1. What is ECU
ECU (Electronic Control Unit), also known as “vehicle computer” or “onboard computer”, is a dedicated microcontroller for automobiles. It consists of a microprocessor (CPU), memory (ROM, RAM), input/output interfaces (I/O), analog-to-digital converters (A/D), and other large-scale integrated circuits, just like a regular computer. In simple terms, “the ECU is the brain of the car.”

2. What is ECU Modification?
ECU modification refers to changing the method of processing problems (the originally set ECU program) to achieve the goal of altering engine operation. The so-called “ECU program” is actually a set of algorithms stored in memory that processes signals transformed from input devices through controllers to generate corresponding command signals sent to output devices. Thus, modifying ECU parameters essentially means altering these algorithms.

However, problems arise when input signals exceed the default normal values within the ECU (too much or too little), which not only renders tuning ineffective but may also trigger a fault signal light. What we can do is to ensure that this signal does not exceed normal values; either abandon the original set rules, which means not using the original computer; or cunningly use another computer to implement your algorithms while simultaneously “deceiving” the original factory ECU.
3. Methods of ECU Modification
This leads us to three methods of ECU modification. ECU modification is a general term that can be divided into directly changing the ECU hardware and modifying the internal program. The “deceptive” methods mainly include three types.
1. Replacement Type
Directly changing the ECU hardware is commonly seen in racing circuits as “replacement computers”. For instance, using a “full replacement ECU” to control the engine, brands like Motec and Haltech are well-known for their complete replacement computers. This type of modification is usually paired with heavy engine hardware modifications, as the engine’s operating temperature, intake volume, fuel injection quantity, compression ratio, and other data greatly exceed the original factory settings. This means that after substantial modifications, the original factory ECU can no longer meet the hardware demands, making this competitive product the most suitable choice.

Replacement computers do not need to consider the limitations of factory data; all data can be set freely by technicians. Although replacement computers have immense adjustability, they lack fixed forms and specifications, requiring everything to start from scratch, which places very high demands on technicians. For instance, stabilizing idle speed after getting the vehicle to start normally can take one or two days of tuning, making this type of computer more suitable for professional racing teams with no cost concerns.
2. Write-in Type
Write-in modified ECUs retain the hardware of the original factory ECU and utilize a method of writing new operating management programs into the ECU. Since the original factory set program is altered, write-in ECUs are also known as rewritten ECUs or colloquially as “flashed computers”. Although this modification method is limited by the original factory ECU and sensors, and the adjustable range is relatively small, it has gained popularity among modification enthusiasts in recent years due to its non-destructive nature to other factory functions and its stability and safety.
Many brands offer ECU programs tailored for specific models, and some popular write-in ECU modification brands even promote their ECU programs as being optimized for local fuel types, climates, etc. They can choose low torque enhancement, peak horsepower increase, or even fuel-saving ECU modification programs that outperform factory settings.
3. External Type
External modified ECUs work by “secretly” replacing signals to deceive the ECU with protective programs to achieve the goal of altering execution programs. First, the external ECU intercepts the signals fed back to the ECU from various sensors, modifies the signals that need adjustment (which can be understood as cheating, aiming to trick the factory ECU), transforming what would normally exceed the factory ECU’s recognized limits into normal signals inputted to the factory ECU. Once the factory ECU receives the “normal signal”, it outputs the execution program set by the factory to the external ECU, which then modifies the signals (the commands from the factory ECU are not suitable for the executing components to work).

After this series of actions, a successful deception is completed. The adjustable range of external modified ECUs lies between the other two methods. However, due to the increasing performance and self-protection capabilities of modern automotive ECUs, the operational difficulty of external computers is also increasing.
In summary, each of the three methods has its own advantages and disadvantages. Replacement types are suitable for heavy modifications or competitive modifications, write-in types are suitable for stronger original ECU protection and light modifications, while external computers are suitable for light to moderate modifications and correspond to original ECUs that are easier to modify data.
4. Control Theory of Engine ECU:
It is necessary to understand the control principles of the engine ECU: first, the working state of our engine is a closed-loop control: the working rules of the engine are set through fixed programs (air-fuel ratio and ignition timing under different working conditions). An oxygen sensor is added to the exhaust pipe to determine the engine’s working state, whether the fuel quantity is too much or too little; a knock sensor is added in the cylinder to determine whether the ignition timing is advanced or delayed; a temperature sensor can determine whether the combustion chamber temperature is normal to adjust the fuel supply and protect the engine, etc. These situations are sent to the ECU, which continuously adjusts the fuel injection quantity and ignition timing based on the feedback.
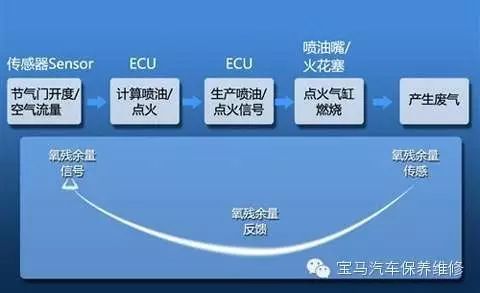
The ECU collects the working state information from various parts of the engine through various sensors (including temperature sensors, pressure sensors, rotational sensors, flow sensors, position sensors, oxygen sensors, knock sensors, etc.), which is transmitted to the ECU via responsible transmission lines. Once the ECU receives these signals, it analyzes them to determine the functional status of various engine components and their operational conditions, and then automatically computes based on pre-written programs what actions the executing components should take under these conditions, subsequently sending commands to the executing components to instruct them to work.
『This is a temporary closed-loop control schematic. If the “oxygen residual feedback” is removed, it becomes an open-loop control without feedback. Currently, all ECUs use closed-loop control, making engine management more precise.』
A simple analogy: the whole process is like a hair lightly touching your nostrils; the nasal hair (sensor) sends the touch information to the brain (ECU), which analyzes the information, confirming that a foreign object has entered the nostrils, and then sends commands to various parts of the nostrils to initiate gas expulsion, thus achieving the goal of cleaning the foreign object. If the impact of the foreign object exceeds the system’s capacity, it will be accompanied by loud sneezing sounds (signal alarms, fault codes).
5. Controls Achievable by Engine ECU
1. Fuel injection control: up to 4 injections can be achieved per working cycle (currently, national III diesel engines only use two per cycle – pre-injection and main injection).
2. Fuel quantity control: including pre-injection quantity self-learning control and deceleration cut-off control.
3. Fuel timing control: including main injection timing, pre-injection timing, and timing compensation.
4. Rail pressure control: including normal and rapid rail pressure control, rail pressure establishment and overpressure protection, fuel injection pressure relief control, and rail pressure limp home control.
5. Torque control: including transient torque control, acceleration torque control, low-speed torque compensation, maximum torque control, transient smoke control, and turbocharger protection control.
6. Overheat protection: when coolant temperature, oil temperature, and intake temperature are too high, the ECU will enter overheat protection mode, limiting engine power.
7. Cylinder balance control.
8. EGR control.
9. Variable geometry turbocharger (VGT) control.
10. Auxiliary starting control (motor and glow plugs).
11. System state management.
12. Power management.
13. Fault diagnosis.
6. Principles of ECU Modification
We have learned that the engine control system is simply composed of three parts: sensors, central control unit (ECU), and executing components. Theoretically, as long as these three systems are functioning normally, the engine can operate normally (when other hardware is in a normal state). However, normal operation is merely the minimum requirement for internal combustion engines. Setting aside the performance of engine displacement, component strength, precision, intake and exhaust systems, ignition, fuel supply systems, cooling systems, etc., the ECU program settings for factory models consider exhaust emission performance, fuel economy, durability, and even whether they are suitable for urban driving (power output characteristics, emphasizing low torque output).

The original computer sets the most stable fuel injection and ignition parameters based on different engine loads and speeds, ensuring that combustion temperatures do not become too high and that the mixture is neither too rich nor too lean, while also considering the differences in fuel quality across different regions (conservative ignition timing control). However, since it is widely applicable, this setting is necessarily conservative. By changing the ECU program to more precisely control fuel injection amounts, ignition timing, etc., engine combustion efficiency or power performance can be enhanced, or both can be balanced.
It is essential to understand that internal combustion engines generate power by burning fuel, so the ratio of fuel to air is crucial. A lean mixture (air-fuel ratio greater than 14.7) can save fuel, while a rich mixture (air-fuel ratio less than 14.7) can provide more power. Of course, the terms “rich” or “lean” are only applicable under normal working conditions of the engine; excessively low or high mixture ratios cannot achieve good operational conditions, and the air-fuel ratio tuning varies depending on specific conditions.
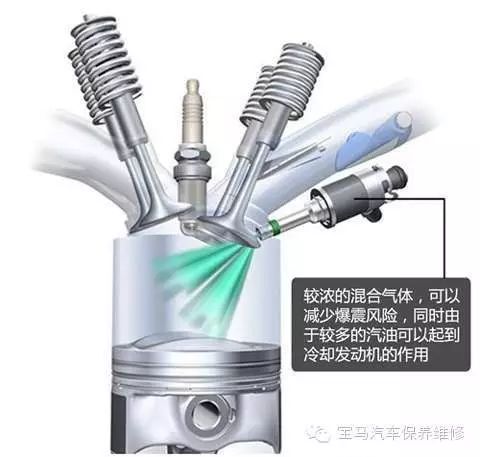

Taking the air-fuel ratio as an example, performance modifications are not merely about changing one aspect; they often require changes to other components, such as the fuel supply system. Frequently, after increasing horsepower to reduce knocking and better dissipate heat from the engine, more fuel injection is adjusted, which is why performance enhancements often result in higher fuel consumption than before modifications. The reasons for black smoke or flames during enhanced power performance become understandable.
7. Will ECU Modification Affect Engine Lifespan?
This is surely one of the most concerning questions for everyone. Indeed, after ECU modifications, we can achieve more powerful performance, but we also worry about whether the engine can handle it. In fact, this issue is not difficult to resolve. First, for modifications that do not significantly boost power, the original engine structure and material design can fully handle the increased power output. By precisely adjusting the air-fuel ratio and ignition timing, output can be increased, but the fuel quality requirements will be higher. As long as low-quality gasoline and insufficient octane gasoline are avoided, there should be no issues. For vehicles with more significant tuning and modifications, additional cooling systems may be needed to help lower engine temperatures; for heavy modifications, engine internals may need to be reinforced (replaced), so durability is a relative concern and cannot be definitively answered.

8. Why Do Turbocharged Engines Show Greater Power and Torque Increases After ECU Upgrades Compared to Naturally Aspirated Engines?
This is not difficult to understand; the boost value of a turbocharger can be adjusted. As the boost value increases, the result is an increase in intake density, meaning more oxygen molecules per unit volume. As long as the fuel supply and ignition parts keep pace, horsepower will naturally increase significantly. However, compared to naturally aspirated engines, turbocharged engines have more stringent and sensitive requirements for fuel quality and temperature, and high horsepower also demands greater strength from the engine hardware.
9. Issues Related to Automotive ECU Upgrades
The following are clarifications on related issues from authoritative figures engaged in automotive ECU upgrade services, for reference only!

1. Many people are concerned about whether flashing the ECU will have negative effects on the vehicle. Based on your expertise and experience, can you share your professional insights?
Answer: This is a hot topic of discussion. Almost every car owner considering flashing their ECU is concerned, as they worry it may shorten engine lifespan. In fact, this concern arises from a misunderstanding of what upgrading the ECU means. In the industry, upgrading the ECU refers to program optimization, which is the best calibration based on the engine configuration to improve engine efficiency. As long as ECU programs are calibrated within reasonable and correct ranges, they will not affect engine lifespan. For example, it’s similar to the Windows 7 system we use; why are there different versions for laptops and desktops, as well as other devices running Windows 7? Microsoft constantly updates Windows 7 to make it safer, more convenient, and faster for users. Therefore, we see our Windows 7 systems automatically updating to the latest versions periodically. The ECU program is akin to an operating system, providing reliable and stable working conditions for the engine. Replacing it with a high-quality version will enhance its operational efficiency.
2. Why don’t car manufacturers tune the ECU programs to the best settings?
Answer: Car manufacturers keep the ECU programs in a conservative and stable state upon leaving the factory because they do not know where their vehicles will be sold. Local climate, temperature, fuel quality, driving habits, and maintenance practices can all vary. To ensure that the vehicles they produce can withstand the harshest environments while still functioning for extended periods, the original cars retain 5% to 30% of their power as a limitation.
Additionally, manufacturers can differentiate ECU program versions based on vehicles sold to different regions or models. For example, two different models with different prices but using the same engine and ECU can have different ECU programs based on the model’s grade.
3. Can you discuss whether the effects of ECU upgrades are noticeable?
Answer: Many people have likely seen various reports online; for naturally aspirated models, there can be a 5% to 10% increase, while turbocharged models can see increases of up to 30%. Generally, after the upgrade, drivers notice that the throttle feels lighter, the previous throttle delay time is reduced, shifting is smoother than before, and the jolting sensation during gear shifts is significantly lessened. A strong forward thrust is felt when the throttle is suddenly pressed. These are all signs of increased engine power. I won’t use too many fancy words to describe it; simply put, the car feels more “responsive” than before.
4. Another question that car owners are concerned about: after upgrading, will fuel consumption increase?
Answer: Not necessarily. Some models actually become more fuel-efficient after flashing the ECU, as the engine produces more power within the same time unit. When traveling the same distance, the throttle pedal may need to be pressed less than before. For example, what previously required 2/3 throttle to produce torque now only requires 1/3 throttle. This is because upgrading the ECU improves the efficiency ratio rather than simply increasing output power. This misunderstanding that flashing the ECU will lead to higher fuel consumption is common.
Furthermore, flashing the ECU program is essentially about enhancing driving pleasure. It does not equate to driving fast or speeding. In addition to increasing horsepower, it also improves vehicle handling performance. It is not about increasing horsepower to exceed speed limits but rather enjoying the driving experience within legal speeds.
5. After upgrading the ECU for increased power, what else should be noted?
Answer: First, I recommend reinforcing the vehicle’s braking system after ECU upgrades. Some models’ original brakes are just adequate for braking. After flashing the ECU, the increased horsepower may lead to the original brakes being insufficient.
Second, shorten the original maintenance cycle. Due to the increased power output of the engine, the internal components will experience higher torque loads. To ensure the engine’s maximum lifespan, I believe it is necessary to shorten the maintenance cycle.
6. What do you think about the future development prospects of the ECU tuning industry?
Answer: Abroad, ECU tuning has become a common practice, with many automotive modification shops offering ECU upgrade services. Additionally, there are numerous professional ECU calibration companies abroad that have mastered safe and stable tuning techniques. As long as vehicles are ECU-controlled, whether they are trucks, motorcycles, or yachts, they can be tuned. In our country, this technology is still in its infancy and has not yet been widely recognized or accepted.
 BMW Car Maintenance and Repair
BMW Car Maintenance and Repair
BMW Usage Tips | BMW Maintenance and Repair | BMW News and Information | Other Automotive Related
 WeChat ID: bmwbaoyangweixiu Long press to identify the QR code to subscribe
WeChat ID: bmwbaoyangweixiu Long press to identify the QR code to subscribe
The most professional and popular new media WeChat account for BMW cars, welcome to read!