Click the blue text to follow us

Today, let’s talk about how to get started with embedded system development.
First, what is an embedded system?
It is a dedicated computer system that is application-centric, based on computer technology, with customizable software and hardware, suitable for applications with strict requirements on functionality, reliability, cost, size, and power consumption.The most common embedded systems are microcontroller (MCU) systems, including the well-known 51 microcontroller and STM32 microcontroller.
Secondly, what can you do by learning embedded systems?
Embedded system development is an important skill in course design, graduation projects, and academic competitions, and it serves as a solid foundation for innovation, entrepreneurship, project development, and academic research.

How to get started with embedded systems?
My recommended learning path for embedded system development:
Basic knowledge learning -> 51 microcontroller development -> STM32 microcontroller development -> RTOS system development -> Embedded Linux development
Next, I will mainly introduce how beginners with no background can get started with microcontroller software development.
Basic Knowledge Learning
As Laozi said: “The tree that is a thousand feet tall grows from a tiny sprout; the nine-story platform rises from a pile of earth; the journey of a thousand miles begins with a single step.” The importance of theoretical foundation is self-evident. Embedded system development is roughly divided into hardware and software.

Feiling development board
Hardware Part
Hardware refers to the physical components of embedded devices, including processors, memory, peripheral interfaces, sensors, actuators, etc. Hardware design involves selecting appropriate components and interfaces, circuit design, layout, and manufacturing. It is generally presented as a PCB circuit board, and beginners can use breadboards or purchase finished products.

Software Part
Software refers to the program code that runs in embedded systems, used to control and manage hardware. Software development includes writing applications, drivers, and operating systems (such as real-time operating systems) for embedded systems to achieve the desired functions and tasks. Beginners can learn the basic functionalities using bare-metal examples.


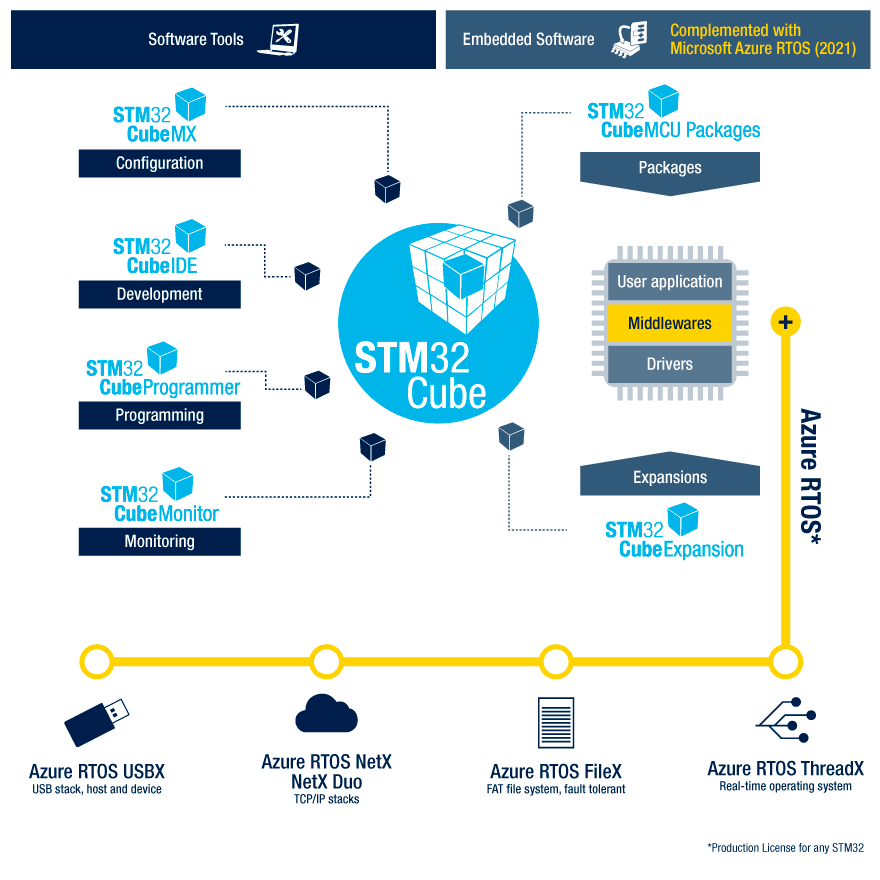
STM32Cube ecosystem
Basic hardware knowledge mainly involves circuit analysis fundamentals, analog circuit fundamentals, digital circuit fundamentals, common components, and the use of simulation tools.Basic software knowledge mainly involves C language fundamentals, data structures, and communication technology fundamentals.Finally, the principles of computer organization that involve both hardware and software.
The above basic knowledge does not require complete mastery to start embedded development; learning basic knowledge is a gradual process. “Three feet of ice does not freeze in a single day.” Beginners only need to learn a general overview, and in future practice, they can refer back and consolidate their knowledge, experiencing the enjoyment of “initially narrow, but after walking several dozen steps, it opens up clearly.”
I recommend an important learning method: Practice-oriented approach.In most cases, our time and energy are limited, and it is not necessary to fully understand the principles. After a superficial familiarity, we can directly engage in practical work to consolidate knowledge.
51 Microcontroller Development
After a superficial familiarity with the basic knowledge, I recommend the “outdated” 51 microcontroller, which has a wealth of learning resources. Its register-based development approach allows beginners to systematically understand microcontrollers. Compared to mainstream microcontrollers like STM32, its internal structure is relatively simple, making it easier to get started, and the development board is cheaper.

51 microcontroller chip
Recommended materials include the Puzhong 51 microcontroller and Guo Tianxiang’s 51 microcontroller tutorial. The learning path is roughly: In software, mainly understand the microcontroller, familiarize with programming and data operations, light up an LED, key detection, serial communication, timers, interrupts, ADC, etc.;In hardware, mainly understand basic module circuits, clock circuits, be able to read schematics, and attempt to draw the minimum system schematic and PCB.
“If the accumulation of water is not thick, it cannot support a large boat.” Learning the 51 microcontroller is crucial for solidifying the foundation of embedded systems.
STM32 Microcontroller Development
STM32 is a more complex 32-bit microcontroller architecture, with stronger computing capabilities, more peripherals, and interfaces, capable of handling more complex tasks and applications.

STM32 microcontroller chip
Common development methods include register development, standard library development, and HAL library development. Given the inefficiency of register development and the obsolescence of standard library development, I recommend learning HAL library development, but it is still essential to understand the fundamental register development. “Without the way, one can seek the technique; with the technique but no way, one stops at the technique.” One must not be ignorant of the underlying principles.

Comparison of STM32 development methods
Recommended materials include the ZDAS and Wildfire STM32F103 or STM32F407 development boards, which come with complete and detailed learning documentation and video tutorials, making them very suitable for beginners. The learning content roughly includes: GPIO input/output operations under complex architecture, interrupt management, UART communication, IIC communication, SPI communication, DMA transfer, bus architecture, clock architecture, and the use of complex peripherals (LCD screens, IMUs, servos, motors, WiFi modules, etc.).
By this point, combined with specific knowledge, you can design small projects like balance cars and smart homes.


To summarize, I recommend an overall practice-oriented approach where you learn by doing. First, learn the basic knowledge, but do not seek to master it all at once. Secondly, refer to video tutorials and study materials to learn about the basic functions and principles of the 51 microcontroller. Then, refer to video tutorials and widely consult materials to learn about the complex architecture of STM32 and the use of external devices. Finally, design a project based on the microcontroller to test and consolidate your knowledge.

THE END
Doing every little thing to perfection is an attitude.
Automated News Promotion Center
Striving to create each issue, presenting quality to you.


Copywriter | Guo Tianci Editor | Guo Tianci
Reviewed by | Gu Xuanyuan