
As mobile phone enthusiasts,
we often encounter slow internet speeds.
“Trying to reconnect” makes a comeback seem like a luxury.
“Buffering” leaves our brewing emotions nowhere to go.
So, the question arises:
Does wind really affect Wi-Fi signal?
Why do the changes in tension of a broken rope and a broken spring differ?
by It’s like this
Determining whether a broken rope, spring, or rod will cause a change in force actually involves considering the time it takes to return to its original shape after breaking. Objects like ropes and rods are considered rigid bodies, and the deformation that occurs under stress can be almost negligible, so the recovery time after breaking is also virtually insignificant; while a spring undergoes elastic deformation when stressed, and it requires time to return to its original state after breaking.
By Aaron Chen
Why do book covers curl up after being placed for a long time?
by Anonymous
Generally, the curling of book covers is mainly caused by moisture. We have discussed issues related to book covers (paper) many times, and most of the time, it is due to cellulose causing problems. We have previously introduced cellulose, which contains multiple hydroxyl groups (hydrophilic groups) that form hydrogen bonds with each other, like a neatly lined-up group of children, and the entry of water molecules disrupts this harmonious group, increasing the stress on the paper fibers. The front of the paper is more affected by water molecules than the back, causing it to curl up. Of course, the cover may also curl due to external forces when we read the book, which also affects the fibers on the surface of the paper, causing bending.
By Aaron Chen
Can mirrors reflect radiation? If I play with my phone in front of a mirror, will the radiation be much less?
by Anonymous
The radiation from mobile phones is primarily electromagnetic radiation, and the reflective layer of a mirror is metal, which has a broad spectrum of ability to reflect electromagnetic waves. According to the formulas given by electrodynamics, the loss rate is proportional to (frequency)^(1/2). For electromagnetic waves, taking the general Wi-Fi signal as an example, the frequency is 2.4GHz, while the frequency of visible light is about 4 to 7*105GHz. Therefore, the reflectivity of a mirror for Wi-Fi signals is higher than for visible light. Thus, playing with a phone in front of a mirror does not reduce the radiation received by a person (in fact, it may increase it due to the reflection from the mirror)..
By Luna
If two eggs with the same mass and shape, one raw and one cooked, are given the same force at the same point, which one will stop first when freely rotating on a smooth plate?
by Nihil
The raw egg will stop first. When the raw and cooked eggs start rotating at the same angular speed, the cooked egg’s protein, yolk, and shell are one entity and will rotate around the axis together, while the liquid contents of the raw egg will start moving with the shell’s rotation, gradually gaining speed. Thus, the cooked egg has more energy and will spin longer. Additionally, the fluidity of the raw egg will cause it to shake after rotation, leading to a quicker stop as it no longer rotates around the initial axis.
By Aaron Chen
Does strong wind really affect Wi-Fi signals?
by Anonymous
It is generally believed that strong winds do not directly affect the propagation of Wi-Fi signals, as Wi-Fi signals are essentially electromagnetic waves. The router transmits electromagnetic waves directionally, and wind is formed by uneven air density distribution. The speed of electromagnetic wave propagation is minimally affected by air, almost negligible.
According to Maxwell’s equations, the speed of electromagnetic wave propagation (the speed of light) depends on the conductivity and permeability of the medium. The speed of light in a vacuum is currently the maximum speed of material movement in nature, and the dielectric constant of air is very close to that of a vacuum. Generally, it is considered that the difference in speed of light between vacuum and air is minimal. Changes in air density cause only slight variations in dielectric constant, which has a minor impact on Wi-Fi signal transmission.
However, on rainy or snowy days, we often notice a significant decrease in internet speed. This is because, on rainy days, the air is filled with a large number of water molecules that can absorb electromagnetic waves in the microwave band. Additionally, when the size of snowflakes or raindrops is appropriate, strong scattering can occur, reducing the power of directional transmission and affecting signal transmission. In such cases, the impact on electromagnetic wave propagation is significant.
Nonetheless, to answer this question with scientific rigor, we must point out that in extreme cases, strong winds may destroy outdoor routers or the cables connecting the routers to the internet, which could affect the transmission and reception of Wi-Fi signals.
By Luna
Why are the edges of shadows blurry when viewed closely?
by Muzan@Lower Crescent One
This physical concept is called penumbra. Let’s assume the light source is a point source and the object is a sphere; the tangent drawn from point A to the sphere distinguishes the shadow region (shadow) from the illuminated area. In real life, there is no ideal point light source, so the light source is not a point, leading to the existence of both internal and external tangents. The area between these two tangents is the penumbra. Compared to the umbra and the illuminated area, the penumbra receives partial illumination, and the closer it is to the umbra, the dimmer it is. This penumbra is what we see as the blurry edge of the shadow.
By Aaron Chen
Why do some USB plugs heat up while others do not, even though they look the same?
by Geige
First, the heating of plugs is due to the thermal effect of electric current. Therefore, we only need to look at the differences in current limits among those “seemingly” identical USB ports.
For convenience, let’s take the very common USB Type-C port as an example. Although USB ports look the same, they can actually have many differences… because the history of USB ports is quite long, leading to various physical interface shapes and different numbers and positions of internal circuits. The same Type-C physical interface can support different protocols, as shown in the table below, which correspond to different current limits.
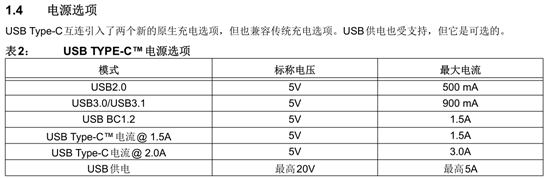 Type-C Power Options
Type-C Power Options
Due to the differences in plugs, different plugs likely correspond to different modes, so those with higher current get hotter, while those with lower current do not heat up as much. Lastly, here’s a fun fact about USB ports: if the rectangular USB port (Type-A) originally supports USB 3.0, if you insert it slowly, it will revert to USB 2.0, and the data transfer speed will slow down. So when inserting a USB drive, remember to be: steady, accurate, and fierce…
Reference: Introduction to USB Type-CTM, Andrew Rogers, Microchip Technology Inc.
By NKXXX
Question team for this issue:
Physics Institute Aaron Chen, Luna, NKXXX
Write down your questions for next week, same time on Friday~

↓ Scan the QR code below to ask questions quickly ↓

Last issue was also exciting
A charge suddenly appears in the distance; can you sense it instantly?| No.193
 Editor: Buyan
Editor: Buyan
Recent Popular Articles Top 10
↓ Click the title to view ↓
1. Treasure Winter, Scientists Only Understood This Is the Easiest Season to Lose Weight 10 Years Ago
10. Symmetry! Symmetry! Still Symmetry!
Click Here to View All Previous Popular Articles
