(L"other system \r\n"); } GetComputerName(szComputerName, &nSize); wprintf(L"computer name is %s \r\n", szComputerName);
nSize = MAXBYTE; GetUserName(szUserName, &nSize); wprintf(L"user name is %s \r\n", szUserName);}
int main(){ GetSysInfo(); system("pause"); return 0;}Running the above code may produce an error
error C4996: ‘GetVersionExW’: declared deprecated
Need to disable SDL
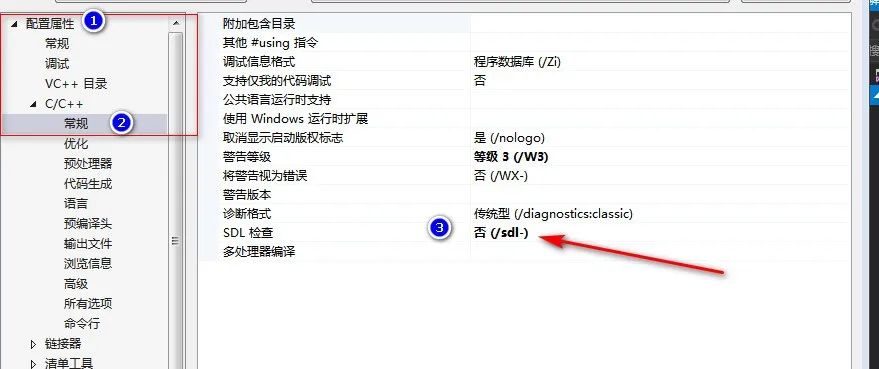

Want to know more
Quickly scan the code to follow