Click on the aboveGuomai IoT to learn about IoT intelligence
The McKinsey report indicates that by 2025, the economic benefits brought by the Internet of Things (IoT) will range from $2.7 trillion to $6.2 trillion. As a crucial entry point for data collection in the sensor layer of IoT, sensors are expected to experience explosive growth in the coming years.
First, let’s understand the basic concept of sensors. A sensor is a detection device composed of a sensitive element and a conversion element, capable of sensing the measured quantity and converting the detected information into electrical signals (such as voltage, current, frequency, or phase) according to certain rules for output, ultimately providing data sources for data analysis and artificial intelligence in IoT applications.
The wave of IoT is about to arrive. What are the research directions of sensor technology?
Wireless Sensors (UGS)

Wireless Sensors
In fields such as smart transportation, smart cities, smart agriculture, industrial IoT, and disaster prevention, humans must ensure that the data obtained from the sensing layer is comprehensive and accurate for a complete perception of the physical world. This means that IoT systems need to deploy a large number of sensors based on the application field and specific requirements. In some cases, aerial dispersal methods are used for large-scale deployment. Therefore, the connection between sensors and IoT systems cannot rely on physical connections but must use wireless channels for data transmission and communication.
Smart Sensors

Smart Sensors
Smart sensors integrate sensors with microprocessors using embedded technology, turning them into smart data terminal devices with environmental perception, data processing, intelligent control, and data communication functions. They possess self-learning, self-diagnosis, and self-compensation capabilities, as well as composite perception abilities and flexible communication capabilities. Consequently, the data fed back to the IoT system by the sensors during physical world perception will be more accurate and comprehensive, achieving precise perception.
In microelectronics, the smaller the characteristic size of integrated circuits, the higher the integration level, the faster the operating speed, and the better the performance. Smaller sensors in IoT systems also mean more convenient deployment and better performance.
MEMS (Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems) utilize traditional semiconductor processes and materials to integrate micro-sensors, micro-actuators, micro-mechanical structures, signal processing, control circuits, and interfaces, communication, and power into one miniature device or system. This small, low-cost, integrated, and intelligent sensing system is an important development direction for future sensors and is the core of IoT. Therefore, the MEMS sensor field has become a key focus for related enterprises.
Wireless Ad Hoc Networks
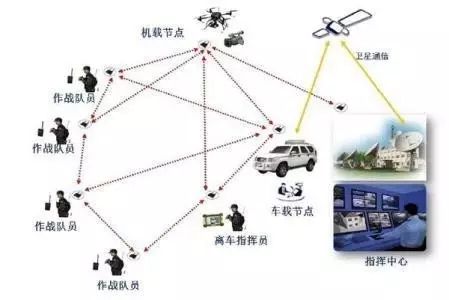
Wireless Ad Hoc Networks
When it comes to wireless ad hoc networks, many readers may find it somewhat unfamiliar, but its importance cannot be overlooked. Compared to traditional networks, wireless ad hoc networks adopt a “peer-to-peer” mobile communication mode that does not require a base station, allowing all connected devices to dynamically form a network during mobility.
What are the advantages of this networking method?
First, one advantage is the absence of a central control node, meaning there are no routers for packet routing and forwarding; furthermore, during operation, if one node leaves the network, the network topology will dynamically change, forming a new topology. This networking technology is highly regarded in military and vehicular networks.
Ultimately, the three main research directions of sensor technology will converge, promoting the birth of wireless sensor networks (WSN).
Major Sensor Suppliers at Home and Abroad
Famous foreign sensor companies:
Bosch, STMicroelectronics, Honeywell, Freescale, Texas Instruments, ADI, NXP, Philips, Infineon, Hitachi, etc.
Famous Chinese sensor companies:
Hanwei Electronics, Dali Technology, Huagong Technology, Yuanwanggu, Nawei Technology, GDH Infrared, Goertek, AVIC Electric Measurement, Dunan Environment, Silan Micro, etc.
Currently, the global sensor market is mainly dominated by several leading companies from the USA, Japan, and Germany. There are approximately 22,000 types of sensors globally, while China has about 7,000 types and varieties of conventional sensors, with more than 90% of high-end sensors still heavily reliant on imports. Digital, intelligent, and miniaturized sensors are severely lacking.
Three Major Sensor Production Bases in China
Currently, there are three major sensor production bases in China: the Anhui base, primarily focused on establishing economies of scale for force and light sensitivity; the Shaanxi Sensitivity Technology Industry Group, mainly focused on establishing economies of scale for voltage sensitivity, thermal sensitivity, and automotive electronics; and the Heilongjiang base, primarily focused on establishing economies of scale for gas and humidity sensitivity.
Driven by the enormous prospects of sensors, the number of sensor enterprises in China is also increasing. In terms of related technologies, Chinese enterprises have basically developed the R&D capabilities for mid- and low-end sensors and are gradually expanding into high-end fields.
The gap between China and the USA, Japan, and Germany in the sensor field provides space for our growth and points the way forward. In the era of IoT, the market’s enormous demand for sensors, coupled with the participation of many local enterprises, is expected to yield remarkable achievements for the Chinese sensor industry.
From:OFweek Smart Hardware Network
[Reply: 2016BG can download the “2016 China Smart City Development Level Assessment Report”]
Disclaimer
Unless otherwise stated, the content on this site comes from the internet, WeChat public accounts, and other public channels, and does not represent the views of this site. It is for reference and exchange purposes only. The copyright of the reprinted articles belongs to the original author or institution. If there is any infringement, please contact us for deletion. — Guomai IoT – China’s IoT and Intelligent Manufacturing Think Tank (http://www.im2m.com.cn)

Click to read the original text to get the registration link for the government big data development and cooperation seminar.
