In the rapidly evolving automotive industry, process automation is key to reducing the cost of enabling automotive features. However, for many car manufacturers, updating defective software still means recalling tens of thousands of vehicles, which is undoubtedly a costly endeavor as it requires physical access to the hardware.

A client of Concept REPLY faced a similar issue. To enable a new feature in the vehicle, technicians needed to spend 45 minutes coding via the CAN bus using special hardware and software tools. Concept REPLY helped solve this problem by allowing the vehicle’s car-sharing module to independently execute the coding process.
“
Solution: Making the Onboard Module an “Intelligent Executor”
Weighing Two Technical Approaches
Option One
01
The client server coordinates the tasks, with the onboard shared module acting only as a CAN bus interface. However, this means deploying a complex array of services on the server side to manage real-time interactions with each vehicle, which is not only time-consuming but also requires each vehicle to maintain a good network connection during remote coding.
Option Two
02
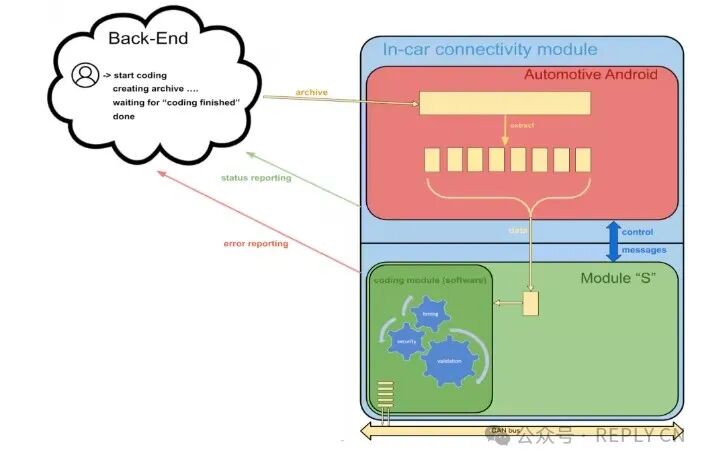
After receiving the server’s data archive, the onboard shared module independently coordinates the entire process (making the module more “intelligent”). This option avoids complex deployments on the server side and reduces reliance on real-time networks.
After collaborating with the client, they chose Option Two, where the client server only needs to generate an archive containing the data required for the vehicle components. The onboard shared module can then independently download the information, write changes to the CAN bus, and continuously verify data while reporting status and errors.
“
Detailed Explanation of the Automated Coding Process
Task Initiation
01
The fleet manager triggers the coding through the server frontend, selects the Vehicle Identification Number (VIN), and creates a list of changes.
Data Preparation
02
The client server generates the data archive and notifies the onboard shared module upon completion.
Module Execution
03
-
The Android subsystem integrated into the onboard shared module downloads the archive, extracts the files, and verifies their integrity, then notifies subsystem “S”.
-
The embedded subsystem “S” connected to the CAN bus initiates a secure coding process: it retrieves data from the Android subsystem piece by piece, writes it to the CAN bus, and verifies the task while reporting status to the backend server in real-time.
Result Feedback
04
After coding is complete, the onboard shared module provides feedback on the final status to the client server.
“
Redefining Software Update Logic in the Era of Connected Vehicles
Concept REPLY successfully delivered a remote automated vehicle coding solution by configuring coding hardware and meeting all safety requirements:
-
Enabling the onboard shared module to manage vehicle functions while providing comprehensive status and error reporting, along with robust verification and rollback mechanisms.
-
Completely eliminating manual intervention in the coding process, reducing the time for clients to manage connected vehicle functions from 45 minutes to 2 minutes.
-
Not only reducing the cost of vehicle customization but also accelerating the development time for new software features.
This solution transforms the traditional coding model that relies on manual and server real-time control into an automated process executed autonomously by the onboard system, providing automotive manufacturers with a replicable template for cost reduction and efficiency enhancement in the trend of Software-Defined Vehicles (SDV).
Selected Highlights from Previous Issues
He Rui Consulting Attends the China (Nanjing) – Italy SME Cooperation Exchange Conference to Promote Cooperation and Development between Chinese and Italian Enterprises
REPLY Drone Solution: A New Journey Towards Efficient Warehouse Management
Rooted in China, Connected to the World, REPLY (China) Empowers with Professionalism