1. Overview of MODBUS Communication
The MODBUS protocol consists of MODBUS protocol over serial links and MODBUS protocol based on TCP/IP. The serial link MODBUS protocol includes MODBUS ASCII (string) and MODBUS RTU.
The MODBUS protocol library provided by 200SMART supports MODBUS RTU communication.
MODBUS RTU sends data in hexadecimal values.
MODBUS ASCII sends data in ASCII code; sending one data using RTU mode requires one byte, while sending using ASCII code requires two bytes, which affects the transmission time.
There are many communication methods for PLC and inverters, but the commonly used and preferred method is MODBUS communication, which is widely applied in actual industrial control. In this issue, we will share how to control inverters with PLC via MODBUS RTU.
2. Detailed Explanation of MODBUS Library Instructions
The library instructions are divided into two types: one is the master library, and the other is the slave library.
The master is the PLC acting as the MODBUS master to actively read data from other devices; the slave is the PLC acting as the MODBUS slave, where other devices read the data. This issue shares the PLC as the master and the inverter as the slave.
STEP7-MinWIN SMART software comes with MODBUS communication library instructions.

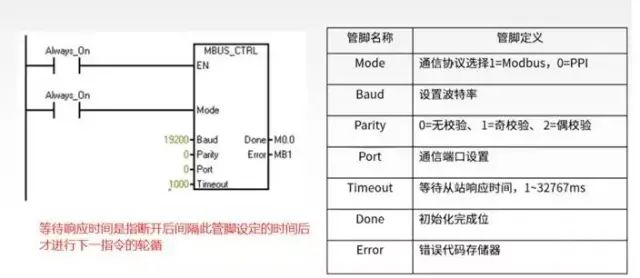
Initialization instruction:
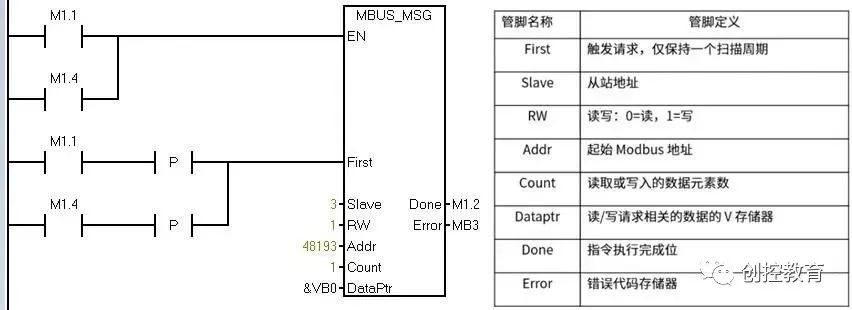
Control instruction:
3. Communication Format (Protocol) of MODBUS RTU
The communication protocol consists of: station number, function code, data address, data content, checksum, and end character.
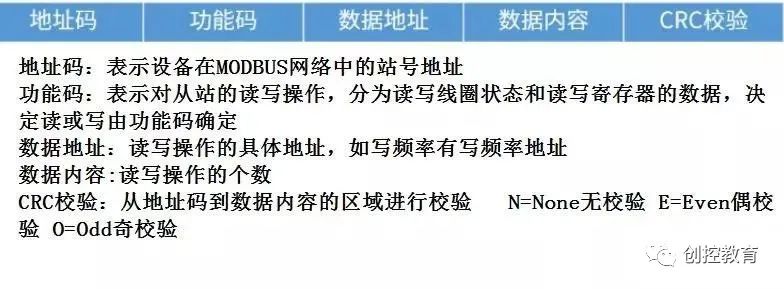
Checksum: N=None no checksum E=Even even parity O=Odd odd parity.
Determine whether the number of 1’s in the data bits is odd or even (for even parity, if the number of 1’s in 16#03 is even, the checksum is 1; if odd, the checksum is 0. For odd parity, if the number of 1’s is even, the checksum is 0; if odd, the checksum is 1).
The function code specifies whether the read operation or write operation is performed on the slave device, and also specifies the type of MODBUS register address. Common function codes include:
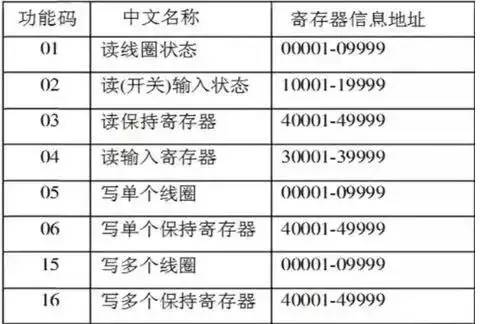
4. Hardware Connection for PLC and Inverter Communication
The terminals related to communication on the inverter are marked A/B RS585+/RS485- or RJ11 port; find the relevant inverter manual to view the wiring definitions of the communication ports. Below is the wiring definition of the communication port for Delta VFD-M series inverters.
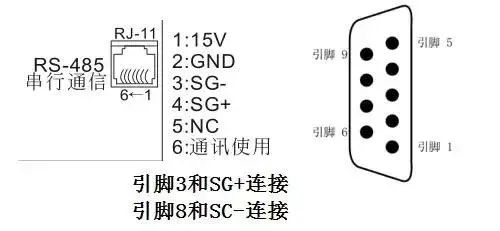
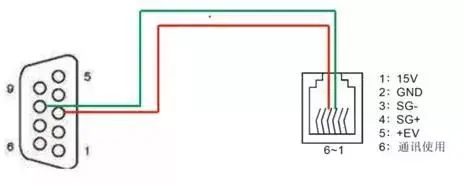
5. Setting Communication Parameters for the Inverter
1. To ensure normal communication between the inverter or instrument and PLC, their interfaces and protocols must be consistent, and besides, the parameter settings must also be consistent.
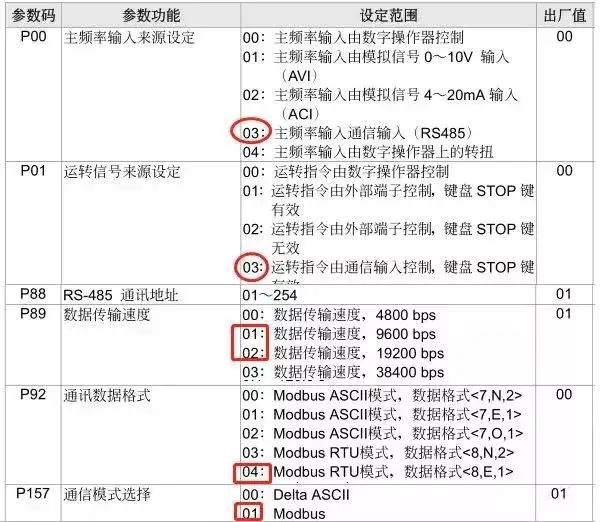
P00 set to 03 (frequency command)
P01 set to 03 (run command)
P88 set to 03 (communication address, between 0-254)
P89 set to 02 (baud rate selection)
P92 set to 04 (data format, 200SMART does not support two stop bits, so you can only choose either 04/05)
P157 set to 01 (the default for the inverter is MODBUS mode)
2. Check the manual for the addresses of feedback parameters such as start/stop, frequency setting, operating frequency, voltage, and current.

Information frame format description
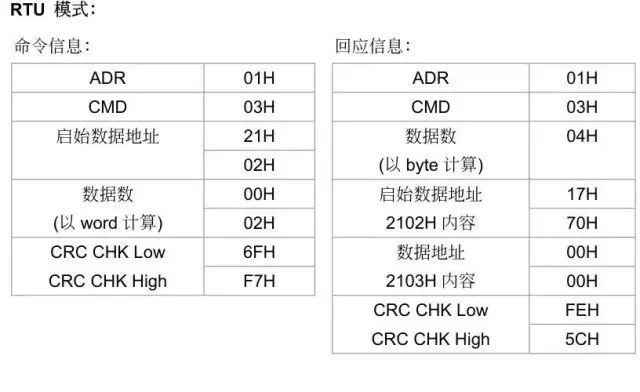
This indicates that the data read from addresses 2103 and 2104 is placed in addresses 17 70 and 00 00.
Definition of protocol parameter addresses:
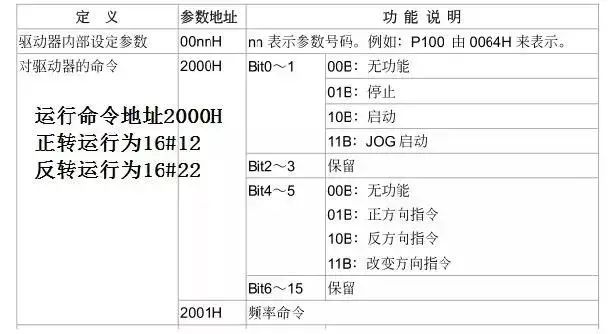
Run command address 2000H frequency command address 2001H
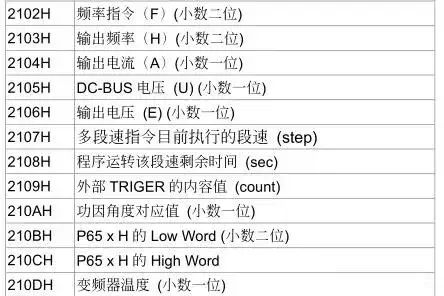
Output frequency address 2103H output current address 22104H
Output voltage address 2106H inverter temperature address 210DH
6. Writing MODBUS Communication Program
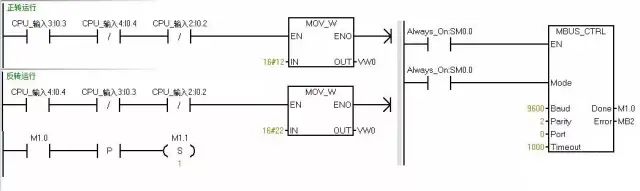
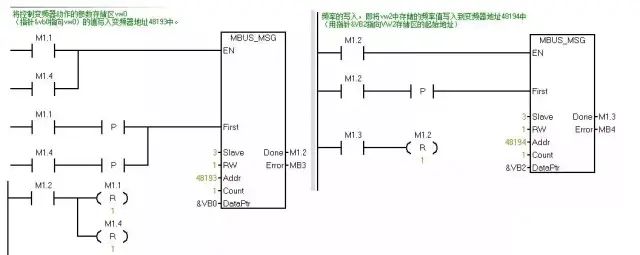
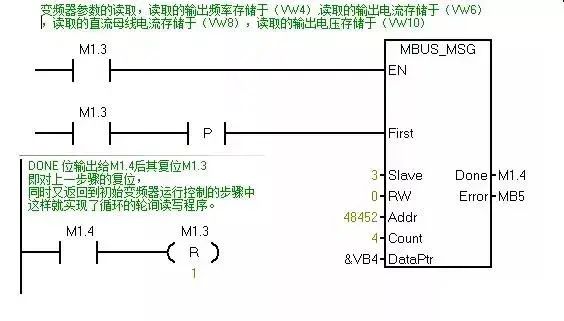
You can add a segment of initialization at the beginning of the program to reset all bits.
(Content sourced from the internet, copyright belongs to the original author)
Disclaimer: If copyright issues arise, please contact for removal!Neither individuals nor organizations bear relevant legal responsibilities.